Coelacanth : Wiki Commons
Coelacanths, an ancient group of fishes once thought to be long extinct, made headlines in 1938 when one of their modern relatives was caught off the coast of South Africa. Now coelacanths are making another splash and University of Alberta researchers are responsible.
Lead U of A researcher Andrew Wendruff identified fossils of a coelacanth that he says are so dramatically different from previous finds, they shatter the theory that coelacanths were evolutionarily stagnant in that their body shape and life-style changed little since the origin of the group.
Wendruff says his one-metre-long, forked tailed coelacanth was an ‘off-shoot’ lineage that lived 240 million years ago. It falls between the earliest coelacanth fossils of 410 million years ago and the latest fossils dated about 75 million years ago, near the end of the age of dinosaurs.
“Our coelacanth had a forked tail, indicating it was a fast-moving, aggressive predator, which is very different from the shape and movement of all other coelacanths in the fossil record,” said Wendruff.
Wendruff’s research co-author, U of A Professor Emeritus Mark Wilson, describes typical coelacanths as having chunky bodies, fins of varying size and broad, flexible tails. “These fish were slow moving and probably lay in wait for their prey,” said Wilson.
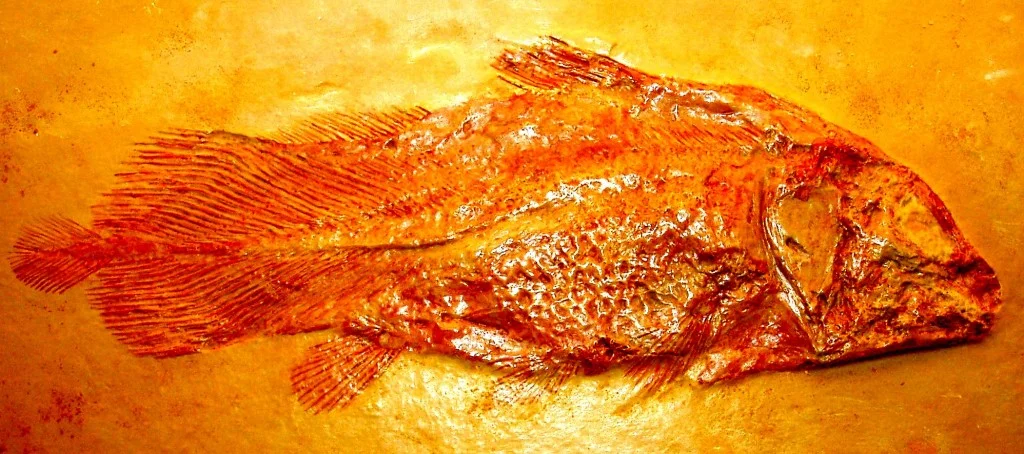
Wendruff’s coelacanth is named Rebellatrix, which means rebel coelacanth. The researchers say Rebellatrix came along after the end-Permian mass extinction 250 million years ago, an event so lethal it wiped out 90 per cent of marine life. Rebellatrix filled a previously unoccupied predator niche, but it didn’t fare well.
“Rebellatrix was likely a spectacular failure in the evolution of cruising predation,” said Wendruff. “Clearly some other fish groups with forked-tails must have outperformed this coelacanth as it does not appear later in the fossil record.”
The fossils of Rebellatrix described by the U of A team were found in the Rocky Mountains near Tumbler Ridge, British Columbia.
The research by Wendruff and Wilson was published May 2, as the cover article in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.




