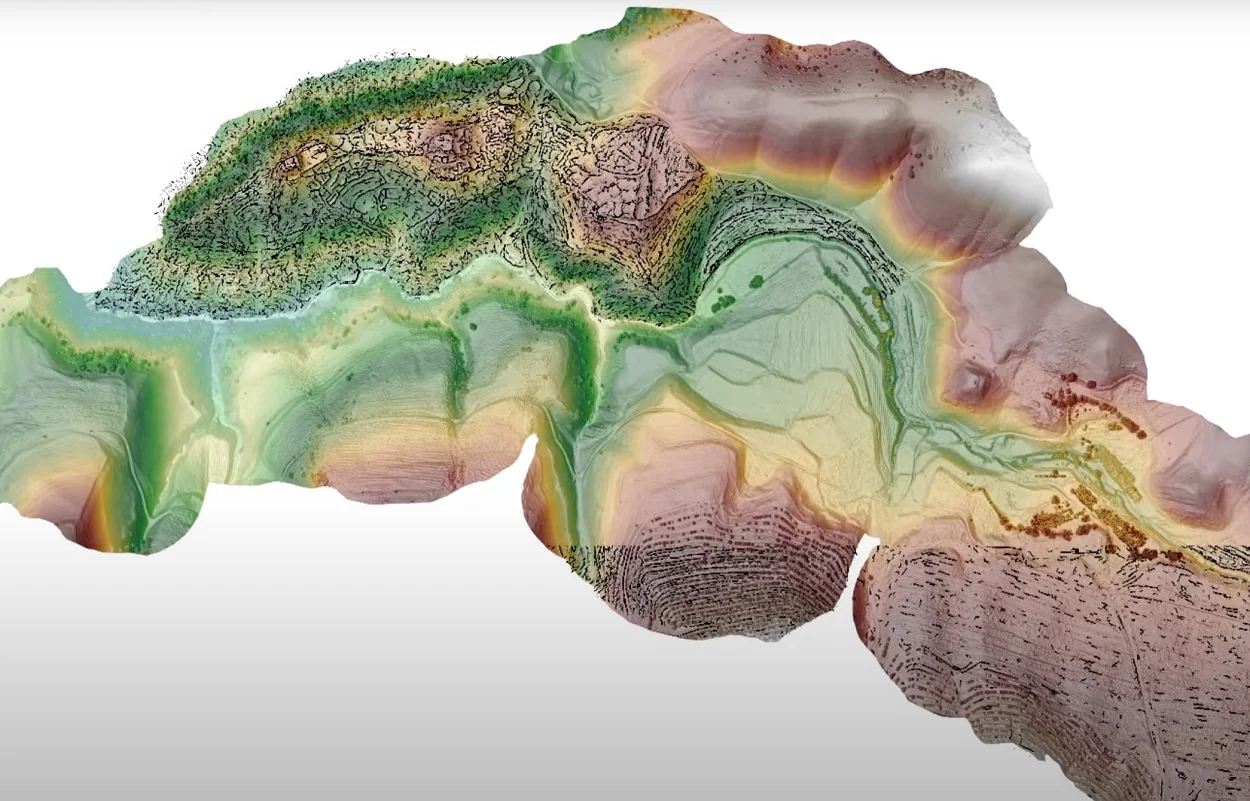
A study published in the journal nature has revealed traces of large-scale urbanisation at two mountaintop cities built over 2,000 metres above sea level in the highlands of southeastern Uzbekistan.
In 2011, Michael D. Frachetti, an Associate Professor of Anthropology at Washington University began a research project at the medieval site of Tashbulak, a city associated with the Qarakhanid Empire. The Qarakhanid Empire was a Karluk Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia from the 9th to the early 13th century AD.
The Qarakhanids founded Tashbulak between the 8th to 11th century AD in a valley in the Mal’guzar highland range, an offshoot of the Pamir Mountains. The city is situated at an elevation of over 2,00 metres above sea level, a height for which only 3% of today’s global population now inhabits.
Following several years of excavations by Frachetti and colleagues, a second city was identified adjacent to Tashbulak which became known as Tugunbulak. Due to the remoteness and poor agricultural conditions, both cities likely survived on trade carried along the medieval Silk Roads from major trading centres in Uzbekistan and China.
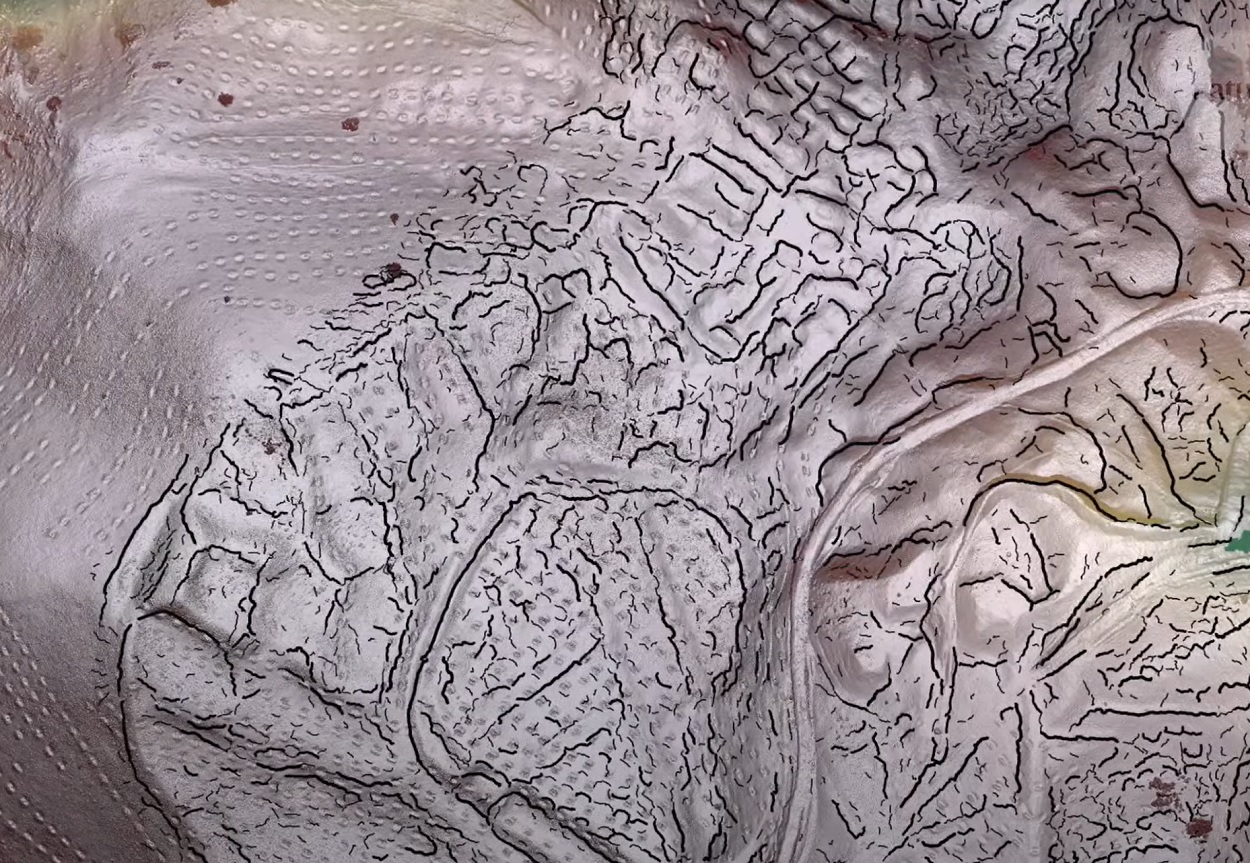
To further understand the extent of both Tashbulak and Tugunbulak, the researchers applied remote-sensing LiDAR to map the archaeological landscape, covering an area of approximately 132 hectares (1.3 square kilometres).
They then used a semi-automated surface-analysis algorithm to identify archaeological features not visible to the naked eye, which revealed a dense urban landscape and hidden traces of linear walls, fortifications, terraces, and numerous structures.
According to the study authors, Tashbulak and Tugunbulak forces us to reconsider notions about the optimal location for establishing a city in so-called ‘peripheral’ areas, which may have played a more important role in medieval trade than previously thought.
“Until now, the highland territories of the medieval Silk Road were seen as barriers to East–West connectivity, or simply as peripheral domains of a ‘nomadic’ world, a traverse between lowland oases and urban hubs of trade and connectivity,” said the study authors.
Header Image Credit : nature
Sources : Nature | https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-03464-5