Dentistry during Viking Age was surprisingly advanced, according to a new study by researchers from the University of Gothenburg.
The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, examined 3,293 teeth found at Varnhem in Västergötland, Sweden. The site contains the remains of a Viking Age settlement, where previous excavations have uncovered skeletal remains from over 171 individuals.
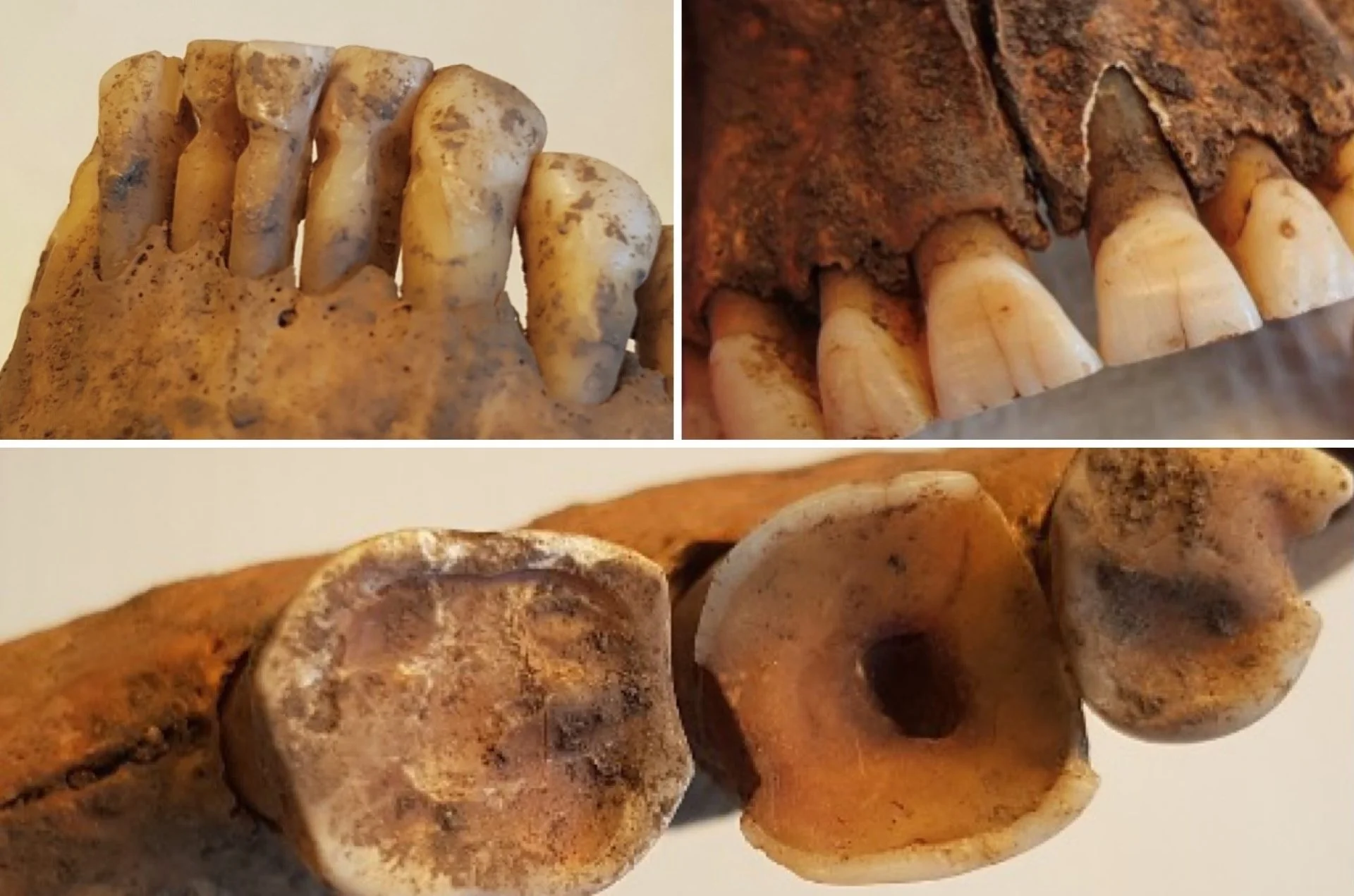
The University of Gothenburg’s Institute of Odontology collaborated with an osteologist from the Västergötland Museum, where the teeth underwent a clinical examination using standard dentistry tools and X-ray examinations.
The results revealed that 49% of the Viking population had one or more caries lesions. Of the adults’ teeth, 13% were affected by caries – often at the roots. However, children with milk teeth – or with both milk and adult teeth – were entirely caries-free.
Among the individuals examined, on average they had lost approximately 6% of their teeth (excluding wisdom teeth) throughout their lifespans. Additionally, the likelihood of tooth loss heightened as individuals aged.
However, according to Carolina Bertilsson, a dentist and Associate Researcher: “There were several signs that the Vikings had modified their teeth, including evidence of using toothpicks, filing front teeth, and even dental treatment of teeth with infections.”
“This is very exciting to see, and not unlike the dental treatments we carry out today when we drill into infected teeth. The Vikings seem to have had knowledge about teeth, but we don’t know whether they did these procedures themselves or had help,” added Bertilsson.
The intentionally filed front teeth could have served as a form of identity marker. In both the current research and prior studies, such cases were exclusively observed in males.
“This study provides new insights into Viking oral health, and indicates that teeth were important in Varnhem’s Viking culture. It also suggests that dentistry in the Viking Age was probably more sophisticated than previously thought,” said Bertilsson.
Header Image Credit : Carolina Bertilsson and Henrik Lund