Archaeologists have discovered an exceptionally well-preserved tomb in the municipality of Giugliano in Campania, Italy.
The discovery was made following an archaeological investigation in the Flegreo Domitiana area, where previous studies have found a high density of burials from the Republican Age to the Roman Imperial Age.
The investigation identified an opus incertum wall first thought to demarcate the boundary of the necropolis, however, upon a closer inspection it was revealed to be the frontage of a monumental chamber tomb.
The tomb was found with a slab made from tuff sealing the entrance, leading to a chamber with preserved frescos across the ceilings and walls.
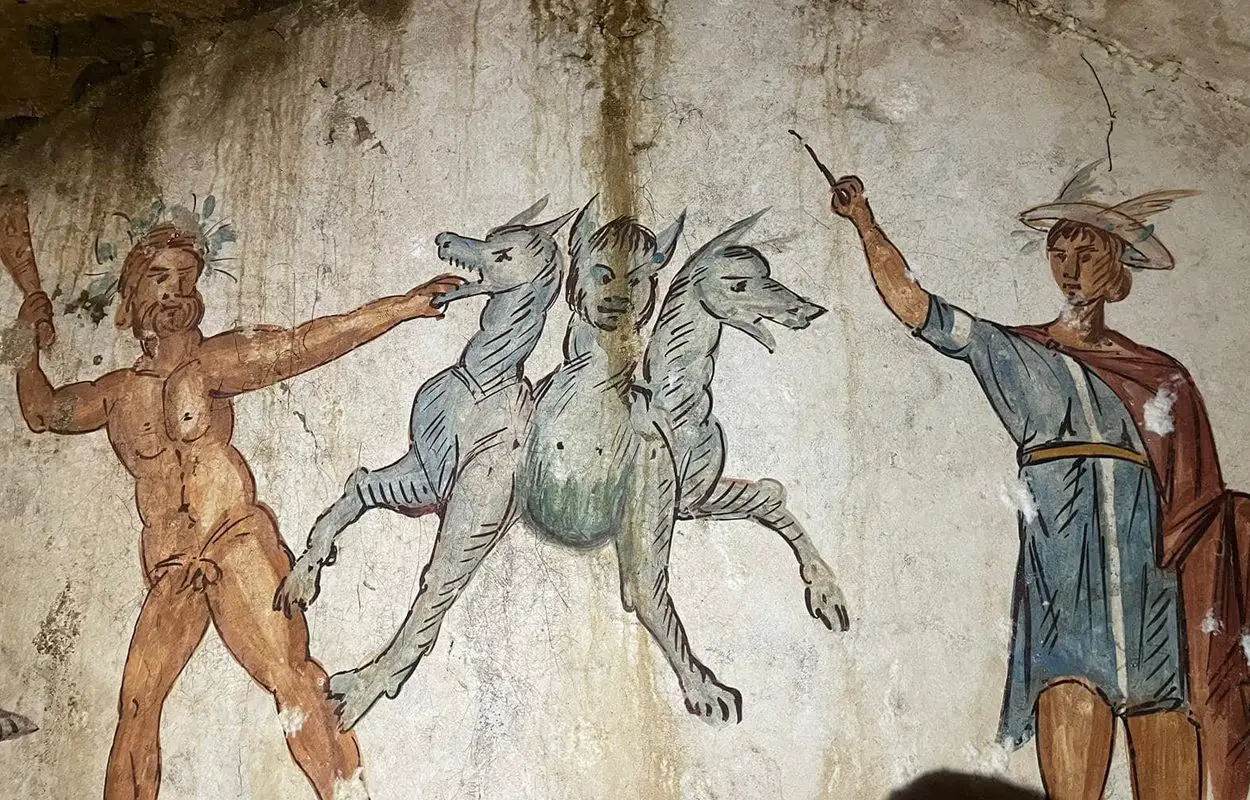
The most notable fresco depicts Cerberus (thus the tomb being designated “Tomb of Cerburus”), the three-headed dog from Ancient Greek mythology. Cerberus, also referred to as the “hound of Hades”, guarded the gates of the Underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. The scene represents the last of Heracles’ twelve labors, in which Cerberus is captured by Heracles.
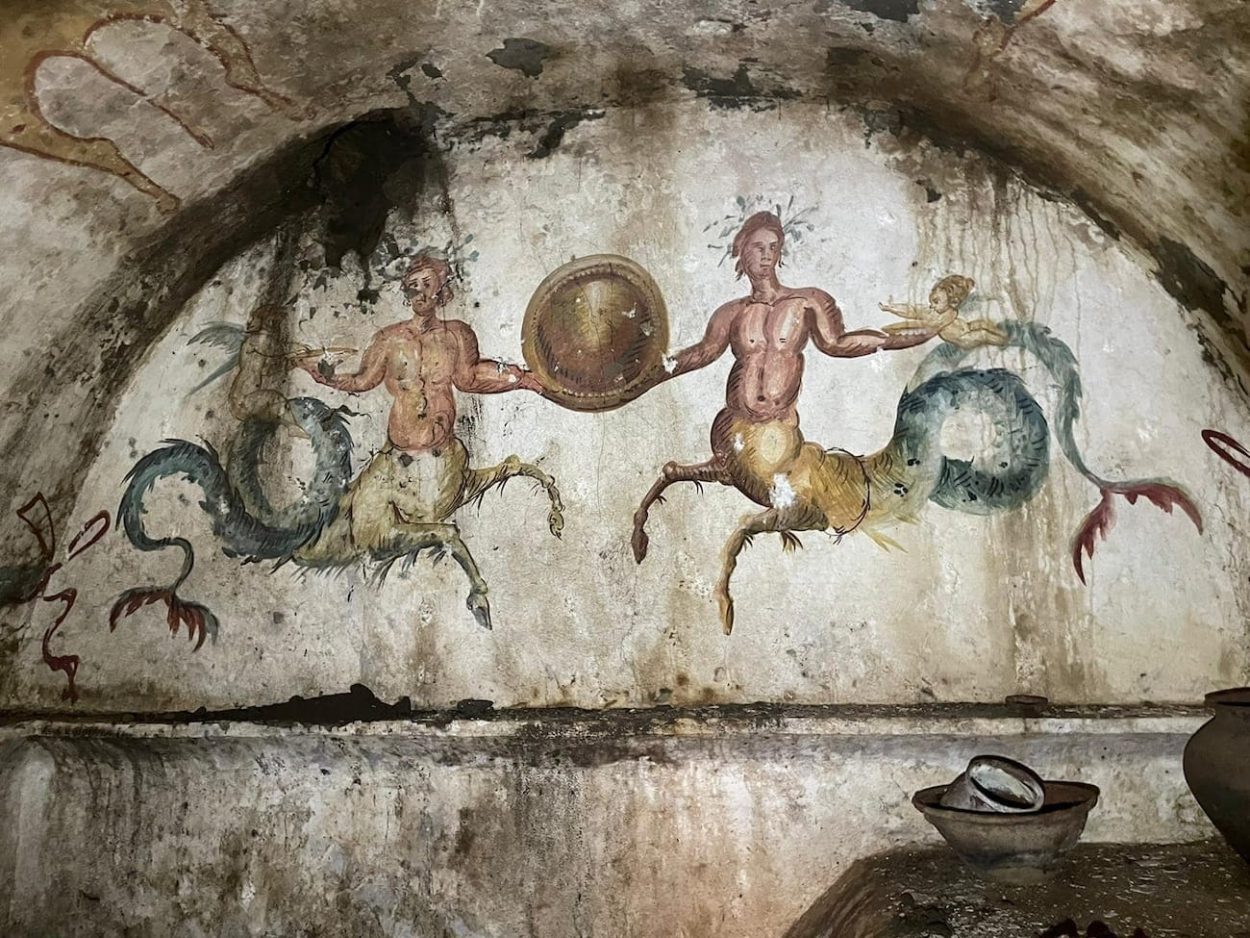
Also depicted in the tomb are mythological scenes of ichthyocentaurs, a centaurine-type sea creature with the upper body of a human, the lower anterior half and fore-legs of a horse, and the tailed half of a fish. The scene shows two ichthyocentaurs facing each other and holding a clypeus (a shield worn by the Greek hoplites and Romans), while being attended by two winged erotes (Roman Cupid-like babies).
According to a press announcement by the Superintendent Of Archaeology, Fine Arts And Landscape For The Naples Metropolitan Area: “The tomb has frescoed ceilings and walls in perfect condition, with mythological scenes that go all around the room and figurative representations among which, a three-headed dog stands out. Three painted klìnai , an altar with vessels for libations, the deceased still placed on the funeral beds with rich objects – complete the picture of a discovery which, in this area, is unprecedented.”
Superintendent Of Archaeology, Fine Arts And Landscape For The Naples Metropolitan Area
Header Image Credit : Ministry of Culture





