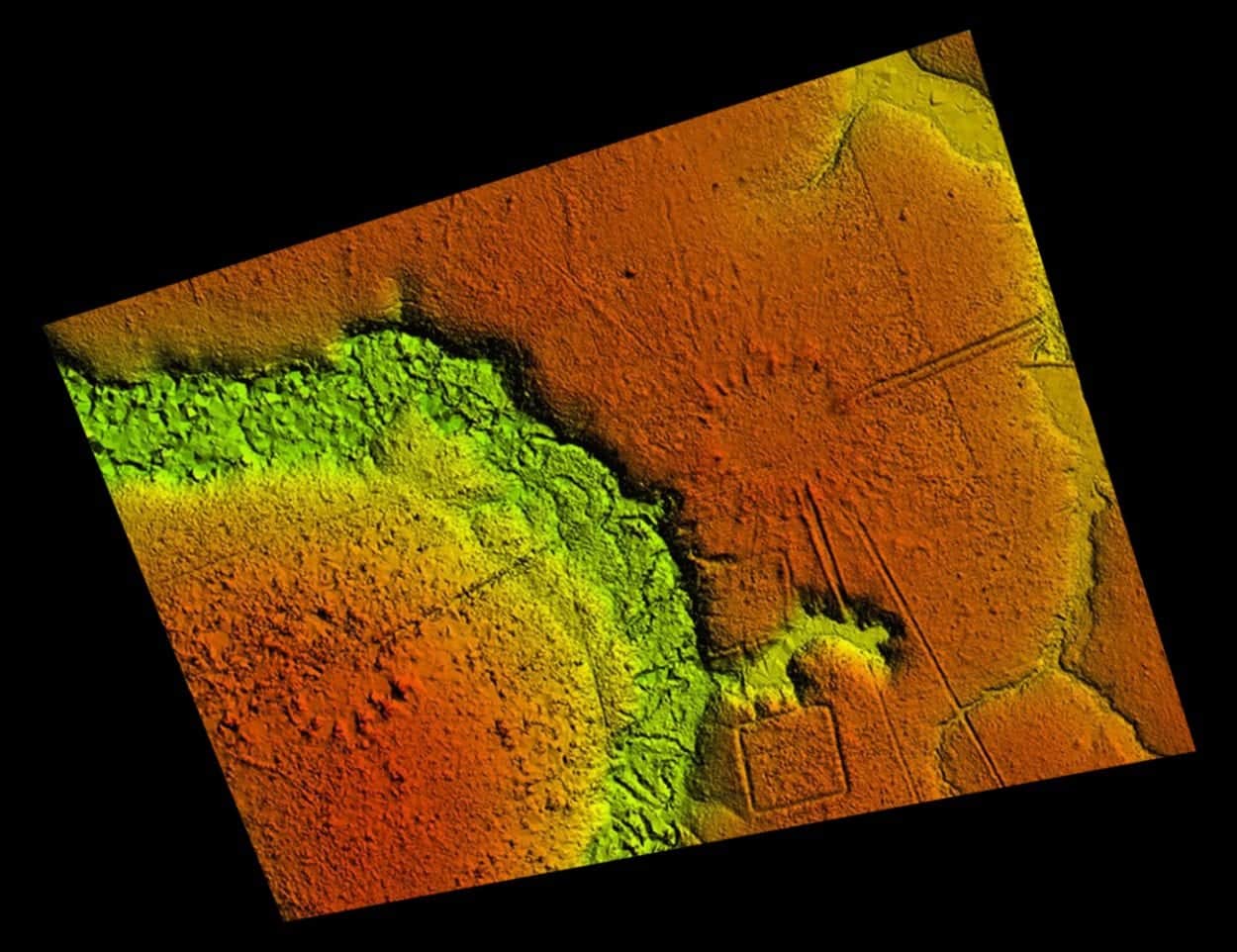
Ancient Amazonian villages built between AD 1300 to 1700 and laid out like a clock to possibly represent the Native American cosmos have been discovered in Brazil’s south Acre State.
The discovery was made by a multi-national team from the University of Exeter, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Instituto do Patrimônio Histórico e Artístico Nacional, Federal University of Pará, Federal University of Acre, and the Brazil National Institute for Space Research, whilst conducting a LiDar scan of the forest canopy.
LiDar (meaning Light Detection and Ranging) is a method of remote sensing using light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth. The differences in the pulsed laser return-times and wavelengths can be used to compile a 3-D digital map of the landscape by removing obscuring features that could hide geological and archaeological features.
The results revealed a distinctive and consistent arrangement of ancient circular villages, connected via a network over many kilometres through paired sunken roads, and high banks that radiate from the village circle like the marks of a clock or the rays of the sun.
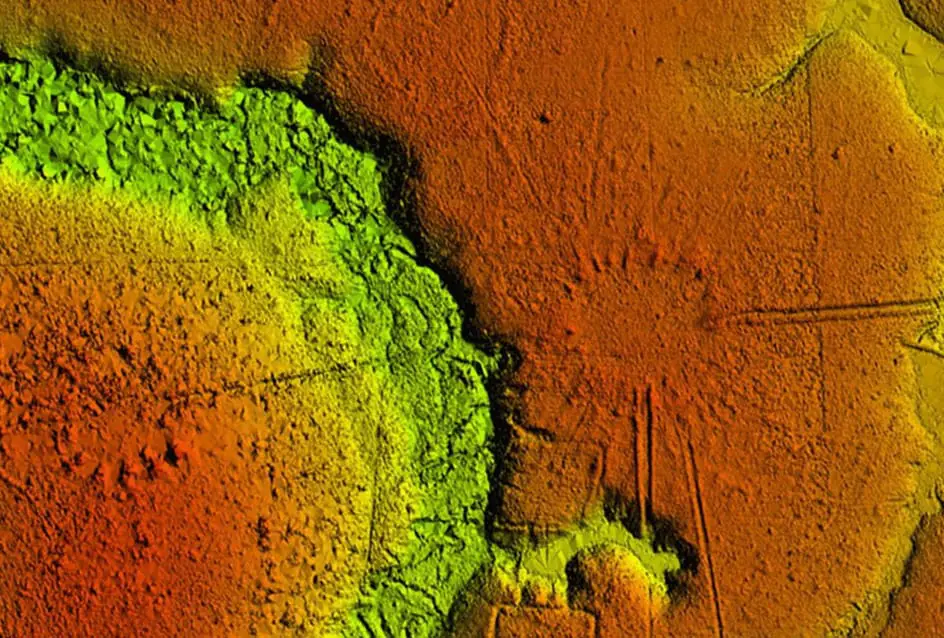

So far, over 35 villages have been documented, mainly consisting of 3 to 32 mounds arranged in a circle, with a diameter from 40 to 153 metres that demonstrates a more complex and spatially organised landscape than previously thought.
Deforestation in the region had previously revealed the presence of large geoglyph earthworks on the landscape with archaeological research also documenting the presence of circular mound villages. However, until now the extent of earthwork constructions, their architectural layouts, and their regional organisation remained hidden beneath the remaining dense tropical forest.
Professor Jose Iriarte from the University of Exeter said: “Lidar has allowed us to detect these villages, and their features such as roads, which wasn’t possible before because most are not visible within the best satellite data available. The technology helps to show diverse and complex construction history of this part of the Amazon. Lidar provides a new opportunity to locate and document earthen sites in forested parts of Amazonia characterised by dense vegetation. It can also document the smallest surficial earthen features in the recently opened pasture areas.”
Header Image Credit : University of Exeter