Buhen was an ancient Egyptian settlement and fortress, located on the West bank of the Nile in present-day Sudan.
Buhen was first settled during the Old Kingdom, possibly by Sneferu (the founding Pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt) as a small trading post and copper works until the settlement was abandoned during the 5th Dynasty two centuries later.
During the reign of Senusret III in the 12th Dynasty, several military campaigns pressed into the Kingdom of Kush and established a chain of fortifications consisting of Kumma, Semna, Dabenarti, Askut, Uronarti, Shalfak, Mirgissa, and Buhen.
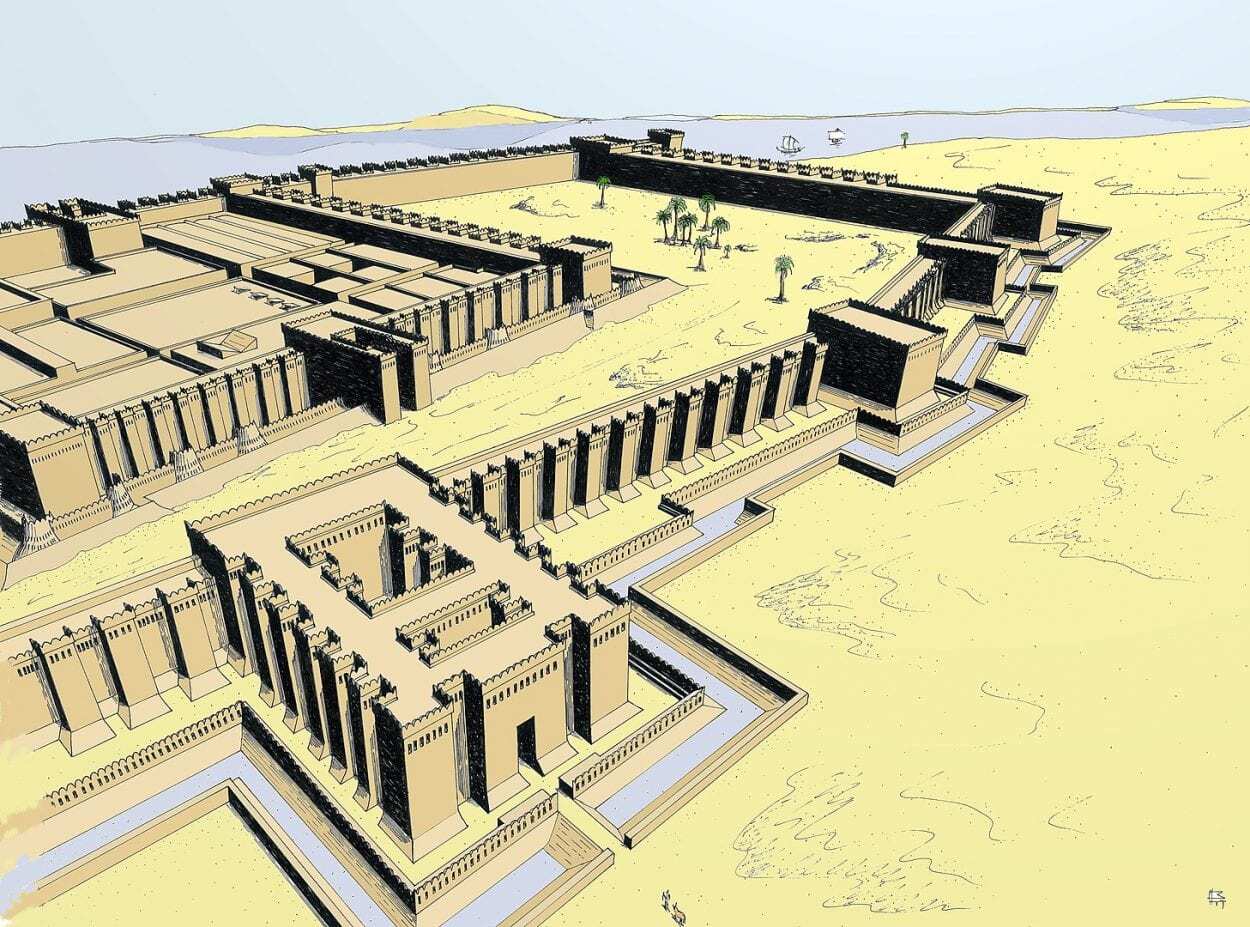
Buhen was the most northern fortress in the chain, positioned along the Nile’s banks to administrate the whole region of the Second Cataract and protect commercial shipping from rebel Nubians in the south.
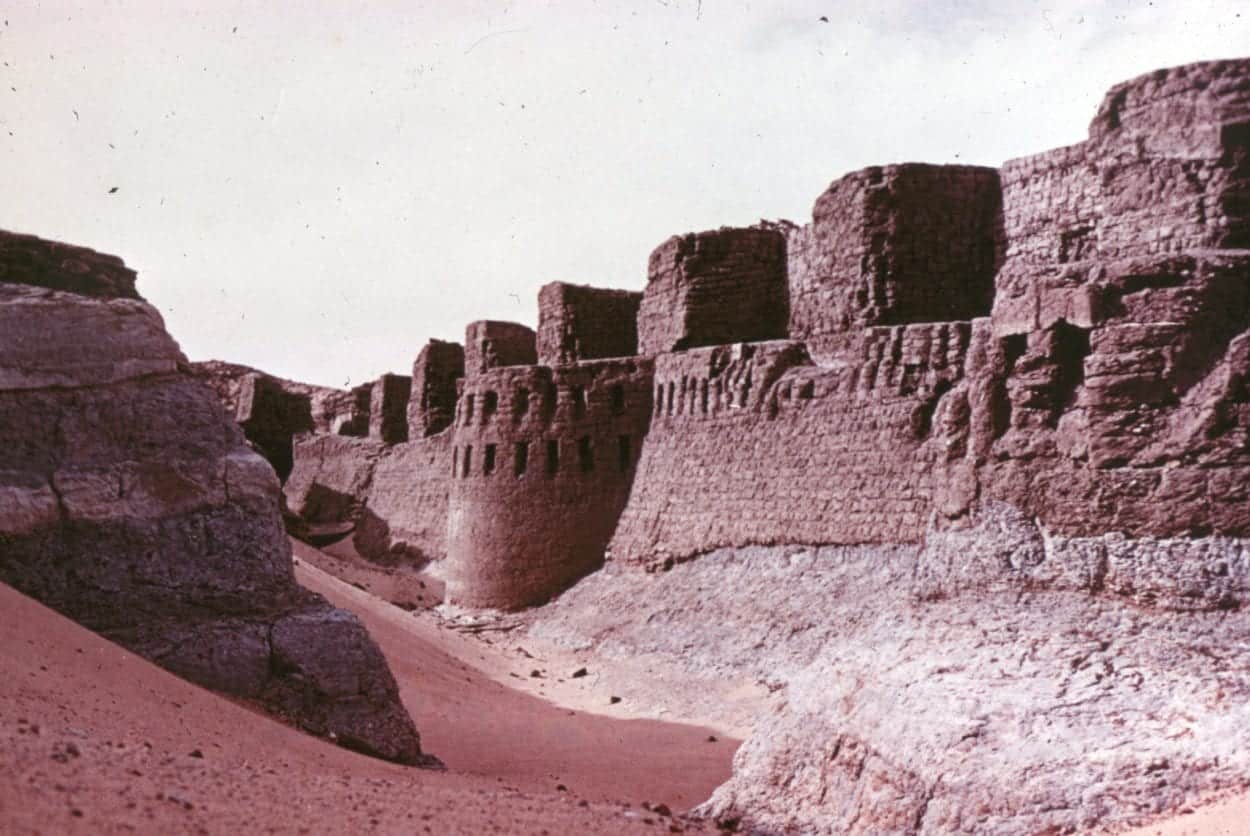

The fort covered an area of 13,000 square metres, extending more than 150 metres in length, and was defended by a 10-metre-high wall made of brick and stone with a surrounding moat.
Within the walls, a small town was established in a grid system, comprising of various administrative buildings, storehouses, and dwellings to house around 1,000 soldiers, 300 archers, and their families. A temple dedicated to Horus was also constructed within the walls of the fort by Queen Hatshepsut (the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt).
Buhen remained an imposing symbol of Egyptian power that survived numerous changes in succession of rule, namely the Egyptians, the Kushites, and the Meroitic peoples. During the 13th Dynasty, the fortress fell to the Kushites until it was recaptured by Pharaoh Ahmose I (founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt).With the construction of the Aswan High Dam and Lake Nasser from 1958 and 1970, various monuments were under threat from being submerged. A UNESCO campaign was created as part of an international effort to record or move archaeological sites, resulting in 22 monuments and architectural complexes being relocated.
Archaeologists conducted excavations of Buhen in the early 1960s to document what was possible in the limited time-frame available, discovering a sprawling settlement adjacent to the fort dating from the Old Kingdom. Rescue excavations also dismantled the temple of Horus, which is now housed in the National Museum of Sudan in Khartoum.
The rising waters reached Buhen in 1964, completely submerging the fortress where it now lies beneath the depths of Lake Nasser today.
Header Image Credit : Franck Monnier – Éditions Safran – CC BY 2.5