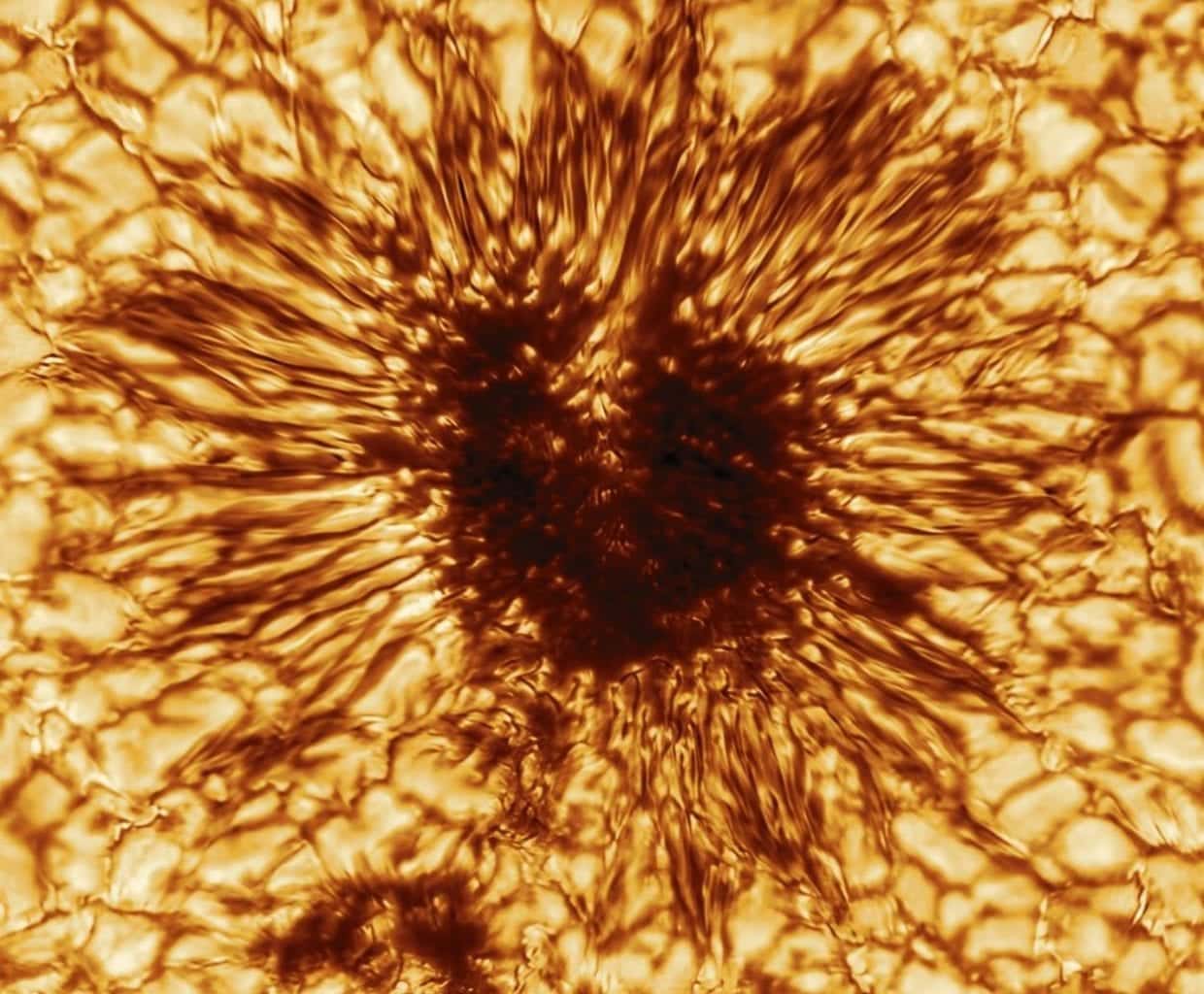
The world’s largest solar observatory, the U.S. National Science Foundation’s Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, just released its first image of a sunspot.
Although the telescope is still in the final phases of completion, the image is an indication of how the telescope’s advanced optics and four-meter primary mirror will give scientists the best view of the Sun from Earth throughout the next solar cycle.
The image, taken January 28, 2020, is not the same naked eye sunspot currently visible on the Sun. This sunspot image accompanies a new paper by Dr. Thomas Rimmele and his team. Rimmele is the associate director at NSF’s National Solar Observatory (NSO), the organization responsible for building and operating the Inouye Solar Telescope. The paper is the first in a series of Inouye-related articles featured in Solar Physics. The paper details the optics, mechanical systems, instruments, operational plans and scientific objectives of the Inouye Solar Telescope.
“The sunspot image achieves a spatial resolution about 2.5 times higher than ever previously achieved, showing magnetic structures as small as 20 kilometers on the surface of the sun,” said Rimmele.
The image reveals striking details of the sunspot’s structure as seen at the Sun’s surface. The streaky appearance of hot and cool gas spidering out from the darker center is the result of sculpting by a convergence of intense magnetic fields and hot gasses boiling up from below.
The concentration of magnetic fields in this dark region suppresses heat within the Sun from reaching the surface. Although the dark area of the sunspot is cooler than the surrounding area of the Sun, it is still extremely hot with a temperature of more than 7,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
This sunspot image, measuring about 10,000 miles across, is just a tiny part of the Sun. However, the sunspot is large enough that Earth could comfortably fit inside.
Sunspots are the most visible representation of solar activity. Scientists know that the more sunspots that are visible on the Sun, the more active the Sun is. The Sun reached solar minimum, the time of fewest sunspots during its 11-year solar cycle, in December 2019. This sunspot was one of the first of the new solar cycle. Solar maximum for the current solar cycle is predicted in mid-2025.
“With this solar cycle just beginning, we also enter the era of the Inouye Solar Telescope,” says Dr. Matt Mountain, president of the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), the organization that manages NSO and the Inouye Solar Telescope. “We can now point the world’s most advanced solar telescope at the Sun to capture and share incredibly detailed images and add to our scientific insights about the Sun’s activity.”
Sunspots, and associated solar flares and coronal mass ejections, cause many space weather events, which frequently impact the Earth, a consequence of living inside the extended atmosphere of a star. These events affect technological life on Earth. The magnetic fields associated with solar storms can impact power grids, communications, GPS navigation, air travel, satellites and humans living in space. The Inouye Solar Telescope is poised to add important capabilities to the complement of tools optimized to study solar activity particularly magnetic fields.
“While the start of telescope operations has been slightly delayed due to the impacts of the COVID-19 global pandemic,” said Dr. David Boboltz, NSF Program Director for the Inouye Solar Telescope, “this image represents an early preview of the unprecedented capabilities that the facility will bring to bear on our understanding of the Sun.”
The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope is a facility of the National Science Foundation operated by the National Solar Observatory under a cooperative agreement with the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. The Inouye Solar Telescope is located on land of spiritual and cultural significance to Native Hawaiian people. The use of this important site to further scientific knowledge is done so with appreciation and respect.
Header Image Credit : NSO/AURA/NSF