According to an announcement by the Rostock City Hall, archaeologists have uncovered a devil curse written on a 15th century tablet in Rostock, Germany.
The discovery was made during construction works for the Rostock town hall extension, where excavations of a medieval latrine revealed an inconspicuous piece of rolled up lead.
Historical records indicate that a 14th-century double-gabled house once occupied the site, described as “one of the most beautiful of its kind in all of Northern Germany.”
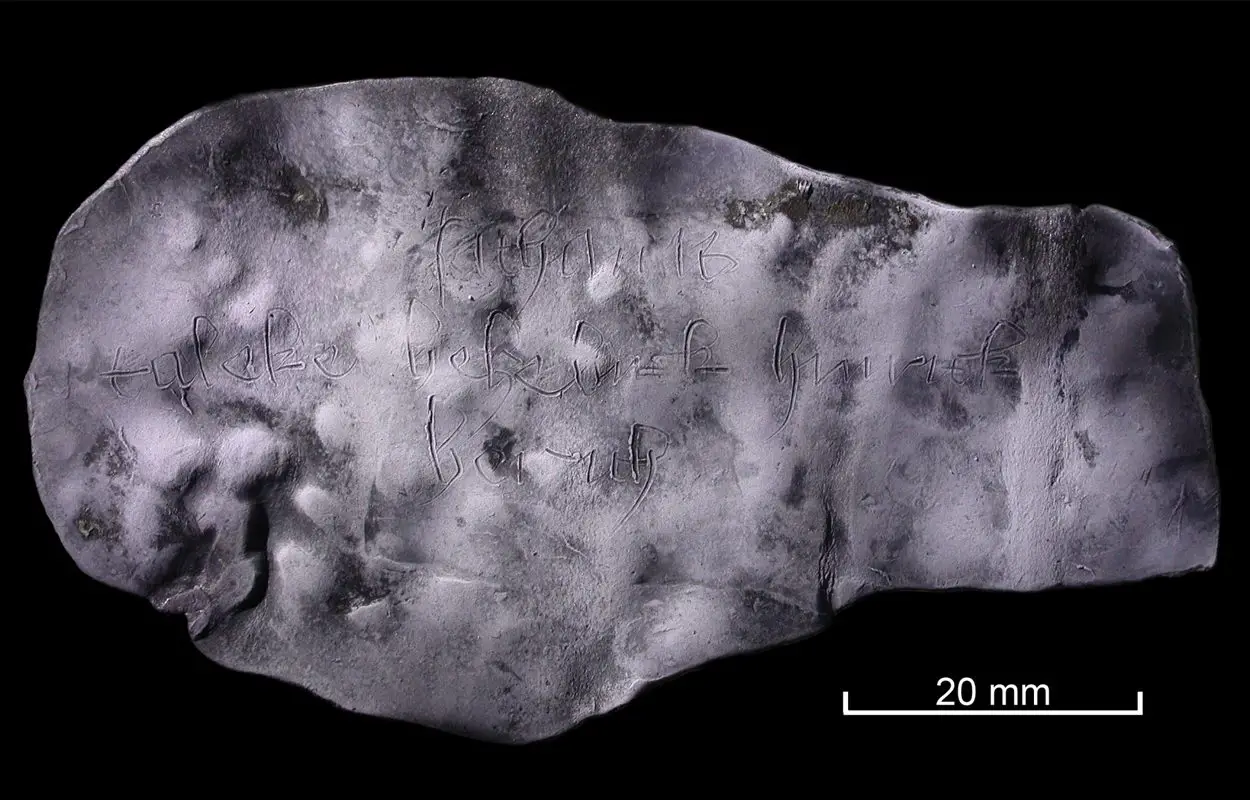
Upon unrolling the lead piece, the words “sathanas taleke belzebuk hinrik berith” became legible, directing a devil curse against a woman named Taleke and a man called Hinrik (Heinrich).
The text is written in Blackletter, also known as Gothic minuscule, or Textura, which was used throughout Western Europe from the 12th century until the 17th century.
Curse tablets were common in antiquity during the Greco-Roman periods, where curses written on thin sheets of lead (rolled up) were used to ask the gods, spirits, or the deceased to perform an action on a person or object, or to exert influence over the target of the curse.
According to the researchers, the discovery in Rostock is incredibly rare, especially with an incantation towards belzebuk (Beelzebub), another name for the Devil (Satan). The mention of Berith in the curse refers to Baʿal Berith, which the Rabbinic tradition also equates with Beelzebub, the Lord of the Flies.
Speculation surrounds the motive for the curse, suggesting intentions such as severing a relationship, feelings of unrequited love, jealousy, or aiming to bring misfortune upon both the named individuals.
Excavations also revealed the remains of cellars and foundations dated to the 16th and 17th century, traces of a former waterway, and a 15th century lusterware blue bowl that originates from Valencia in Spain.
Header Image Credit : Archeology in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (AIM-V)