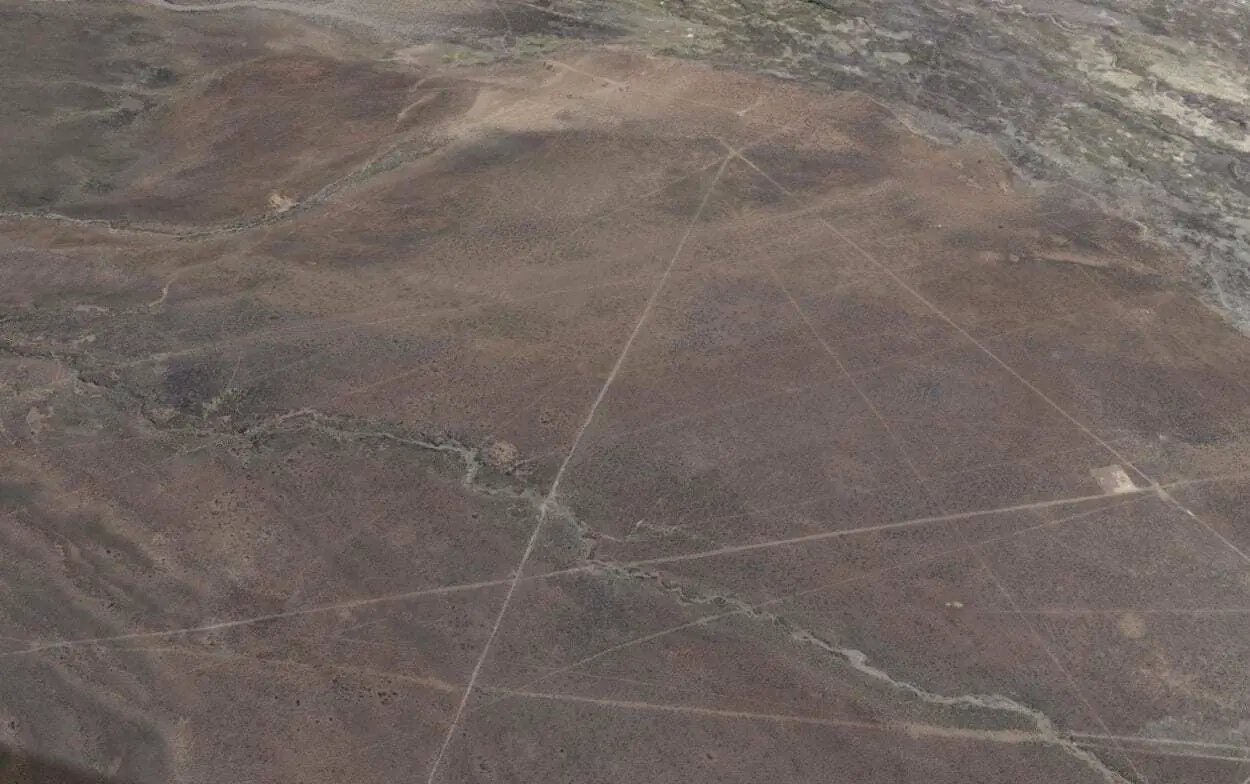
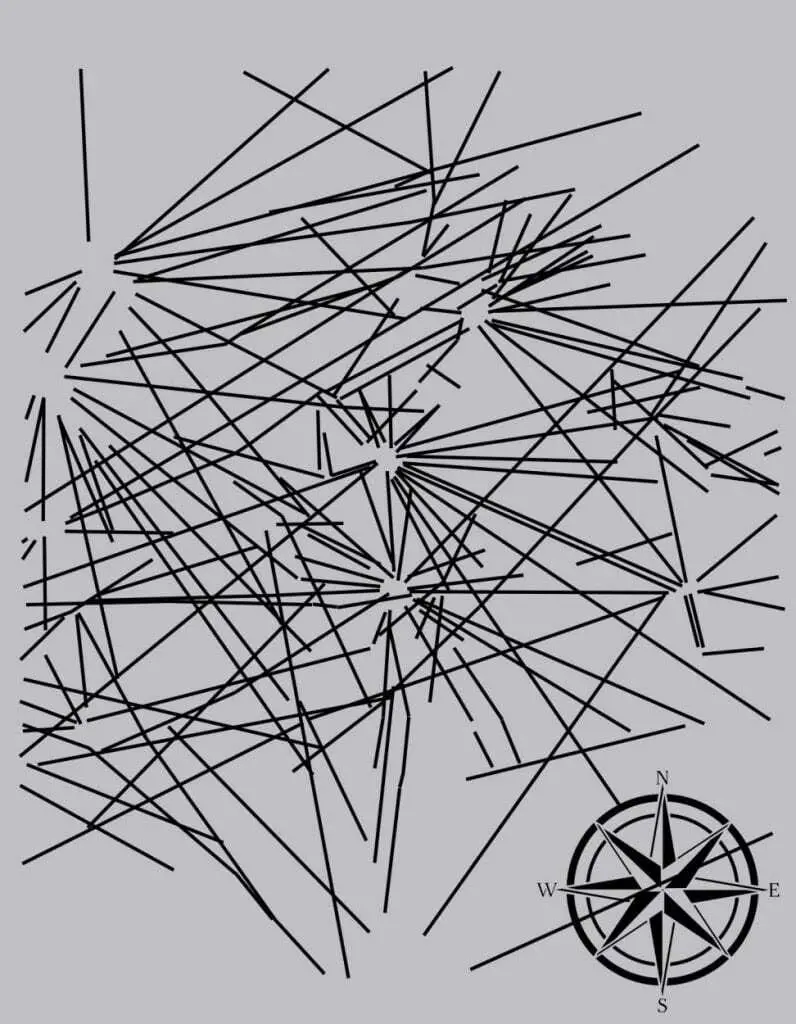
The Sajama Lines is an ancient network of pre-Hispanic linear paths, located in the altiplano, or highlands of western Bolivia near the Nevado Sajama volcano.
The web of lines covers an area of 22,525 square kilometres (almost fifteen times larger than the Nazca lines situated over a thousand kilometres away), and ran a combined length of 16,000 km.
Very little is known about who constructed the lines, with some sources suggesting that they may date from as early as 1000 BC, being constructed over many generations spanning hundreds of years.
The lines were created by scraping aside the dark material of oxidised rock and soil on the altiplano surface to reveal the lighter subsurface layers. Lines vary in length, with some reaching as far as 20 kilometres, passing relatively straight through rugged topography and natural obstacles.
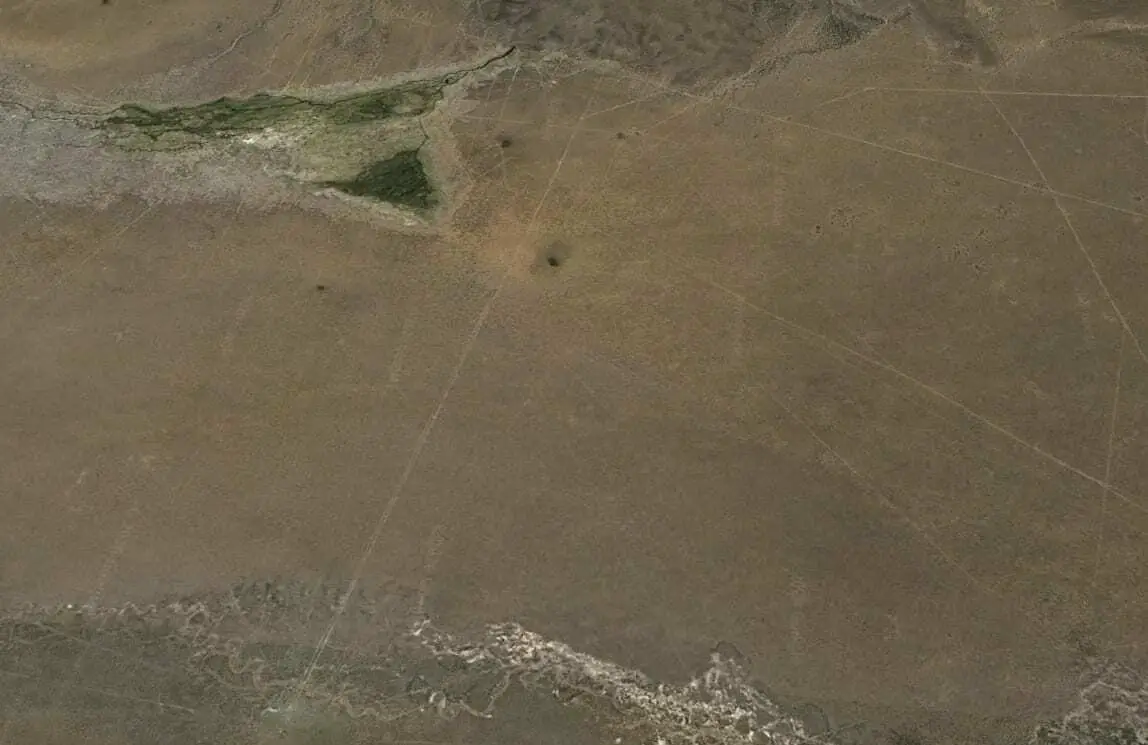

It is theorised that the lines were used by indigenous people to navigate routes on pilgrimages to sacred sites, and to connect them with the villages dotted within the landscape.
Interspersed among the lines, and at points where lines intersect are also the remains of wak’as (shrines), and chullpas (burial towers), with the lines being used into the early colonial period to connect Catholic churches, hilltop shrines, and chapels by the Aymara people, an indigenous nation in the Andes and Altiplano regions (although ethnographic research by Adam Birge suggests that the lines are still in use today).
The presence of prehistoric artifacts and ceramics along the routes of the lines may suggest either the reuse of precolonial places, or the use of pre-colonial artifacts in the creation of sacred places by the Aymara.
The earliest account of the Sajama Lines in western culture was by the Swiss-born, Argentine professor, writer, and self-proclaimed “adventurer” Aimé Felix Tschiffely in 1932.
The lines were eventually brought to the attention of scholars, when anthropologist Alfred Metraux published his research on the ethnographic fieldwork about the Aymara and Chipaya people of the Carangas region.
Header Image Credit : Google Earth





