The field of archaeology has been continuously evolving in 2023, making significant strides in uncovering new historical findings, preserving cultural heritage, and employing innovative technologies to study the past.
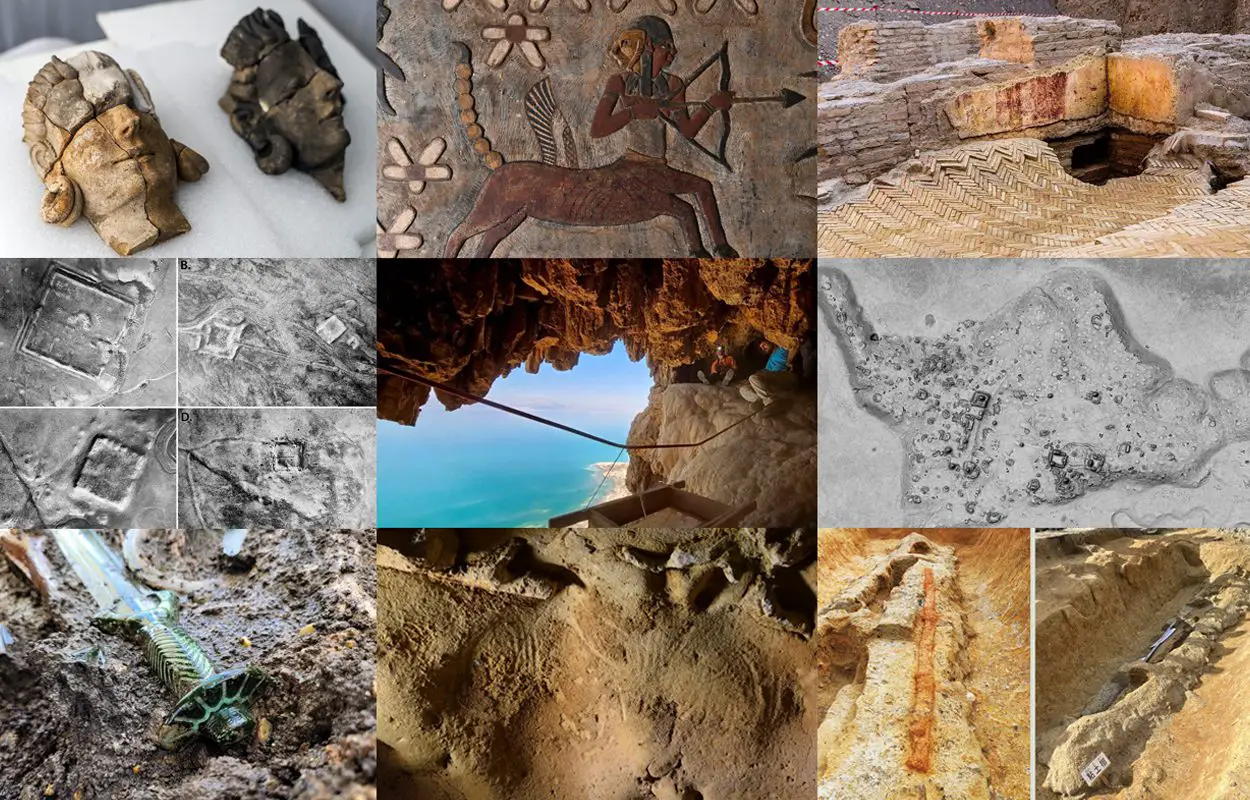
Sealed “Tomb of Cerberus” discovered in Giugliano
Archaeologists have discovered an exceptionally well-preserved tomb containing frescoes in the municipality of Giugliano in Campania, Italy. The most notable fresco depicts Cerberus (thus the tomb being designated “Tomb of Cerburus”), the three-headed dog from Ancient Greek mythology. Cerberus, also referred to as the “hound of Hades”, guarded the gates of the Underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. The scene represents the last of Heracles’ twelve labors, in which Cerberus is captured by Heracles. Find out more
Well-preserved 3,000-year-old sword found in Germany
The sword was found among a deposit of grave goods and weaponry, alongside the remains of a man, woman and child. The discovery is extremely rare for this part of Germany, as most burial mounds have long been looted during antiquity or opened during the 19th century. The sword is similar to the Bronze D type Rixheim swords, in that it uses a solid hilt made by overlay casting of the handle over the blade. Find out more
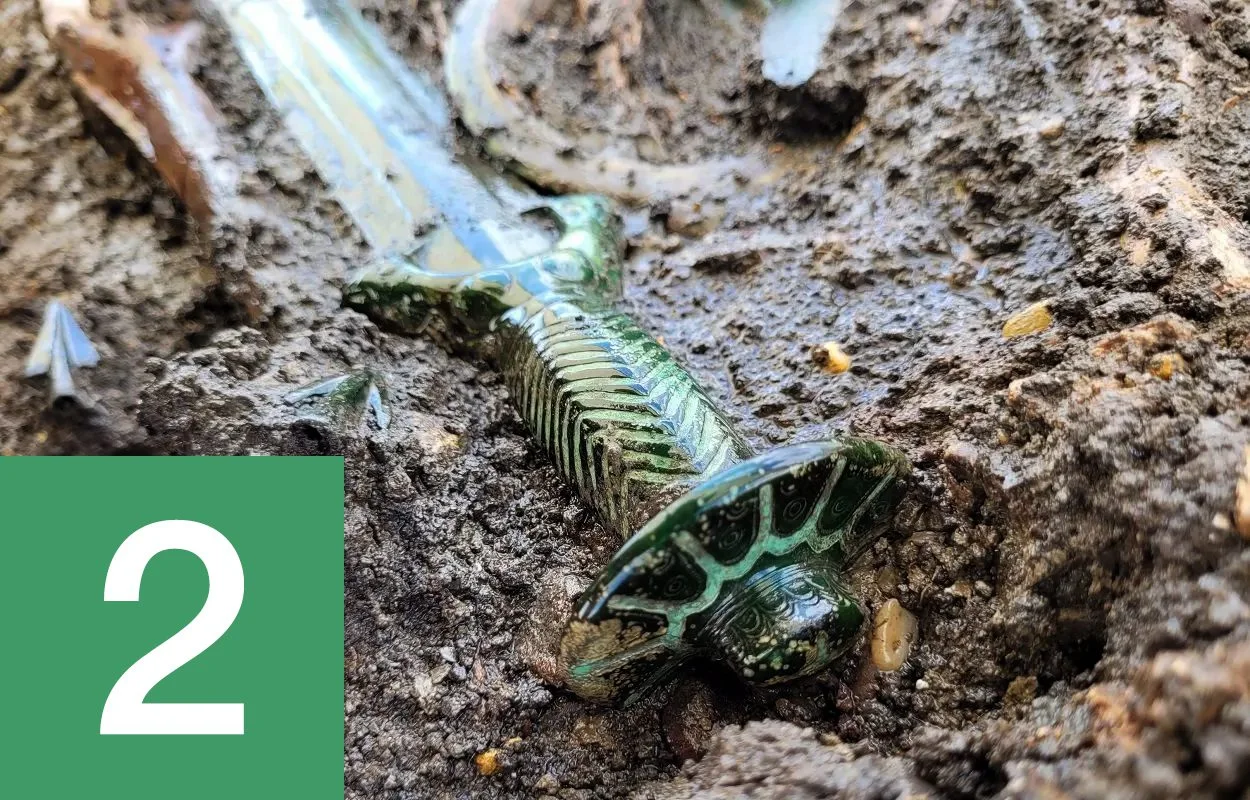
Researchers find oldest known Neanderthal engravings
A study published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE has provided evidence to date the age and origin of engravings discovered on a cave wall in France. Conducted by a team of researchers led by Jean-Claude Marquet from the University of Tours, France, the study confirms that these engravings were undeniably crafted by Neanderthals, making them the oldest known examples of such artistic expressions attributed to this ancient human species. Find out more
Celestial reliefs depicting the heavens uncovered in the Temple of Esna
A team of researchers from the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities, and the Universitaet Tübingen, have uncovered a collection of ceiling reliefs during restoration works in the Temple of Esna. The reliefs are a representation of the heavens that depicts the signs of the zodiac, several planets such as Jupiter, Saturn, and Mars, in addition to a number of stars and constellations used to measure time. Find out more
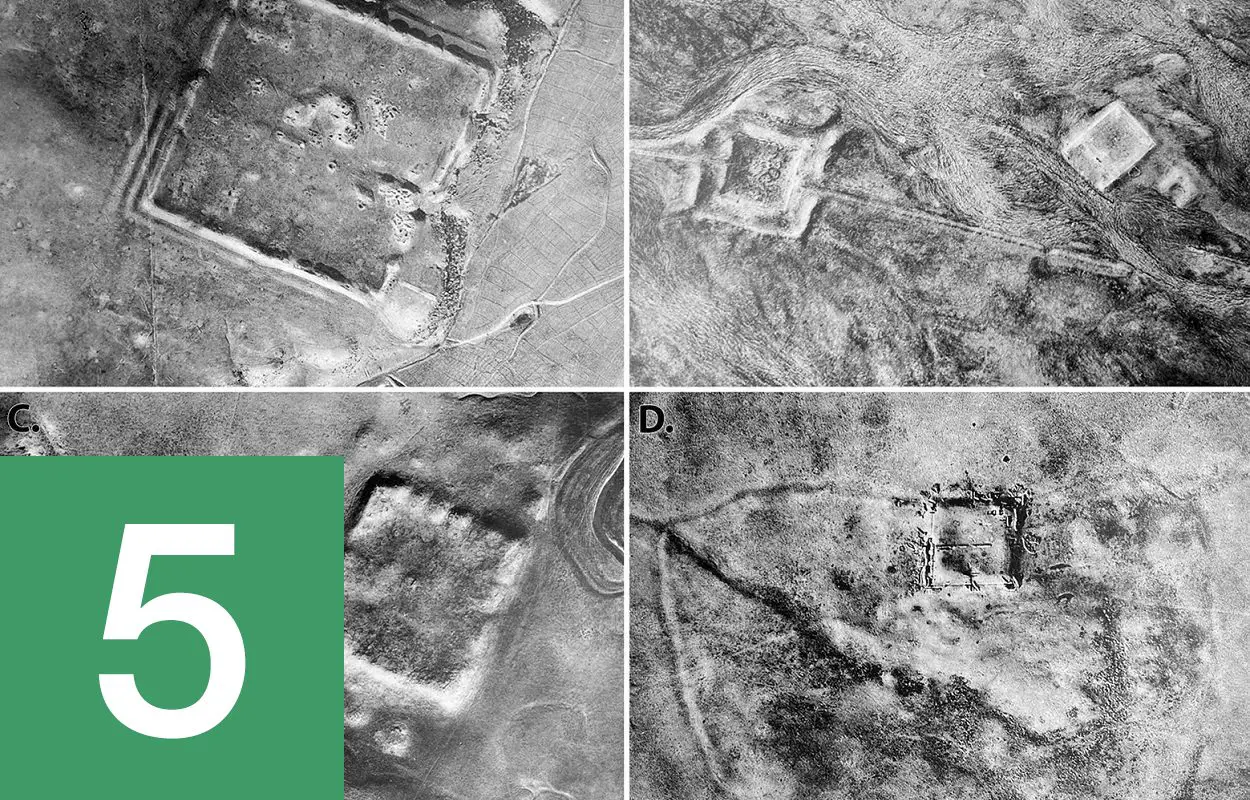
Lost Roman forts discovered using Cold War spy satellites
A study of declassified imagery taken by Cold War era satellites during the 1960s and 70s has led to the discovery of 396 previously undiscovered Roman forts. The forts are spread across the Syrian Steppe in what is now Syria and Iraq to protect the eastern provinces from Arab and Persian incursions. Find out more
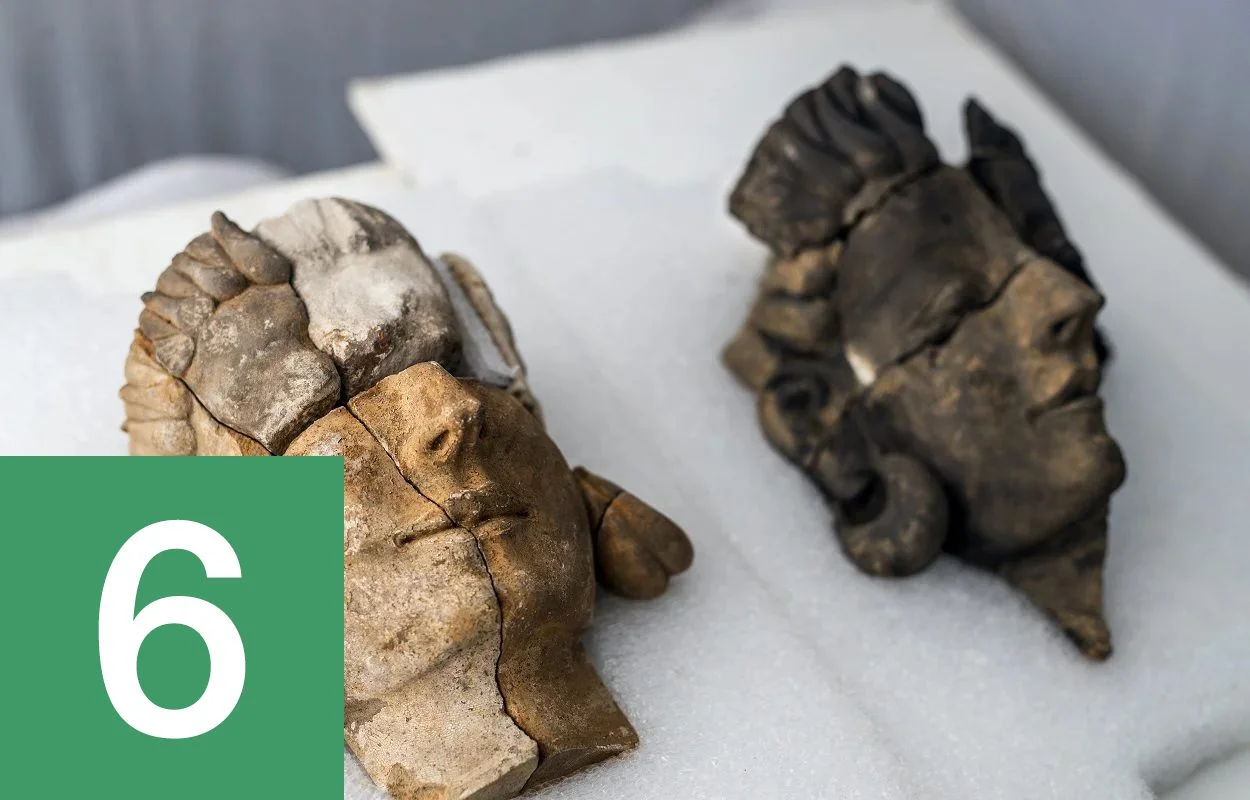
Archaeologists uncover the first human representations of the ancient Tartessos people
A press release issued by the Higher Council for Scientific Research (CSIC) has announced the discovery of figured reliefs depicting human representations during excavations at Casas del Turuñuelo, a Tartessian site in the Province of Badajoz. Two of the reliefs appear to be female figures, which the researchers suggest could be representations from the Tartessian pantheon of gods. The three other reliefs are fragmented and in a poorer state of preservation, however, one of them has been identified as a Tartessian warrior. Find out more
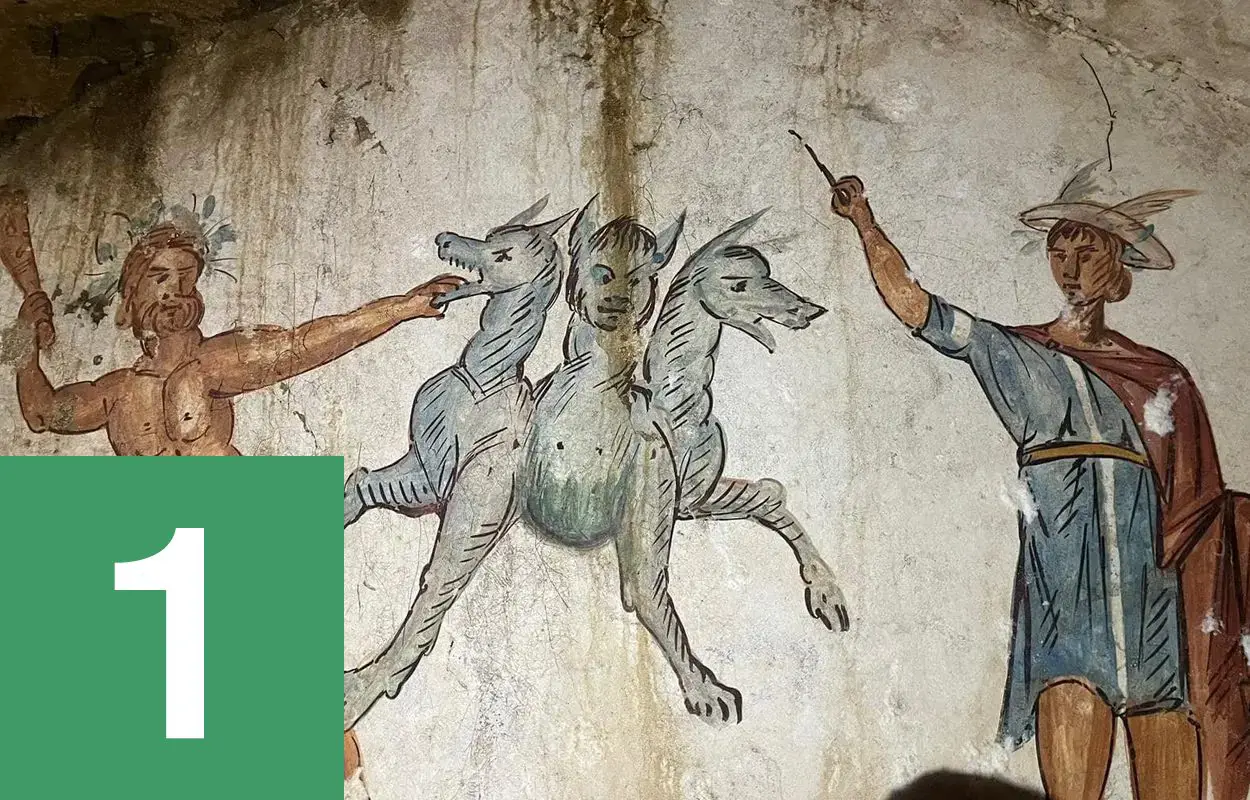
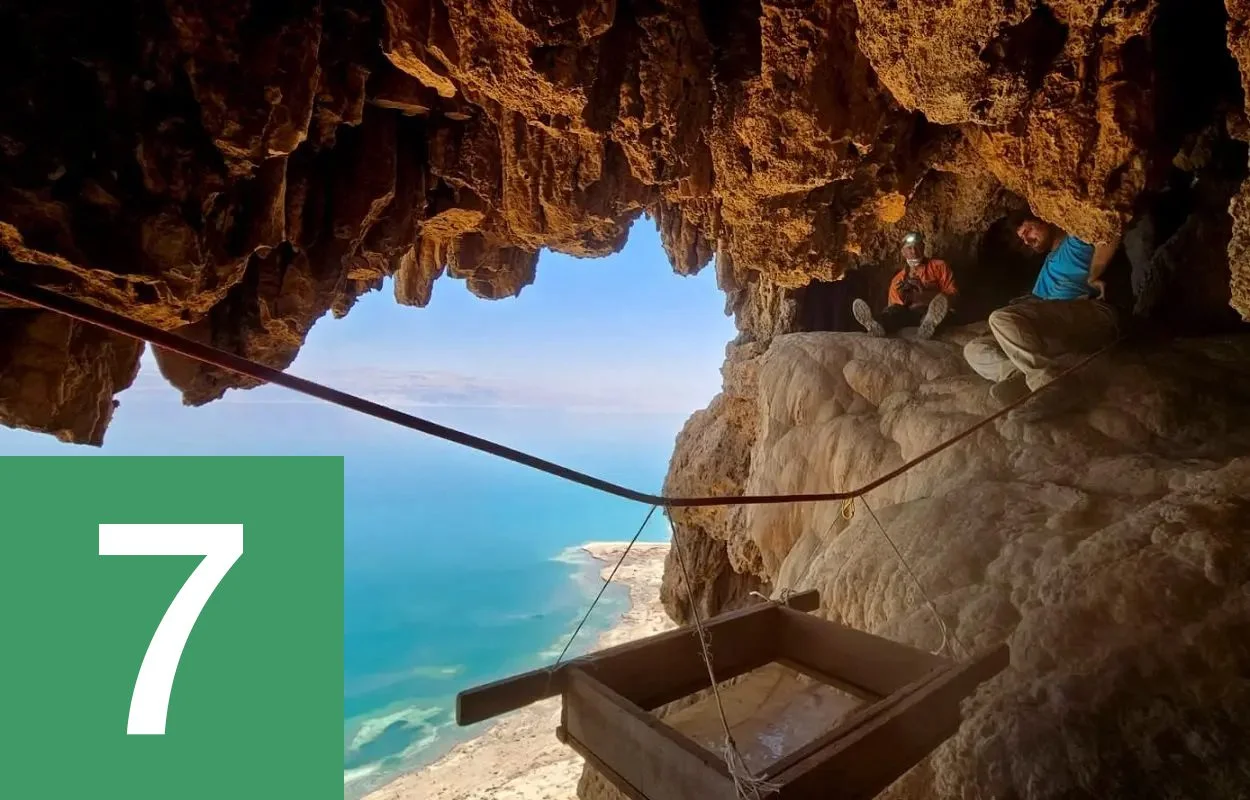
Cache of Roman swords found in desert cave
According to a press announcement by the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), the discovery was made while researchers were inspecting a known Hebrew script inscription written on the walls of a small cave in the En Gedi Nature Reserve, Israel. While on the upper level of the cave, Asaf Gayer from Ariel University, spotted an extremely well-preserved Roman pilum in a deep narrow crevice. Upon notifying IAA, archaeologists have recovered four well-preserved swords that date from the Roman period around 1,900-years-ago. Find out more
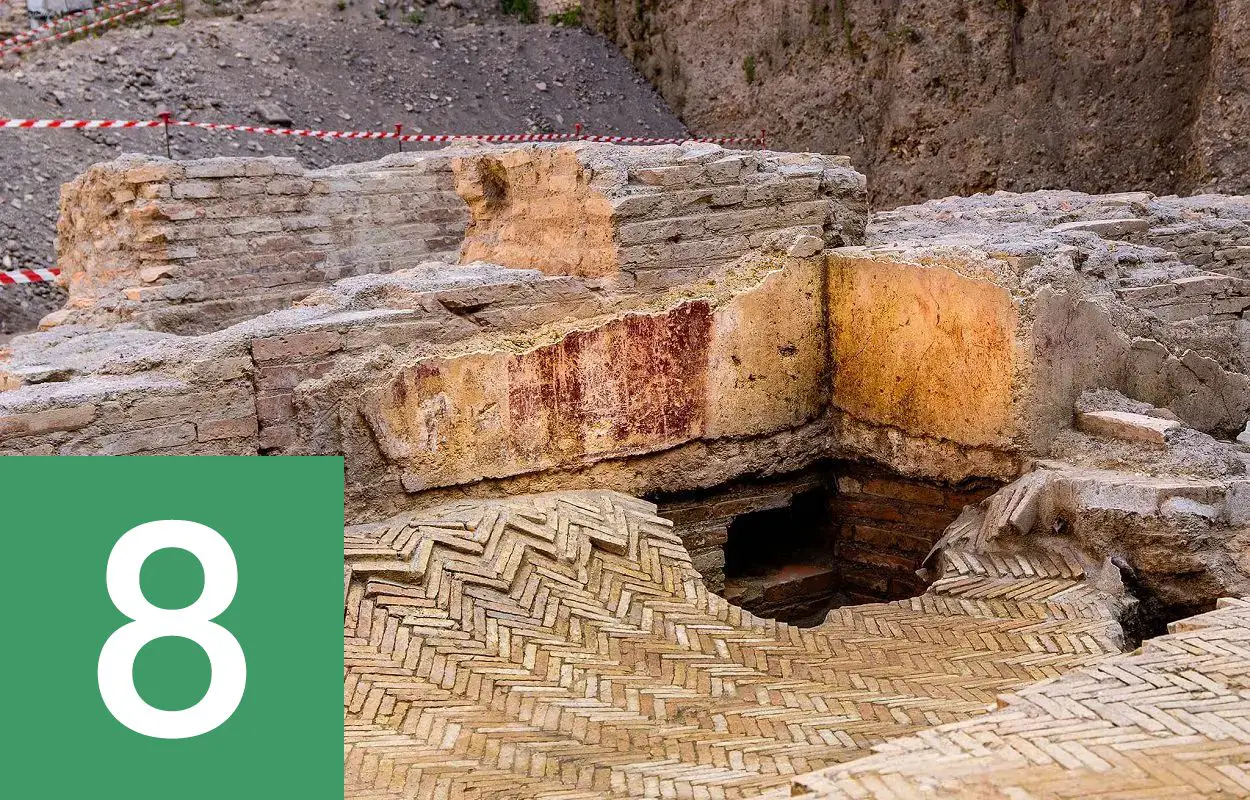
Remains of the Theatrum Neroni used by Nero found in Rome
Excavations conducted by the Superintendence of Rome have uncovered the remains of the Theatrum Neroni, a private theatre erected by Emperor Nero in Rome, Italy. Until now, evidence of the Theatrum Neroni were only known from literary sources such as text written by Pliny the Elder, Suetonius and Tacitus. Nero used the private theatre for rehearsals of his singing performances in the Theatre of Pompey, and may have been where he was witness to the great Fire of Rome in AD 64. Find out more
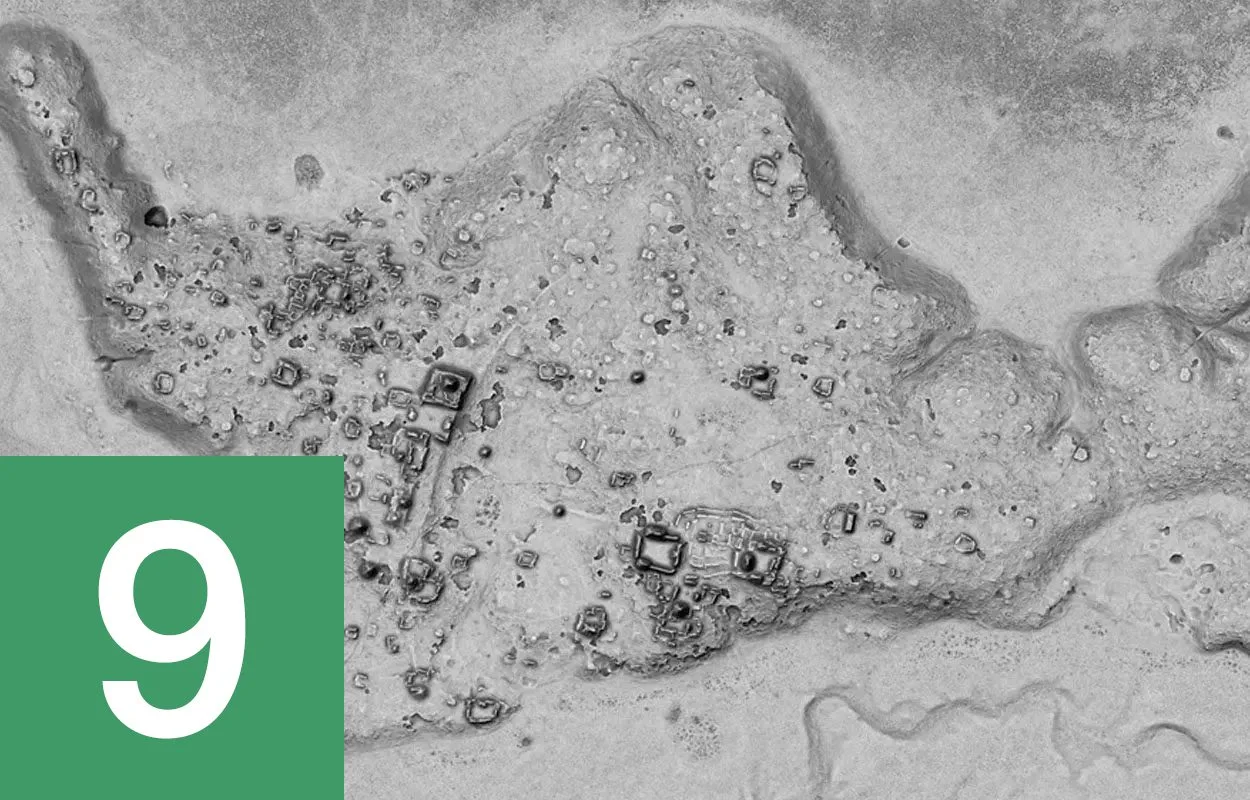
Lost Maya city discovered in Mexican jungle
Archaeologists from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) have announced the discovery of a previously unknown Maya city in the forests of the Balamkú ecological reserve, Mexico. The city has been named Ocomtún (meaning “stone column”) due to numerous cylindrical stone columns that have been uncovered throughout the interior. Archaeologists made the discovery as part of a project to document and map unexplored areas of central Campache using high resolution photography and Light Detection and Ranging (LiDar). Find out more
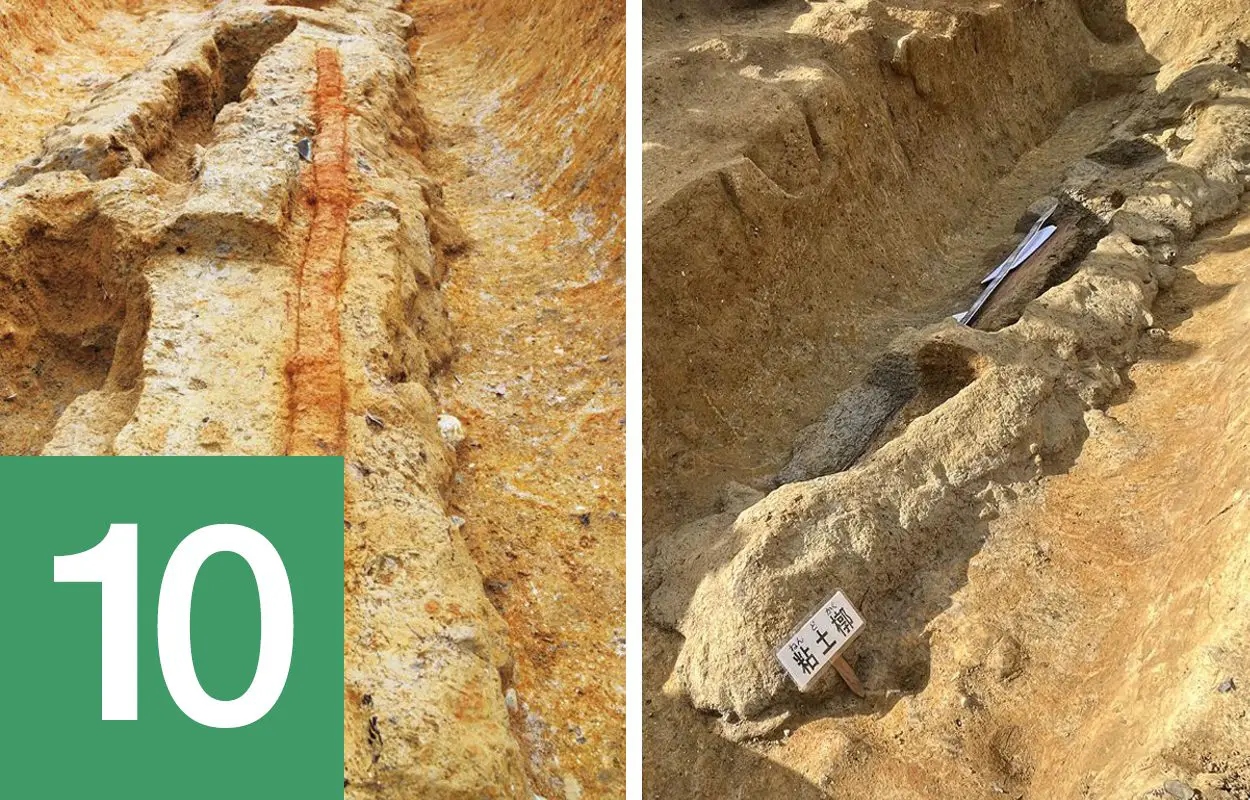
Giant 2.3 metre-long dakoken sword among unprecedented discoveries in burial mound
Archaeologists from the Nara Municipal Buried Cultural Properties Research Centre, working in collaboration with the Nara Prefectural Archaeological Institute of Kashihara, have uncovered a giant 2.3 metre-long dakoken sword during excavations at the Tomiomaruyama burial mound in Nara City, Japan. The sword has a slightly bent blade like a snake, a typical example of a “dakoken” sword related to the worship of the snake god. The sword is the largest discovered intact in Japan, with experts suggesting served a ceremonial purpose to ward off evil. Find out more