A documentary film crew have discovered a large fragment from the Challenger space shuttle, while searching for the wreck of a WW2 aircraft off the Florida coast, United States.
Space Shuttle Challenger (OV-099) was a Space Shuttle orbiter, manufactured by Rockwell International and operated by NASA. Challenger first launched in April 1983 and was the 2nd space shuttler obiter to fly into space after Space Shuttle Columbia (OV-102).
In January 1986, Challenger broke apart soon after launch, killing all seven crewmembers aboard. The disaster was the result of two redundant O-ring seals breaching shortly after lift-off, releasing hot pressurised gas from the right solid rocket booster (SRB) that burned through the aft attachment strut connecting it to the external propellant tank (ET). This, combined with a combination of factors, led to the aerodynamic forces of tearing the shuttle apart.
The loss of Challenger, and later Columbia with its seven astronauts – which broke up on re-entry in February 2003 over the western United States – greatly influenced NASA’s culture regarding safety going forwards.
A fragment of the Challenger was discovered off Florida’s Space Coast during filming for a new series on the History Channel. Upon reviewing underwater footage, experts from NASA confirmed the identification based on the presence of 8-inch (20 centimetres) square thermal protection (heat shield) tiles.
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said: “This discovery gives us an opportunity to pause once again, to uplift the legacies of the seven pioneers we lost, and to reflect on how this tragedy changed us. At NASA, the core value of safety is – and must forever remain – our top priority, especially as our missions explore more of the cosmos than ever before.”
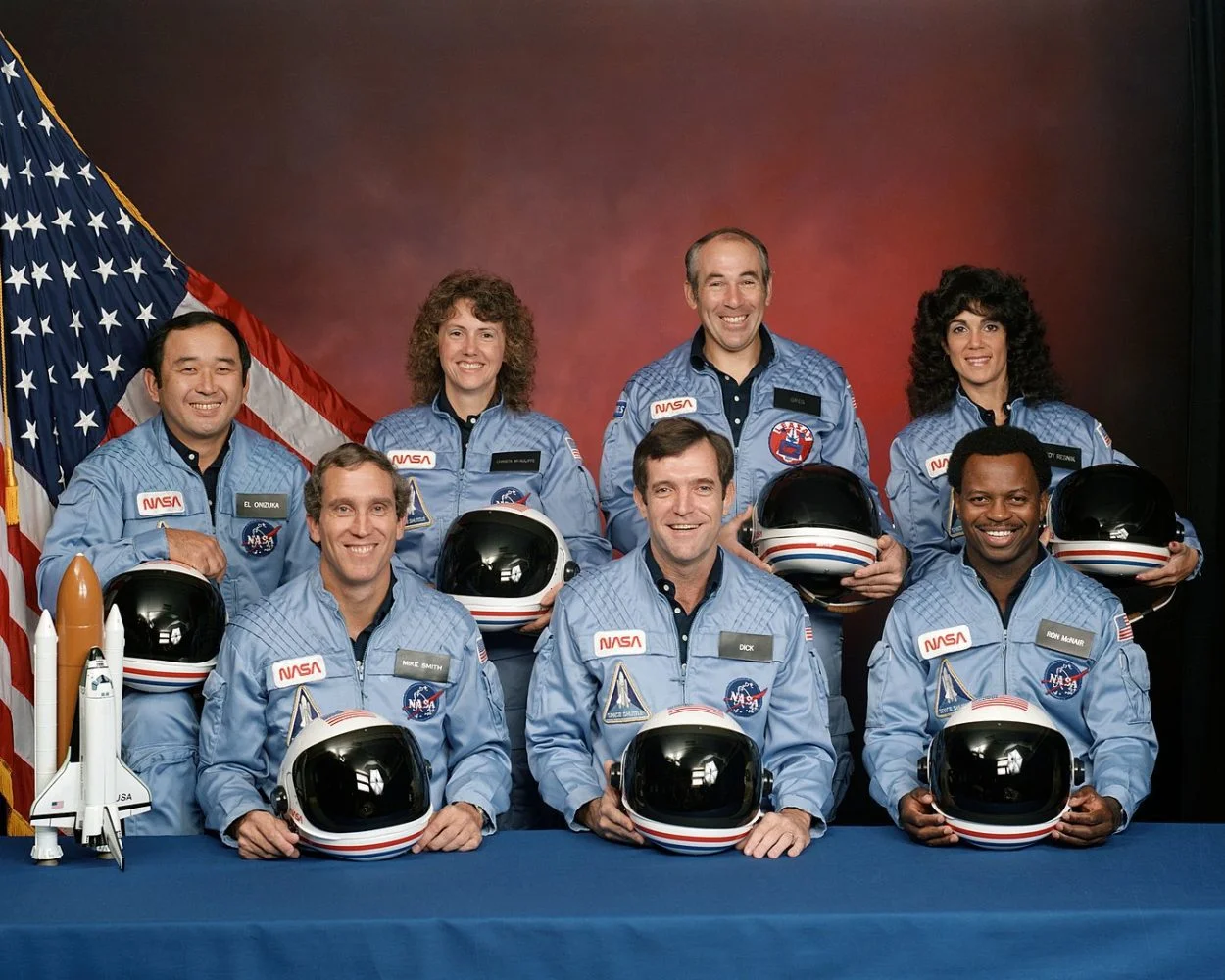

“Challenger and her crew live on in the hearts and memories of both NASA and the nation,” said Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro. “Today, as we turn our sights again toward the Moon and Mars, we see that the same love of exploration that drove the Challenger crew is still inspiring the astronauts of today’s Artemis Generation, calling them to build on the legacy of knowledge and discovery for the benefit of all humanity.”
Header Image – Space Shuttle Challenger – Public Domain