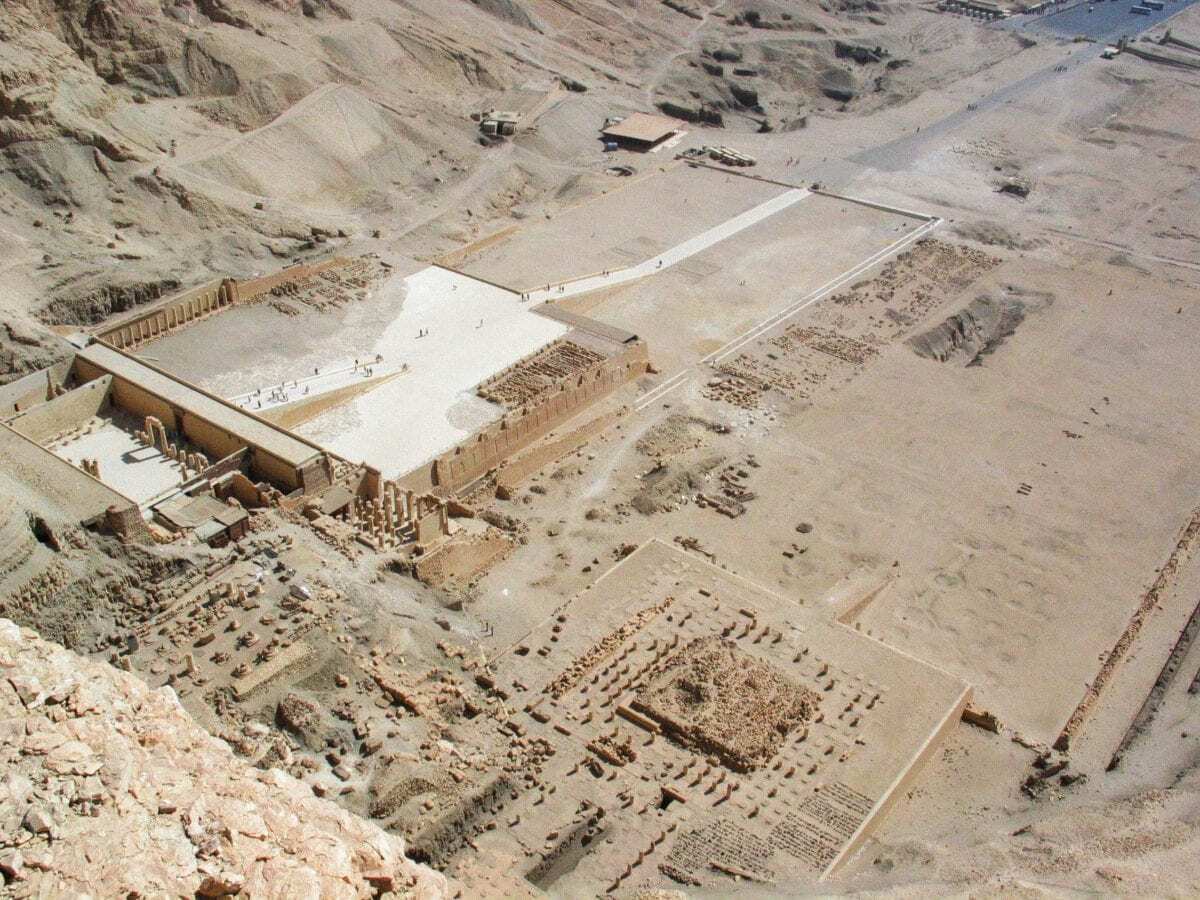
A stone chest excavated by archaeologists near Deir el-Bahari and the temple of Hatshepsut could lead archaeologists from the Institute of Archaeology at the University of Warsaw to a royal tomb.
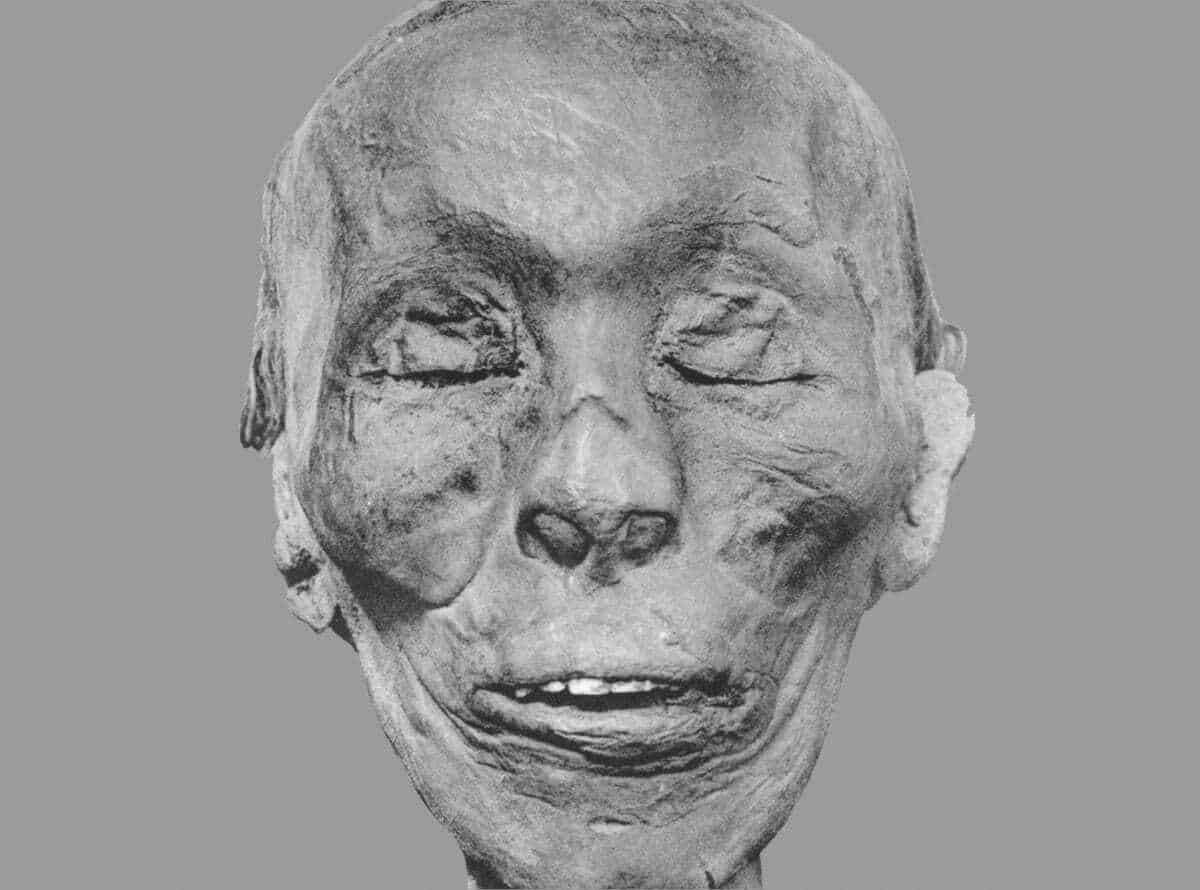
The chest has the name of the Pharaoh Tuthmose II inscribed on the casing. Tuthmose II was the 4th Pharaoh of the 18th dynasty period in Egypt and reigned from 1493 to 1479 BC.
His remains were discovered in 1881 along with many other Pharaohs from the 18th and 21st dynasty that included Ramesses II, also known as Ramesses the Great in Tomb TT320 (DB320), otherwise known as the Royal Cache. Many royals were buried in TT320, as their initial royal tombs were often plundered by grave robbers or in need of restoration.
The chest was discovered near the remains of the temple of Tuthmose III, son of Tuthmose II, and suggests that his original royal tomb before reburial in TT320 may be nearby.

Head of excavations Professor Andrzej Niwiński from the Institute of Archaeology of the University of Warsaw said: “The box itself was about 40 cm long, slightly less in height. It was well camouflaged, it looked like an average stone block. It was only after closer inspection that it turned out to be a box.”
The box, most likely party of a royal deposit, also contained a sacrificial goose and various artefacts wrapped in linen.
Professor Niwiński added: “The royal deposit indicates that a temple was established on behalf of the king, or that a king`s tomb was founded. Since we are in the very centre of the royal cemetery, it is certainly a tomb. Finding this deposit indicates that we are in the process of discovering the tomb.”
Header Image : Thutmose II. Image Credit – G. Elliot Smith