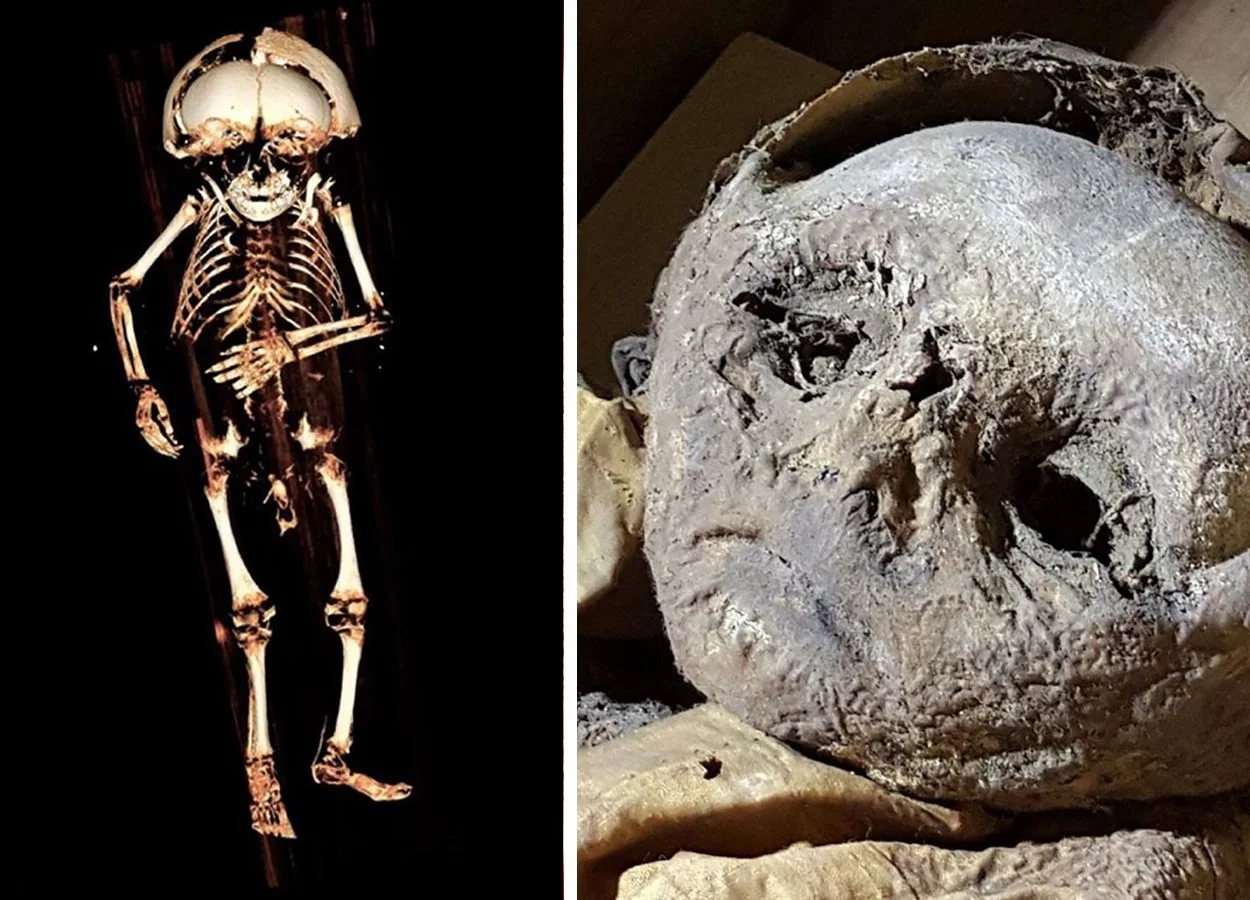
Researchers led by Dr Andreas Nerlich of the Academic Clinic Munich-Bogenhausen, have conducted a ‘virtual autopsy’ of a mummified 17th century child, using cutting-edge science alongside historical records to shed new light on Renaissance childhood.
The child was found in an aristocratic Austrian family crypt, where the conditions allowed for natural mummification, preserving soft tissue that contained critical information about his life and death.
The body was buried in an unmarked wooden coffin instead of the elaborate metal coffins reserved for the other members of the family buried there.
The team carried out a virtual autopsy and radiocarbon testing, and examined family records and key material clues from the burial to try to understand who the child was and what his short life looked like.
“This is only one case,” said Nerlich, lead author of the paper published today in Frontiers in Medicine, “but as we know that the early infant death rates generally were very high at that time, our observations may have considerable impact in the over-all life reconstruction of infants even in higher social classes.”
The virtual autopsy was carried out through CT scanning. Nerlich and his team measured bone lengths and looked at tooth eruption and the formation of long bones to determine that the child was approximately a year old when he died. The soft tissue showed that the child was a boy and overweight for his age, so his parents were able to feed him well – but the bones told a different story.
The child’s ribs had become malformed in the pattern called a rachitic rosary, which is usually seen in severe rickets or scurvy. Although he received enough food to put on weight, he was still malnourished. While the typical bowing of the bones seen in rickets was absent, this may have been because he did not walk or crawl.
Since the virtual autopsy revealed that he had inflammation of the lungs characteristic of pneumonia, and children with rickets are more vulnerable to pneumonia, this nutritional deficiency may even have contributed to his early death.
“The combination of obesity along with a severe vitamin-deficiency can only be explained by a generally ‘good’ nutritional status along with an almost complete lack of sunlight exposure,” said Nerlich. “We have to reconsider the living conditions of high aristocratic infants of previous populations.”
The son of a powerful count
However, although Nerlich and his team had established a probable cause of death, the question of the child’s identity remained. Deformation of his skull suggested that his simple wooden coffin wasn’t quite large enough for the child. However, specialist examination of his clothing showed that he had been buried in a long, hooded coat made of expensive silk.
He was also buried in a crypt exclusively reserved for the powerful Counts of Starhemberg, who buried their title-holders — mostly first-born sons — and their wives there. This meant that the child was most likely a first-born son of a Count of Starhemberg.
Radiocarbon dating of a skin sample suggested he was buried between AD 1550-1635, while historical records of the crypt’s management indicated that his burial probably took place after the crypt’s renovation around AD 1600. He was the only infant buried in the crypt.
“We have no data on the fate of other infants of the family,” Nerlich said, regarding the unique burial. “According to our data, the infant was most probably [the count’s] first-born son after erection of the family crypt, so special care may have been applied.”
This meant that there was only one likely candidate for the little boy in the silk coat: Reichard Wilhelm, whose grieving family buried him alongside his grandfather and namesake Reichard von Starhemberg.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.979670
Header Image Credit: Frontiers