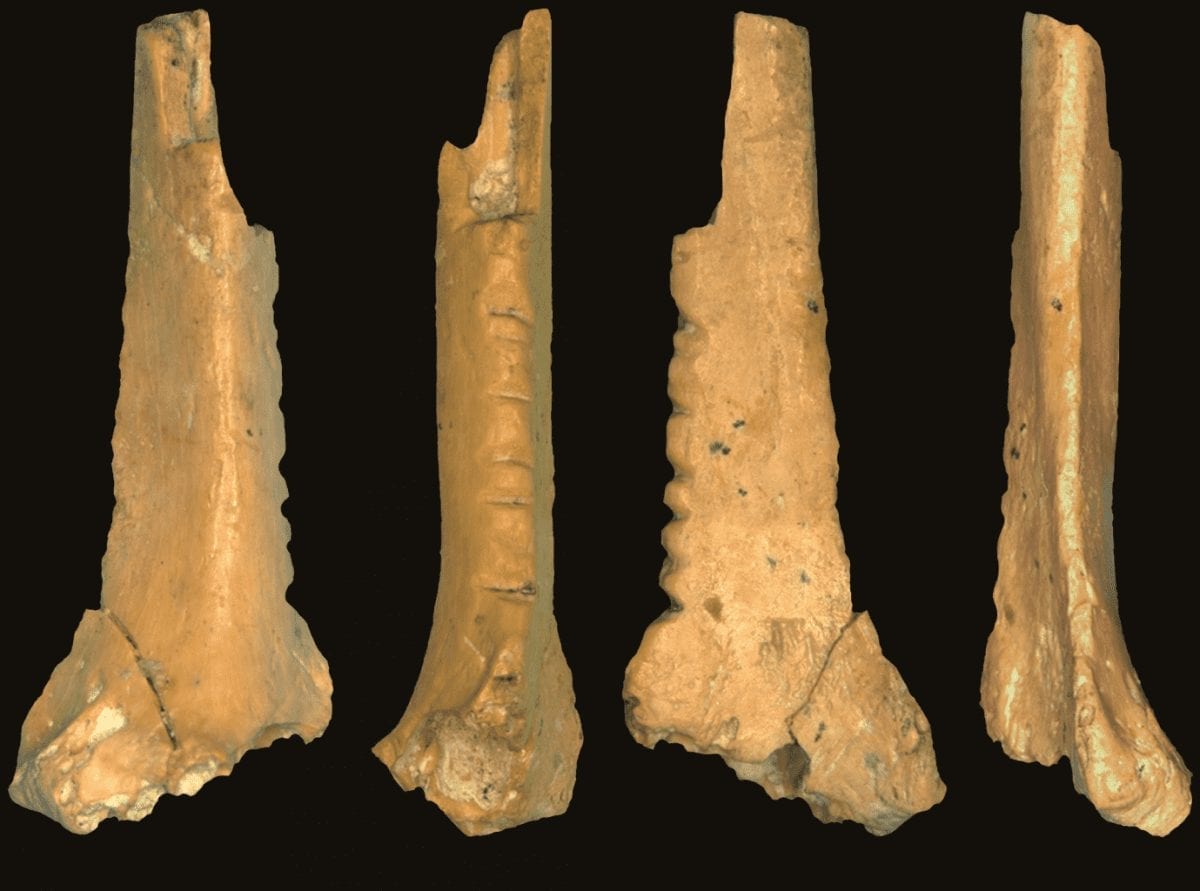
The cognitive abilities of Neanderthals are debated, but a raven bone fragment found at the Zaskalnaya VI (ZSK) site in Crimea features two notches that may have been made by Neanderthals intentionally to display a visually consistent pattern.
Majkic and colleagues conducted a mixed-methods study to assess whether the two extra notches on the ZSK raven bone were made by Neanderthals with the intention of making the final series of notches appear to be evenly spaced.
First, researchers conducted a multi-phase experiment where recruited volunteers were asked to create evenly spaced notches in domestic turkey bones, which are similar in size to the ZSK raven bone.
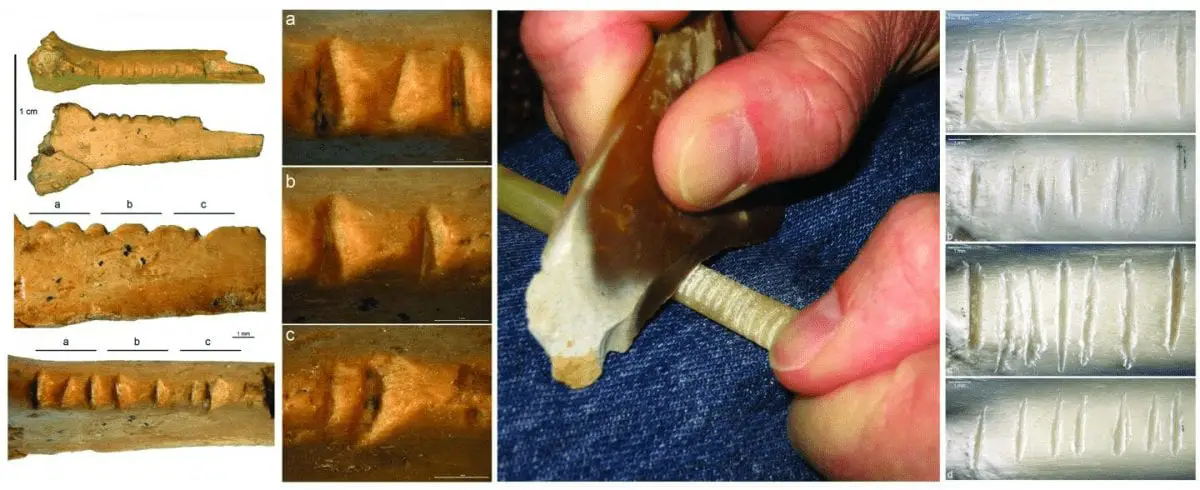
CREDIT : Francesco d’Errico
Morphometric analyses reveal that the equal spacing of the experimental notches was comparable to the spacing of notches in the ZSK raven bone, even when adjusted for errors in human perception. Archeological specimens featuring aligned notches from different sites were also analyzed and compared with the ZSK raven bone specimen.
Researchers concluded that the two extra notches on the ZSK raven bone may have been made by Neanderthals intentionally to create a visually consistent, and perhaps symbolic, pattern.
A series of recent discoveries of altered bird bones across Neanderthal sites has caused many researchers to argue that the objects were used for personal ornaments, as opposed to butchery tools or activities. But this study is the first that provides direct evidence to support a symbolic argument for intentional modifications on a bird bone. Full article