Poverty Point, named after a 19th-century plantation, is an archaeological site and an ancient ceremonial mound and ridge complex, located on the Bayou Macon in present-day Louisiana in the United States.
The site was built over several phases, with the earliest archaeological evidence suggesting that construction began sometime from 1800 BC during the Late Archaic Period, continuing though to 1200 BC.
The builders were an indigenous society of hunter-fisher-gatherers, identified as the Poverty Point Culture who inhabited stretches of the Lower Mississippi Valley and surrounding Gulf Coast.
Over 100 sites have been attributed to the Poverty Point Culture, with anthropologists proposing that they descended from immigrants who came to North America across the Bering Strait land bridge approximately 12,000 to 15,000 years ago.
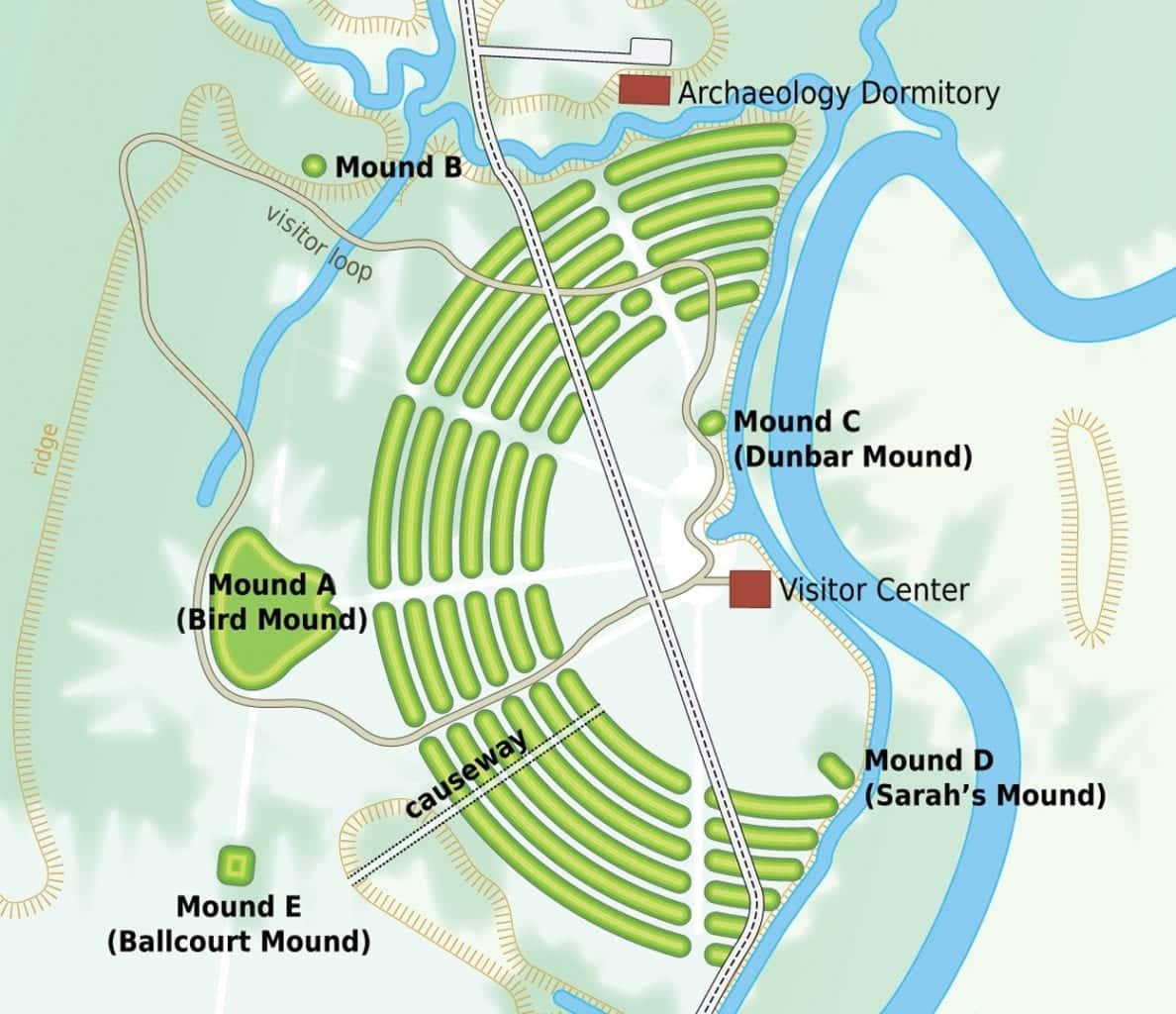
Studies have determined that the builders of Poverty Point levelled the landscape to create a central plaza, surrounded by a series of earthen ridges and mounds that covers an area of around 345 acres (although further investigations have discovered that occupation also extends up to 3 miles along the Bayou Macon).
The earthworks consist of six concentric C-shaped ridges, stretching three-quarters of a mile on the outermost ridge, that today reach varying heights of 0.3 to 6 ft. These encircle the 37.5-acre plaza which contained a series of post circles (as determined by a geophysical study conducted by the University of Louisiana at Monroe and Mississippi State University).
The most distinct features from ground level are the mounds constructed using loess, a type of silt loam soil. The largest of these is Mound A (reaching a height of 72 ft), which is also called the bird mound due to its bird-like shape, as well as being called the “Earth island,” which some scholars have suggested represented the cosmological centre of the site.
The purpose of Poverty Point has been heavily debated, with some theories suggesting that the site was used as a settlement (possibly only for periodic events), or that the complex was essentially a trading hub, or that the site served as a religious centre with an astronomical significance aligned to the solstices.
In 2014, the UNESCO World Heritage Committee inscribed Poverty Point as a World Heritage Site, placing the site’s importance alongside such cultural landmarks as Stonehenge in England, the Pyramid Fields at Giza in Egypt, and the Great Wall of China.
Header Image Credit : Jeffrey M. Frank – Shutterstock





