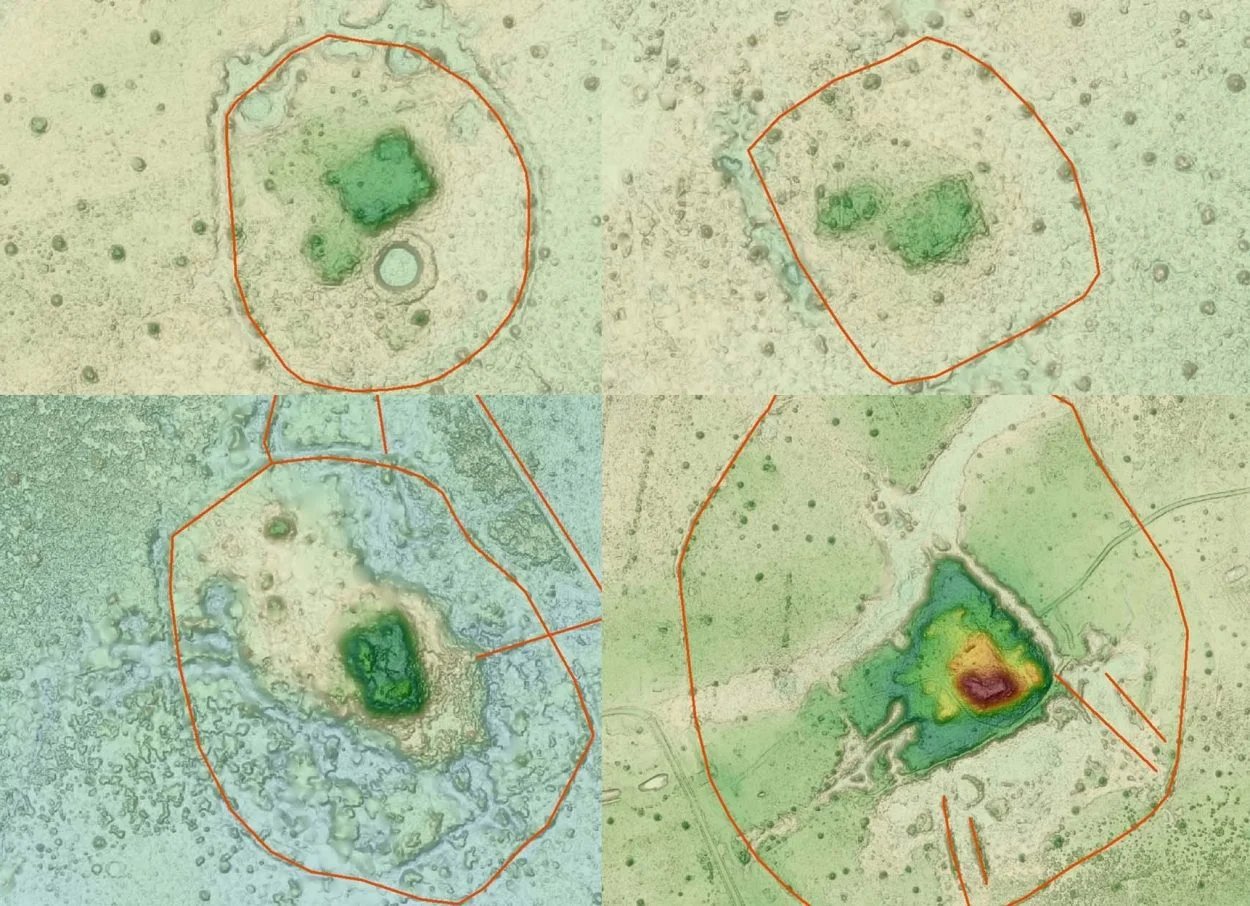
An international team of archaeologists has discovered a network of ancient cities in the Llanos de Mojos savannah-forests of Bolivia using Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging).
The cities were constructed by the indigenous Casarabe culture between AD 500-1400, who built large scale urban centres and a network of reservoirs, causeways and checkpoints comparable only with the Archaic states of the central Andes.
The central spread of the cities covers several hectares, in which the Casarabe built civic-ceremonial U-shaped structures, platform mounds and 21-metre-tall conical pyramids.
Professor Jose Iriarte from the University of Exeter said: “We long suspected that the most complex pre-Columbian societies in the whole basin developed in this part of the Bolivian Amazon, but evidence is concealed under the forest canopy and is hard to visit in person. Our lidar system has revealed built terraces, straight causeways, enclosures with checkpoints and water reservoirs. There are monumental structures just a mile apart, connected by 600 miles of canals, long raised causeways connecting the sites and reservoirs and lakes.”
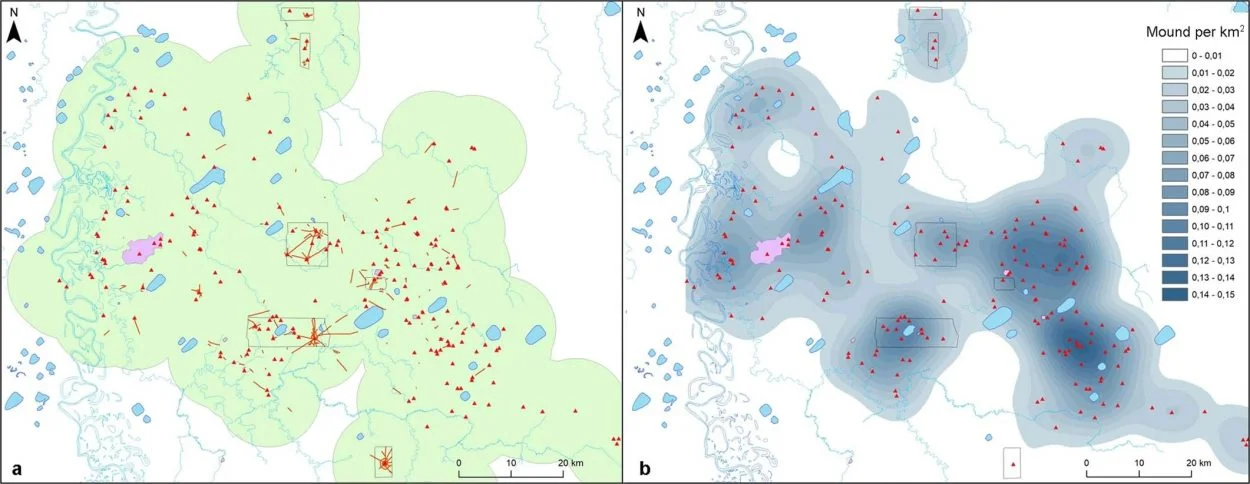
At the time the cities were being built, communities in the Llanos de Mojos transformed seasonally flooded savannas in the Amazon into productive agricultural and aquacultural landscapes. The study shows that the indigenous people not only managed forested landscapes, but also created urban landscapes in tandem – providing evidence of successful, sustainable subsistence strategies, but also a previously undiscovered cultural-ecological heritage.
Dr Mark Robinson of the University of Exeter added: “These ancient cities were primary centres of a regional settlement network connected by still visible, straight causeways that radiate from these sites into the landscape for several kilometres. Our results put to rest arguments that western Amazonia was sparsely populated in pre-Hispanic times. The architectural layout of Casarabe culture large settlement sites indicates that the inhabitants of this region created a new social and public landscape.”
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04780-4
Header Image Credit : Nature