Aquincum is an archaeological site and Roman city, located in modern-day Budapest in Hungary.
The site was originally occupied by the Eravisci, an Iron Age tribe who settled in the traditional region of Transdanubia around the third or fourth century BC and named their settlement “Ak-Ink” meaning “Abundant Water” because of the nearby thermal springs.
The Eravasci were annexed around 12 BC during the Roman conquest of the Pannonians, Dalmatians and other Illyrian tribes and the Romans founded the province of Pannonia. In 103 AD, Emperor Trajan divided Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior with Aquincum serving as the provincial capital.
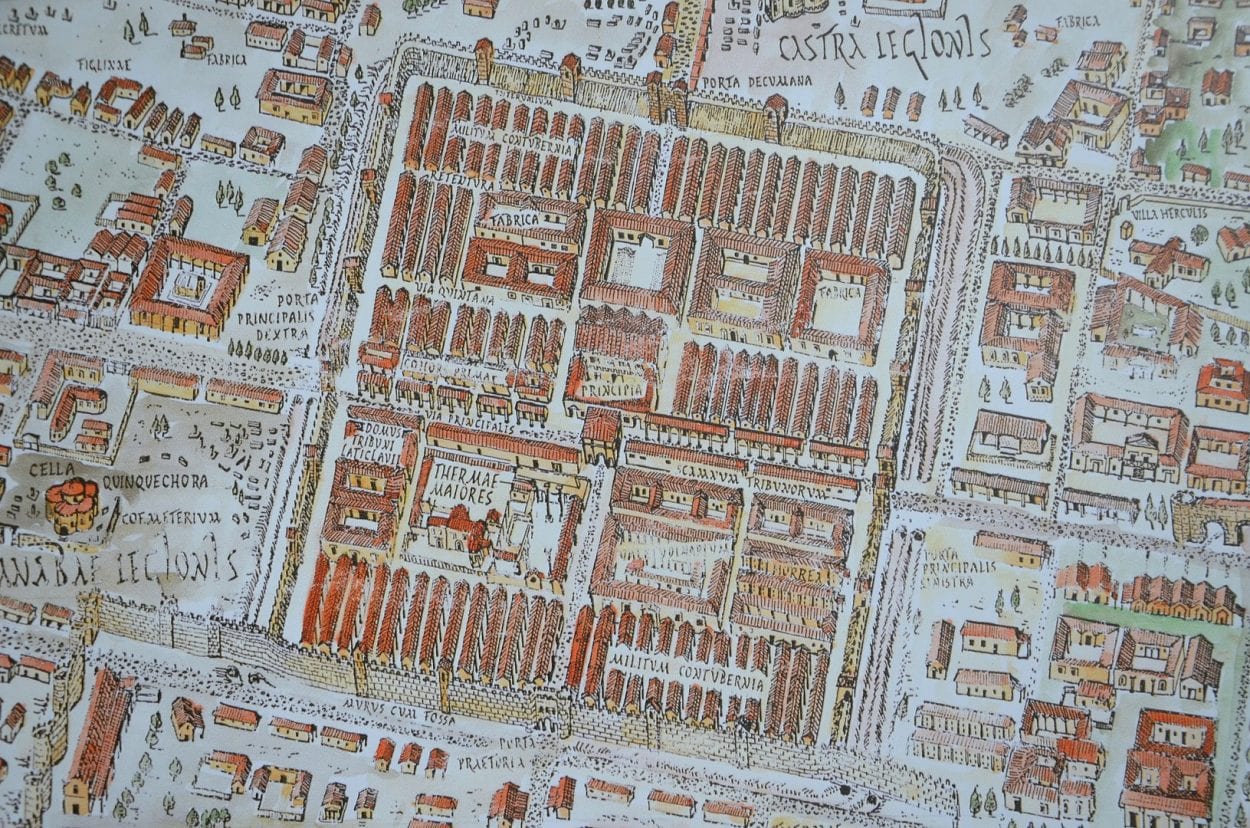
Aquincum was built initially as a frontier settlement and a fortified castrum by Emperor Vespasian on the Roman Limes to support the Germanic border defence. A municipium grew up around the castrum, which was later elevated to the status of a colonia (a term used to denote the highest status of a Roman city) by Emperor by Septimus Severus in AD 194.

At the end of the 2nd century AD, two facing fortresses were built on the left bank of the Danube across from the camp of Legio II adiutrix, Transaquincum and Contra-Aquincum.
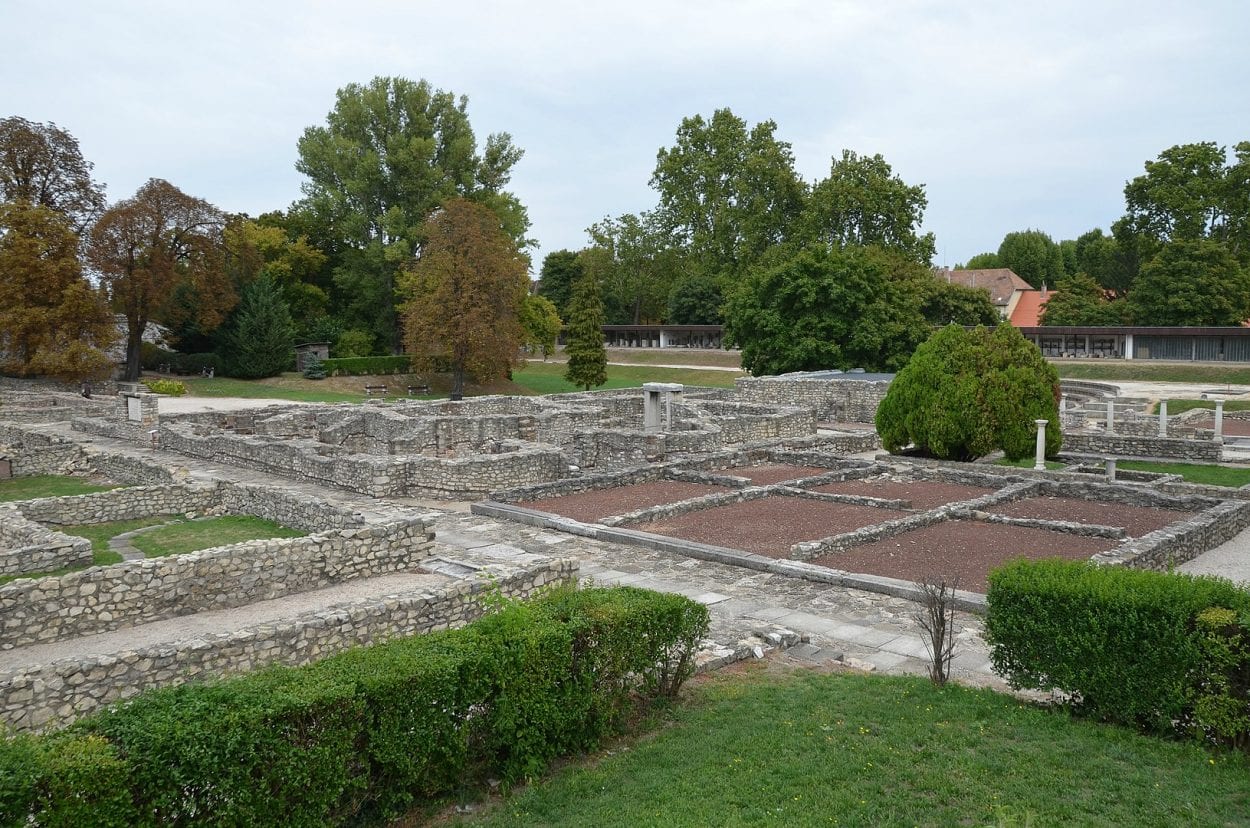
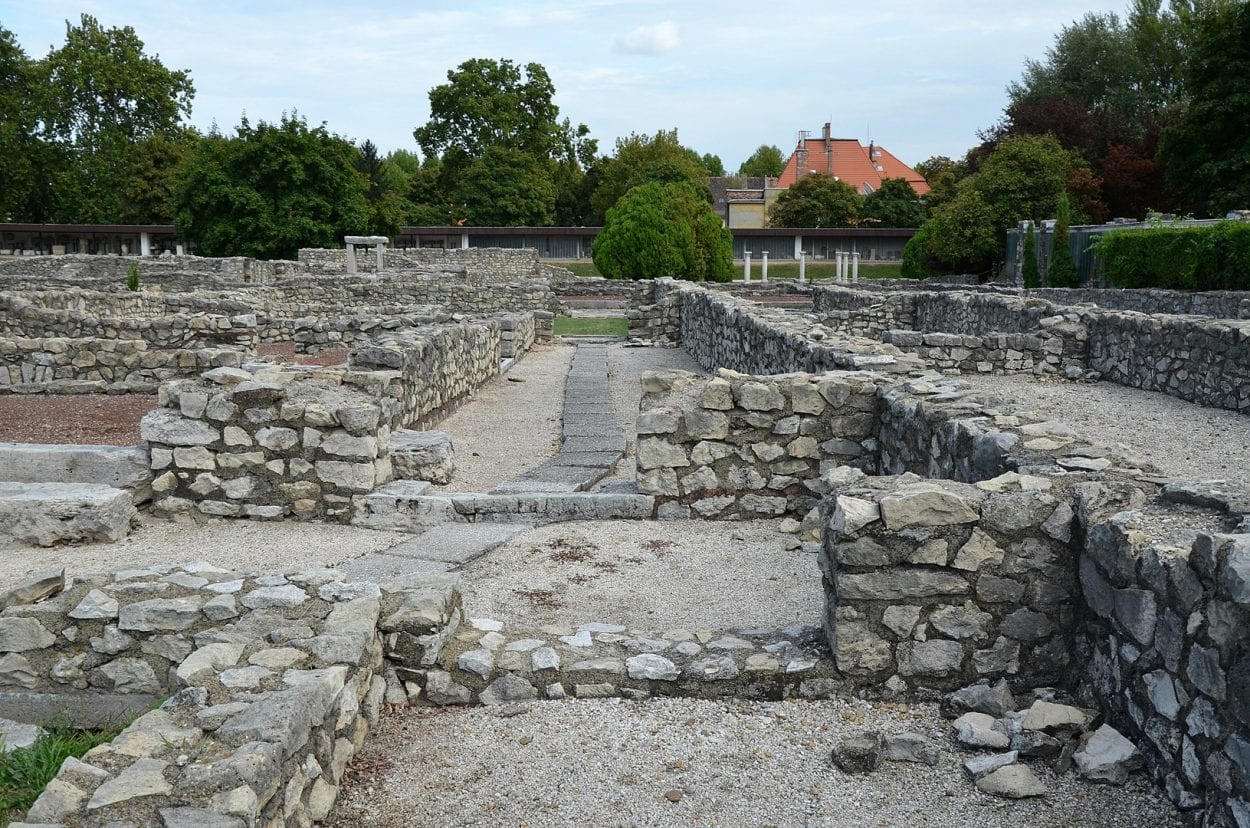
At its peak, the city had at least 30,000 inhabitants covering a large part of the modern-day Óbuda district within Budapest. The city contained several public buildings such as a forum, a basilica, macellum, bathhouses, two Mithraea, a sanctuary of Fortuna and two amphitheatres: the Aquincum Civil Amphitheatre and the Aquincum Military Amphitheatre.
During the middle of the 4th century, Aquincum was under constant Sarmatian attacks from the north and the town began to decline due to a series of contributing factors that effected most Roman population centres in the Western Empire.

The Germanic incursions disrupting the ability to properly maintain an economy and effectively tax its populous, the mismanagement by consecutive Emperors, a reliance on mercenaries without a strong standing army and the loss of territory all contributed to a widespread deterioration of the Western Roman world. The inhabitants gradually left Aquincum, and when the Huns invaded the region around 409 AD they found the city deserted.
Header Image Credit : Carole Raddato – CC BY-SA 2.0