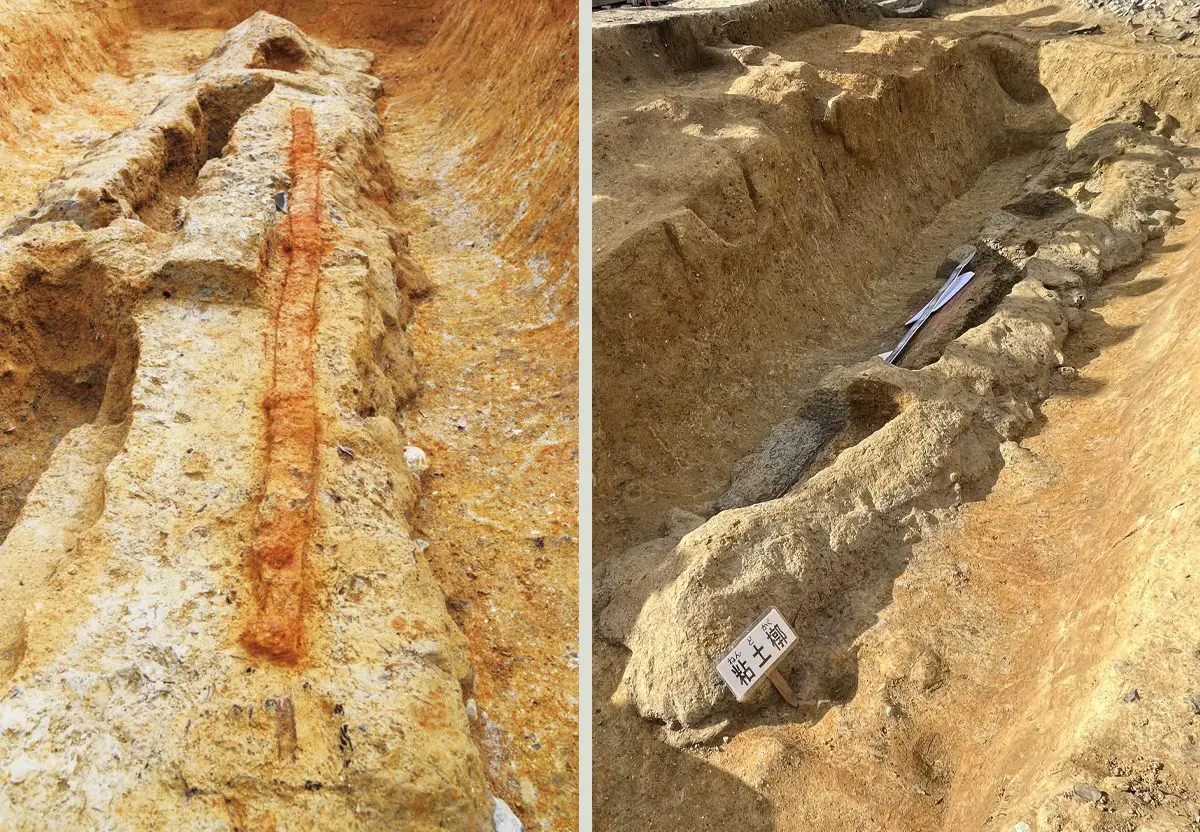
Archaeologists from the Nara Municipal Buried Cultural Properties Research Centre, working in collaboration with the Nara Prefectural Archaeological Institute of Kashihara, have uncovered a giant 2.3 metre-long dakoken sword during excavations at the Tomiomaruyama burial mound in Nara City, Japan.
The Tomiomaruyama burial mound dates from the 4th century AD during the Kofun Period (AD 300 to 538), the earliest era of recorded history in Japan.
The mound has a diameter of 86 metres and rises to a height of 10 metres, with previous excavations uncovering farming tools, utensils, cylindrical copper ware, bronze ware, and several decorated mirrors with god-and-animal motifs.
Recent excavations have uncovered a giant 2.3 metre-long dakoken sword made from iron, along with a shield-shaped bronze mirror in a layer of clay that covers a 5-metre-long wooden coffin.
Typically, bronze mirrors found at archaeological sites in Japan are rounded, however, the one from the Tomiomaruyama burial mound is shield shaped and measures 64 cm in height by 31 cm in width. The centre of the back of the mirror is raised, with two rounded patterns that are identical to the patterns typically inscribed on “Daryukyo” mirrors from the Kofun Period.
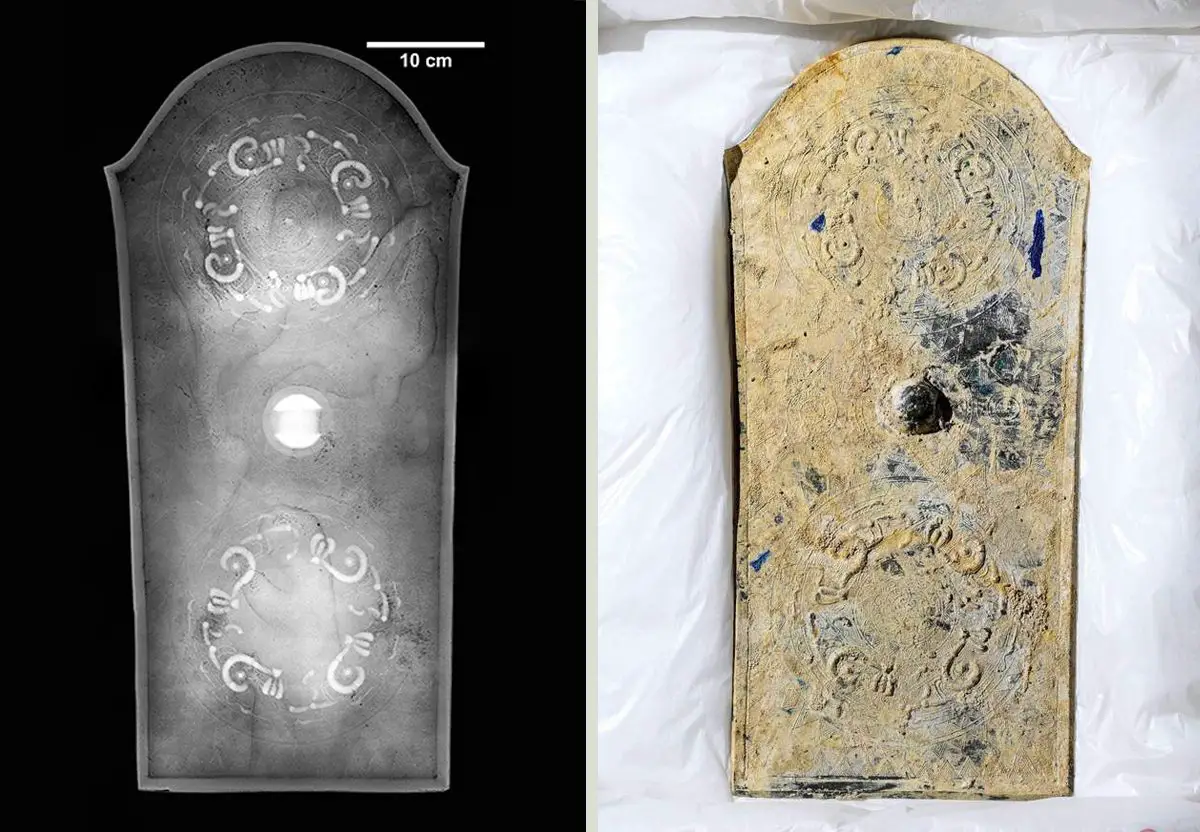
According to the researchers, the surface of the shield-shaped bronze mirror is the largest of any known bronze mirror found in Japan, with the only comparable example in size being the bronze mirror discovered at the Hirabaru ruins in Fukuoka.
The sword, which is around 2.3 metres in length has a slightly bent blade like a snake, a typical example of a “dakoken” sword related to the worship of the snake god. The sword is the largest discovered intact in Japan, with experts suggesting that it had a ceremonial purpose to ward off evil.
The archaeologists are yet to open the wooden coffin, but believe that its contents remain intact as there is no evidence of grave robbing. The team plan to study the coffin’s contents at a later date, with the sword and mirror currently undergoing restoration.
Seigo Wada, Director of the Hyogo Prefectural Museum of Archaeology, told Asia & Japan Watch “I wonder about the status of the person buried with the objects, as the individual was interred with a very unusual sword and mirror. There is a high expectation for the study of the contents of the coffin.”
Header Image Credit : Nara prefectural Archaeological Institute of Kashihara





