Archaeologists from the Lyobaa Project have confirmed a network of subterranean chambers and tunnels beneath Mitla – The Zapotec “Place of the Dead”.
Mitla is an archaeological site associated with the Zapotec culture, located in the Oaxaca Valley in the present-day state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico.
The Lyobaa Project is a multidisciplinary research team led by the Mexican National Institute of History and Anthropology (INAH), the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM), and the ARX Association for Archaeological Research and Exploration.
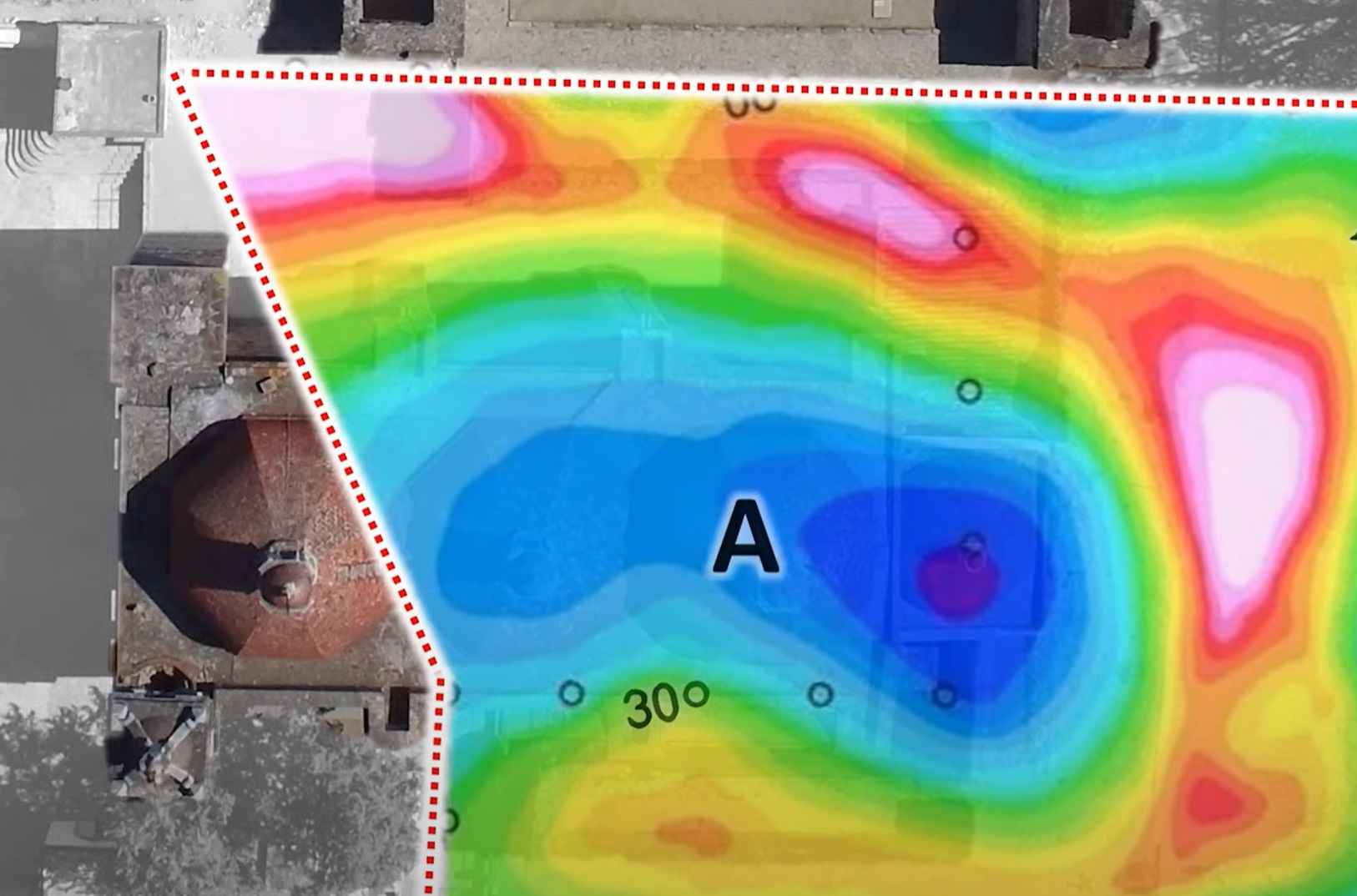
The team used advanced geophysical methods such as Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), Electric Resistivity Tomography (ERT), and Seismic Noise Tomography, revealing a large void beneath the main altar at the Church of San Pablo Apostol at Mitla and a network of tunnels stretching in multiple directions.

According to a press statement by the Lyobaa Project: “This new discovery aligns with ancient accounts, including those of 17th-century Dominican Father Francisco de Burgoa, who described a labyrinth of chambers and tunnels beneath the site, considered by the ancient Zapotecs to be an entrance to the Underworld, or Lyobaa.”
The team also identified further subterranean geophysical anomalies in the Calvario Group, the Arroyo Group, and the South Group of surface structures, which may correspond to more unexplored chambers or tombs.
“Additionally, Ground Penetrating Radar revealed the potential remains of an earlier monumental stairway beneath the present floor level of the Palace in the Columns Group, with important implications for the chronology of the site,” said the Lyobaa Project.
The project intends to corroborate the data with additional probes and archaeological excavations to determine the exact nature of the geophysical anomalies identified.
Header Image Credit : ARX Project
Sources : ARX Project