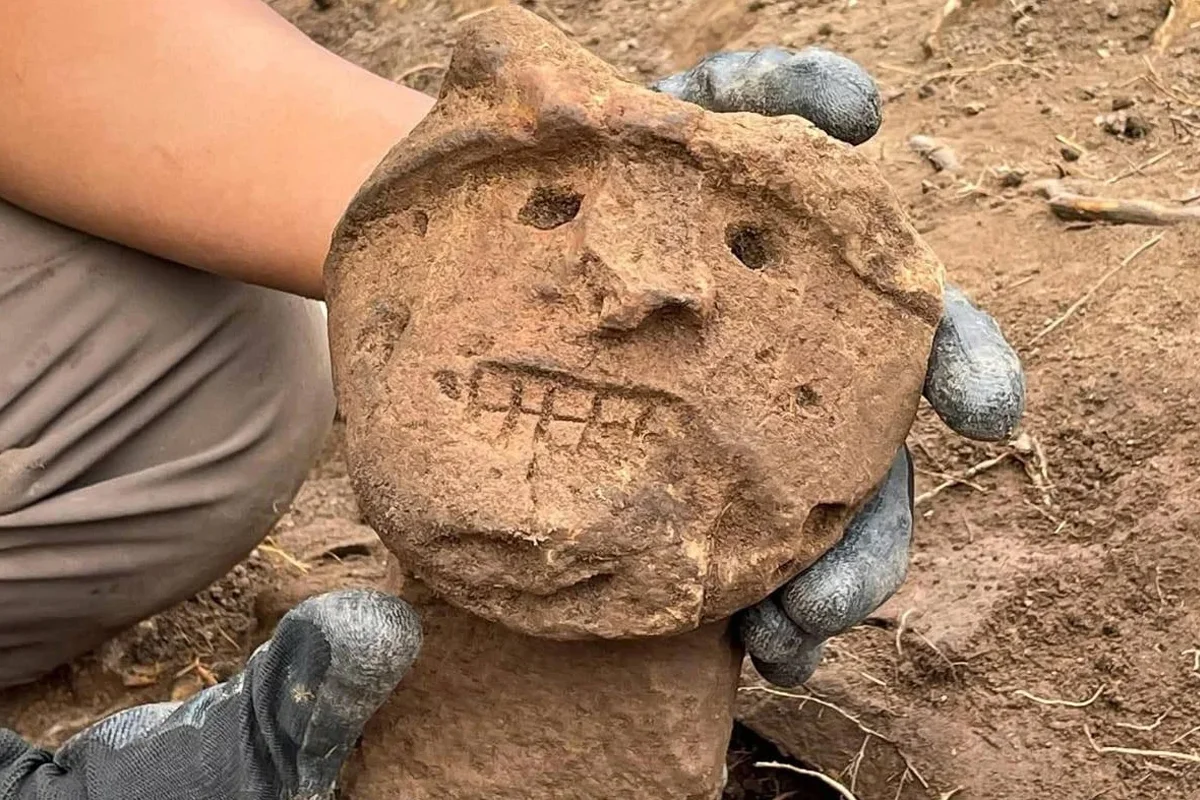
Archaeologists have discovered two ceremonial club heads and approximately 200 pre-Hispanic structures belonging to the ancient Chachapoyas culture during a study in the La Jalca district, located in Chachapoyas province, Amazonas.
The Chachapoyas, also called the “Warriors of the Clouds”, lived in the cloud forests of the southern part of the Department of Amazonas of present-day Peru. The name Chachapoya was given by the Inca, who conquered the civilisation shortly before the Spanish conquest in the 16th century AD.
Since most historical accounts of the Chachapoyas come from Inca and Spanish sources, our understanding of their culture largely depends on archaeological evidence.
Key insights have been uncovered through the study of ancient sites such as the monumental fortress of Kuelap, the settlement of Gran Saposoa, the Atumpucro complex, and the intricate burial chambers at Revash and Laguna de las Momias (“Mummy Lake”).
In a recent study led by the Kuelap Archaeology and Anthropology Research Institute (INAAK) and the Xalca Grande Archaeological Project, archaeologists have uncovered more than 200 previously unknown Chachapoyas structures in the Amazonas using drones and advanced survey tools such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging).
Within the rubble of a perimeter wall surrounding a circular structure, the researchers discovered two unique ceremonial club heads, deliberately placed in a way that suggests religious or symbolic significance.
According to experts, the club heads are reminiscent of the Chavín style, a culture that developed in the northern Andean highlands of Peru, however, it is possible that the discovery reflects a unique form and study to the Chachapoyas region not previously documented.
Header Image Credit : INAAK
Soruces : INAAK





