A study of declassified imagery taken by Cold War era satellites during the 1960s and 70s has led to the discovery of 396 previously undiscovered Roman forts.
The forts are spread across the Syrian Steppe in what is now Syria and Iraq to protect the eastern provinces from Arab and Persian incursions.
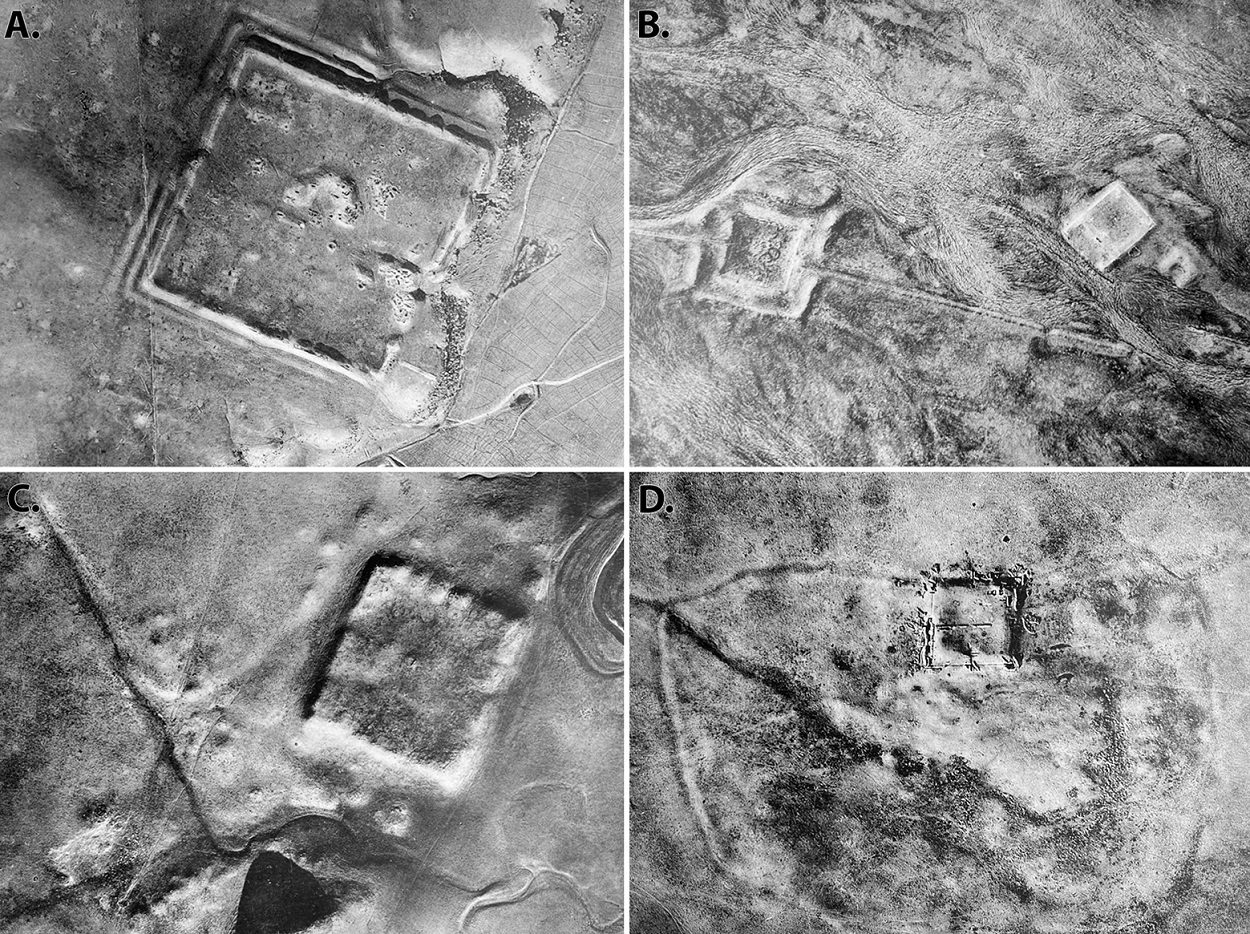
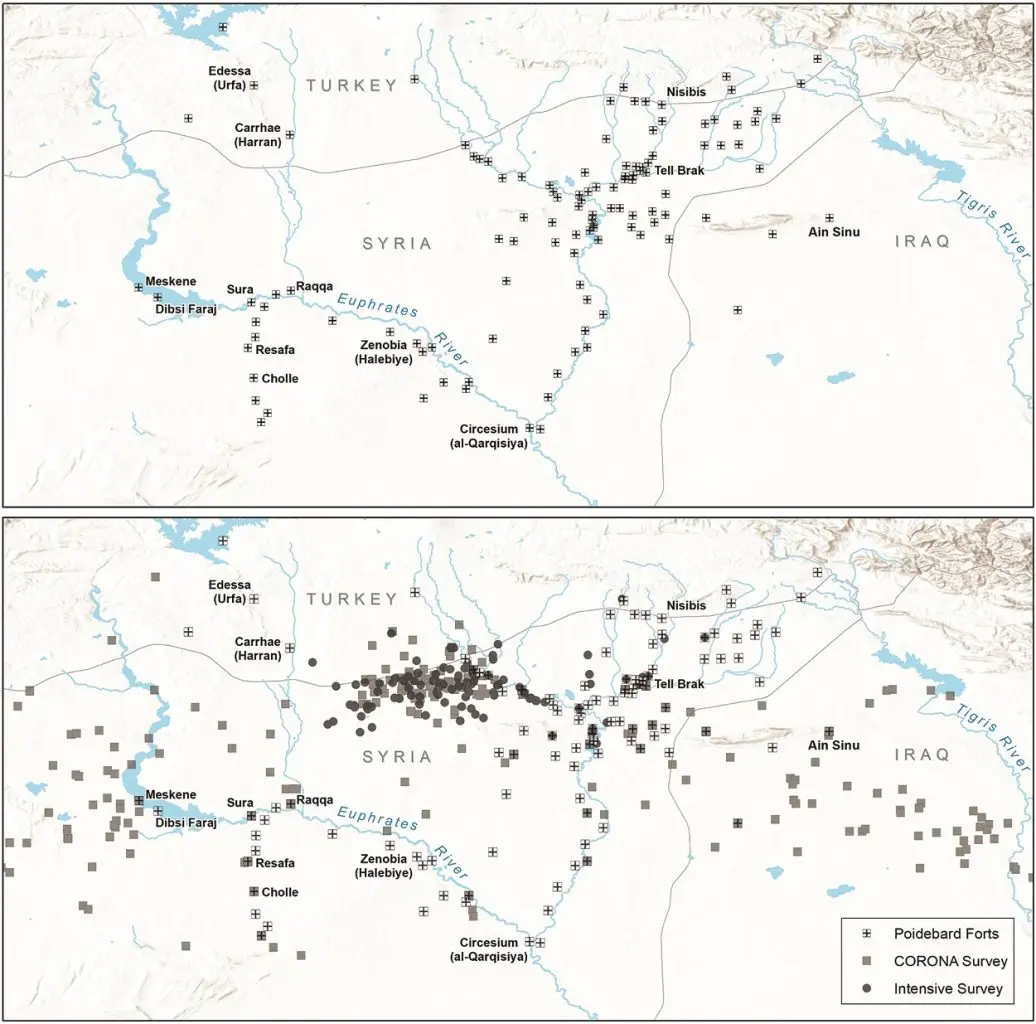
According to the researchers, the forts are in a region where a proposed defensive line of 116 forts were identified in an aerial survey conducted by Father Antoine Poidebard in 1934.
“Since the 1930s, historians and archaeologists have debated the strategic or political purpose of this system of fortifications,” says lead author of the research, Professor Jesse Casana from Dartmouth College, “but few scholars have questioned Poidebard’s basic observation that there was a line of forts defining the eastern Roman frontier.”
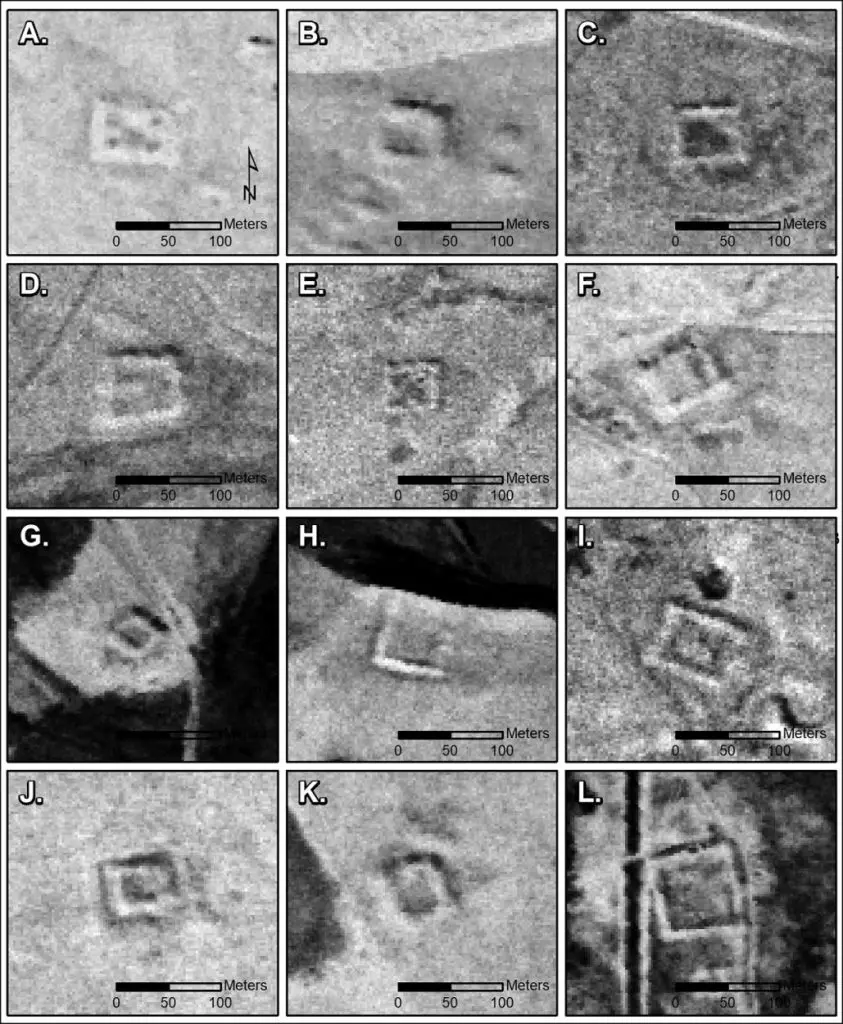
In a study published in the journal Antiquity, a team from Dartmouth College studied the declassified spy satellite imagery which formed part of the first spy satellite programme’s to determine whether Poidebard’s findings were accurate.
Using the forts found by Poidebard’s as a point of reference, the study revealed 396 new fort locations in a landscape that has been severely impacted by modern-day changes in land-use. The forts were found throughout the region spanning from the east to the west, contradicting the theory that they formed a north-south border wall.
Instead, the study suggests that the forts were constructed by the Romans to promote inter-regional trade, safeguarding caravans journeying between the eastern provinces and non-Roman lands, and enabling communication between the eastern and western regions.
Crucially, this suggests that the boundaries of the Roman World were more flexible and inclusive than previously thought. It’s probable that the eastern Roman frontier wasn’t a constant hotspot of violent conflict.
Although the Romans had a strong military presence, they also placed importance on trade and communication with regions beyond their direct rule. Consequently, this revelation could significantly reshape our comprehension of life on the Roman frontiers.
Speaking to HeritageDaily, Professor Jesse Casana from Dartmouth College, said: “We were only able to confidently identify extant archaeological remains at 38 of Poidebard’s 116 forts. In addition, many of the likely Roman forts we have documented in this study have already been destroyed by recent urban or agricultural development, and countless others are under extreme threat.”
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2023.153
Header Image Credit : Antiquity





