Fossil teeth from Italy, among the oldest human remains on the Italian Peninsula, show that Neanderthal dental features had evolved by around 450,000 years ago, according to a study published by Clément Zanolli of the Université Toulouse III Paul Sabatier in France and colleagues.
These teeth also add to a growing picture of a period of complex human evolution that we are only beginning to understand.
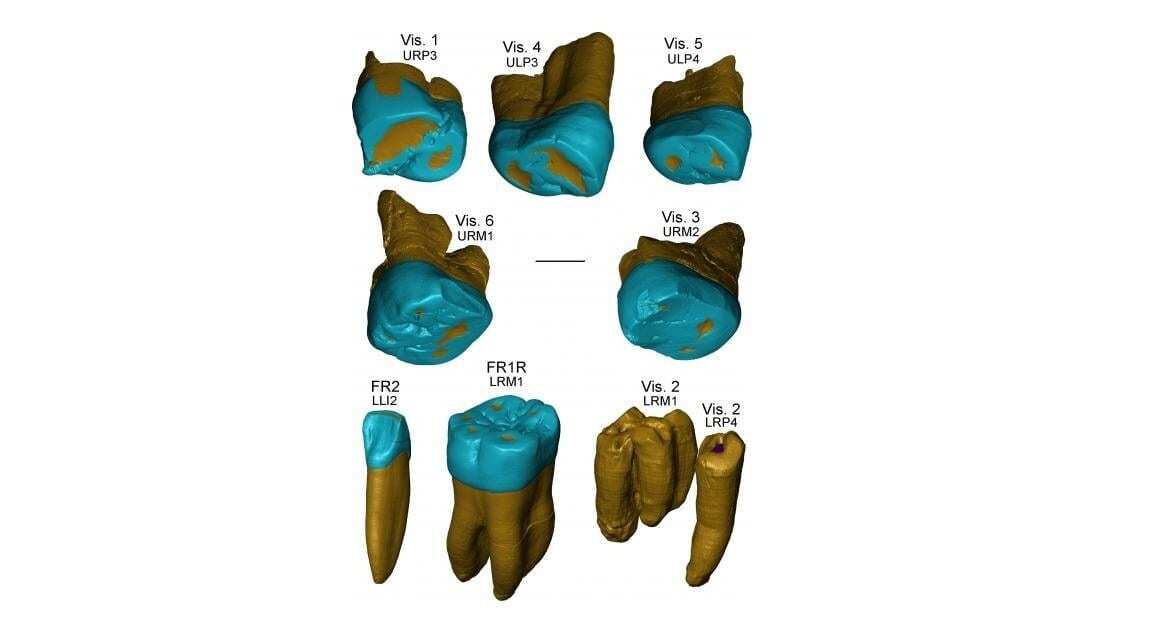
Zanolli and colleagues examined dental remains from the sites of Fontana Fanuccio, located 50km southeast of Rome, and Visogliano, located 18km northwest of Trieste. At around 450,000 years old, these teeth join a very short list of fossil human remains from Middle Pleistocene Europe.
Using micro-CT scanning and detailed morphological analyses, the authors examined the shape and arrangement of tooth tissues and compared them with teeth of other human species. They found that the teeth of both sites share similarities with Neanderthals and are distinct from modern humans.
There has been much debate over the identities and relationships of Middle Pleistocene ancient humans in Eurasia. The discovery of Neanderthal-like teeth so early in the record adds support to the suggestion of an early divergence of the Neanderthal lineage from our own, around the Early-Middle Pleistocene transition.
The teeth are also notably different from other teeth known from this time in Eurasia, suggesting that there may have been multiple human lineages populating the region at this time, adding to a growing list of evidence that the Middle Pleistocene was a time of more complex human evolution than previously recognized.
Zanolli adds: “The remains from Fontana Ranuccio and Visogliano represent among the oldest human fossil remains testifying to a peopling phase of the Italian Peninsula. Our analyses of the tooth internal structural organization reveal a Neanderthal-like signature, also resembling the condition shown by the contemporary assemblage from Atapuerca Sima de los Huesos, indicating that an overall Neanderthal morphological dental template was preconfigured in Western Europe at least 430 to 450 ka ago.”
Header Image – This is a virtual rendering of the Visogliano and Fontana Ranuccio teeth. Credit: Zanolli et al., 2018