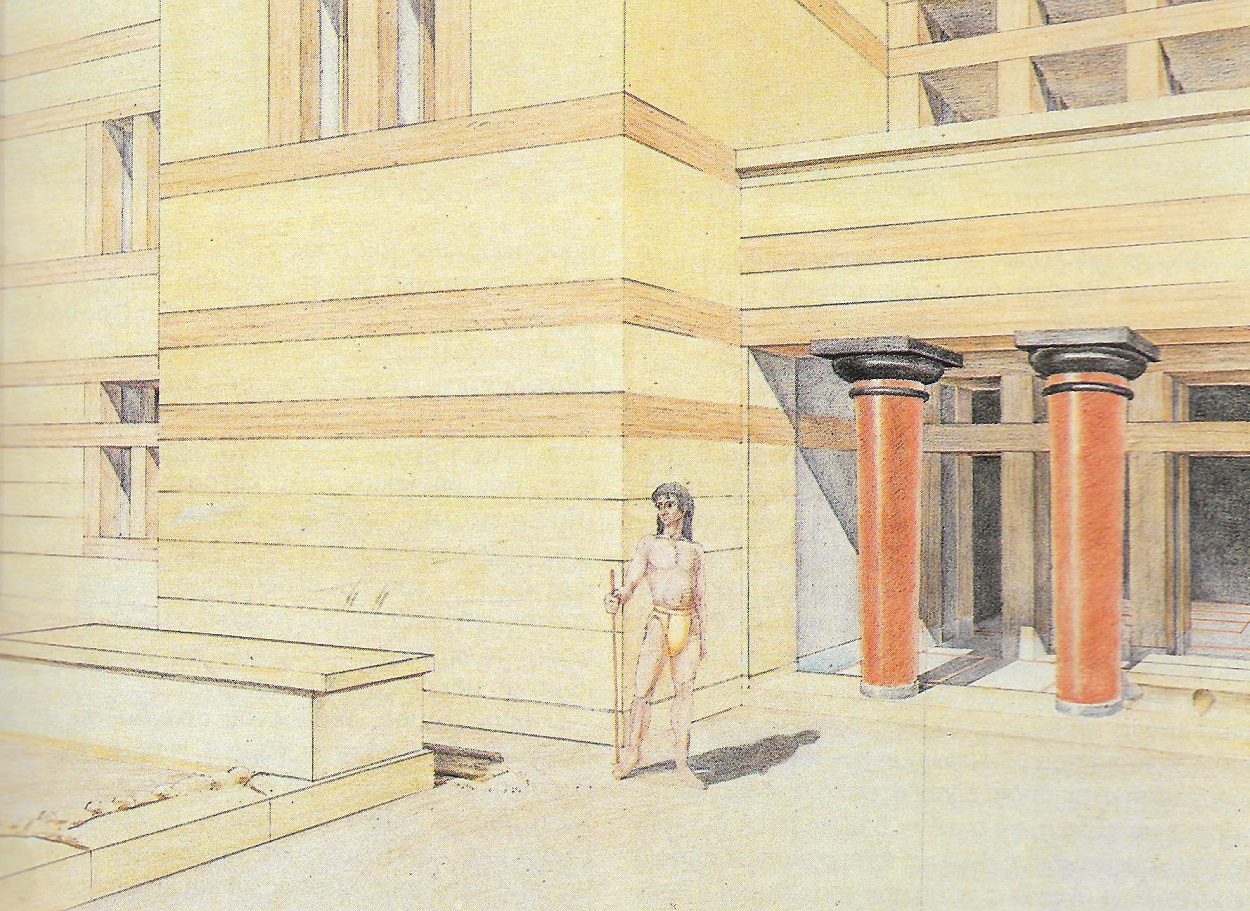
A study of the Minoan palace at Archanas has revealed that numerous architectural features used gypsum to make the palace sparkle.
The palace was built as a summer retreat for the Knossos kings, located in present-day Archanes, a former municipality in the Heraklion regional unit of Crete.
Since 1966, Archanes has been excavated by the Greek Archaeological Society under the supervision of Yannis Sakellarakis and Efi Sapouna-Sakellarakis.
Previous excavations have uncovered ashlar blocks, limestone plaques, stucco floor tiles, kouskoura slabs, blue marble flooring, carved concave altars, and several frescoes that date mainly from the Middle Minoan period.
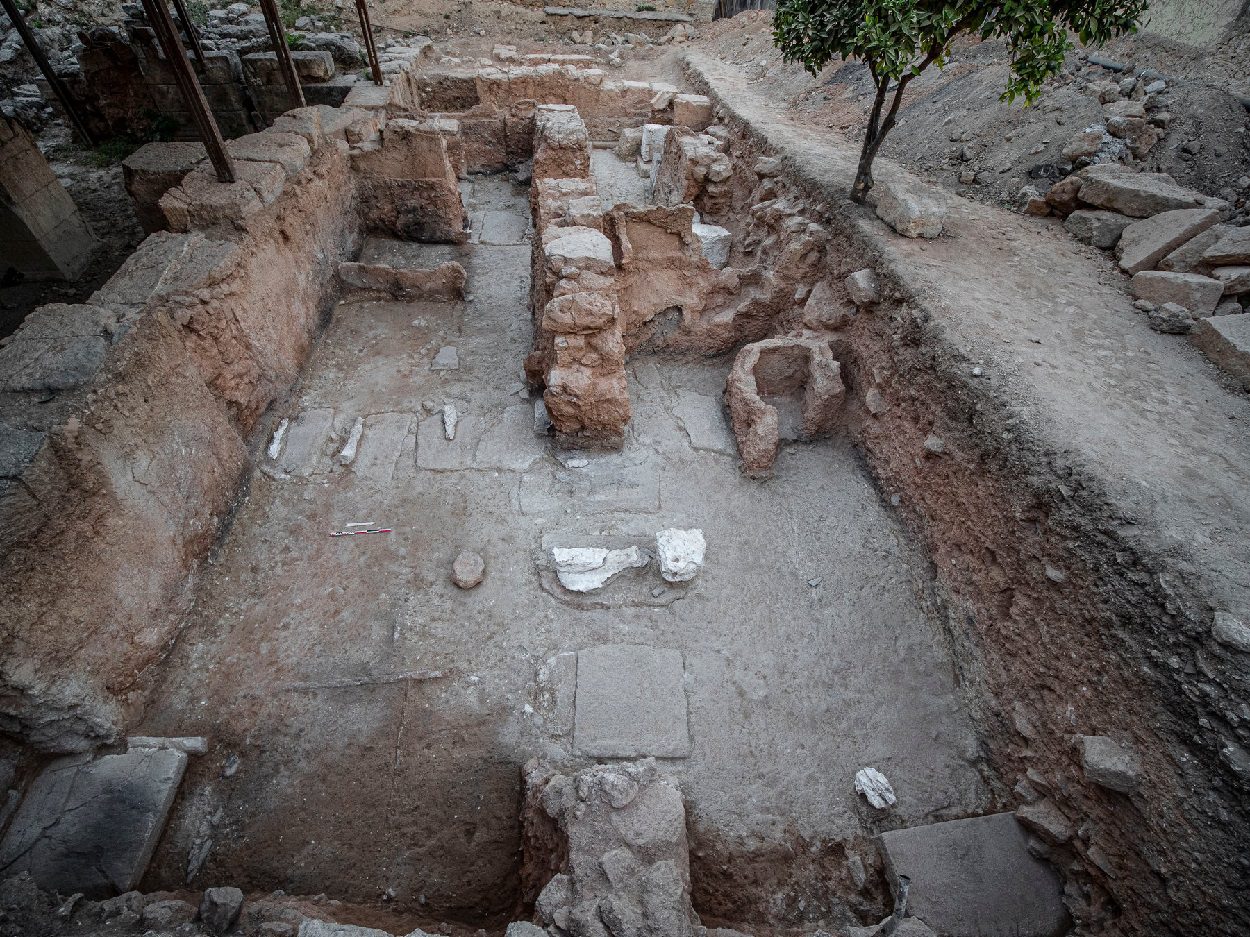

The latest excavation in the northernmost part of the palace has revealed that architectural features such as pilasters, multi-doors, and entrance ways used gypsum to make the palace sparkle.
The word gypsum is derived from the Greek word gypsos, meaning “plaster”. Gypsum occurs in nature as flattened and often twinned crystals, and transparent, cleavable masses called selenite.
Evidence also points to the existence of a sanctuary, as indicated by the limited remnants of stone vessels. These remnants include a crystal vessel, a grey/leucolite vessel, an incised steatite vessel, and assorted obsidian fragments.
It is worth emphasizing that during the YMI period, approximately around 1600 BC, obsidian was not commonly used as a tool in Crete. Consequently, the abundance of obsidian discovered in this location is suggestive of a ritualistic use.
A fragment of a bronze buckle and the foot of a Mycenaean goblet were also found in the upper layers, along with a Doge of Venice coin, as well as a 1963 US coin. Finally, other fragments of conical cups, along with earlier “egg cups” (small vessels) show the disturbance of the layers as evidence of illegal “excavation” in the palace area by the owners of the house that was above it.
Header Image Credit : Ministry of Education