Have you ever wondered exactly when a certain group of plants or animals first evolved?
This week a groundbreaking new resource for scientists will go live, and it is designed to help answer just those kinds of questions.
The Fossil Calibration Database, a free, open-access resource that stores carefully vetted fossil data, is the result of years of work from a worldwide team led by Dr. Daniel Ksepka, Curator of Science at the Bruce Museum in Greenwich, and Dr. James Parham, Curator at the John D. Cooper Archaeological and Paleontological Center in Orange County, California, funded through the National Evolutionary Synthesis Center (NESCent).
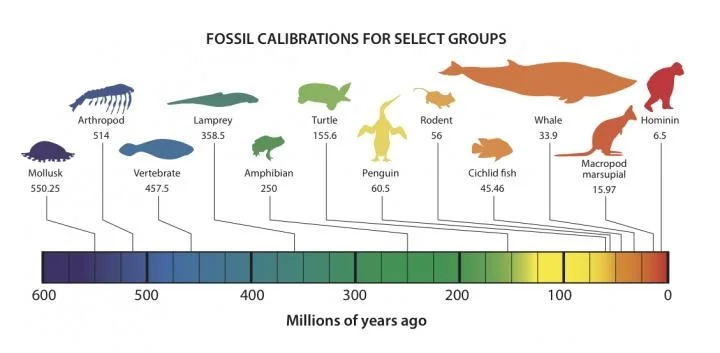
“Fossils provide the critical age data we need to unlock the timing of major evolutionary events,” says Dr. Ksepka. “This new resource will provide the crucial fossil data needed to calibrate ‘molecular clocks’ which can reveal the ages of plant and animal groups that lack good fossil records. When did groups like songbirds, flowering plants, or sea turtles evolve? What natural events were occurring that may have had an impact? Precisely tuning the molecular clock with fossils is the best way we have to tell evolutionary time.”
More than twenty paleontologists, molecular biologists, and computer programmers from five different countries contributed to the design and implementation of this new database. The Fossil Calibrations Database webpage launches on Tuesday February 24th, and a series of five peer-reviewed papers and an editorial on the topic will appear in the scientific journal Palaeontologia Electronica, describing the endeavor. Dr. Ksepka is the author of one of the papers and co-author of the editorial.
“This exciting field of study, known as ‘divergence dating,’ is important for understanding the origin and evolution of biodiversity, but has been hindered by the improper use of data from the fossil record,” says Dr. Parham. “The Fossil Calibration Database addresses this issue by providing molecular biologists with paleontologist-approved data for organisms across the Tree of Life.”
The Tree of Life? “Think of it as a family tree of all species,” explains Dr. Ksepka.




