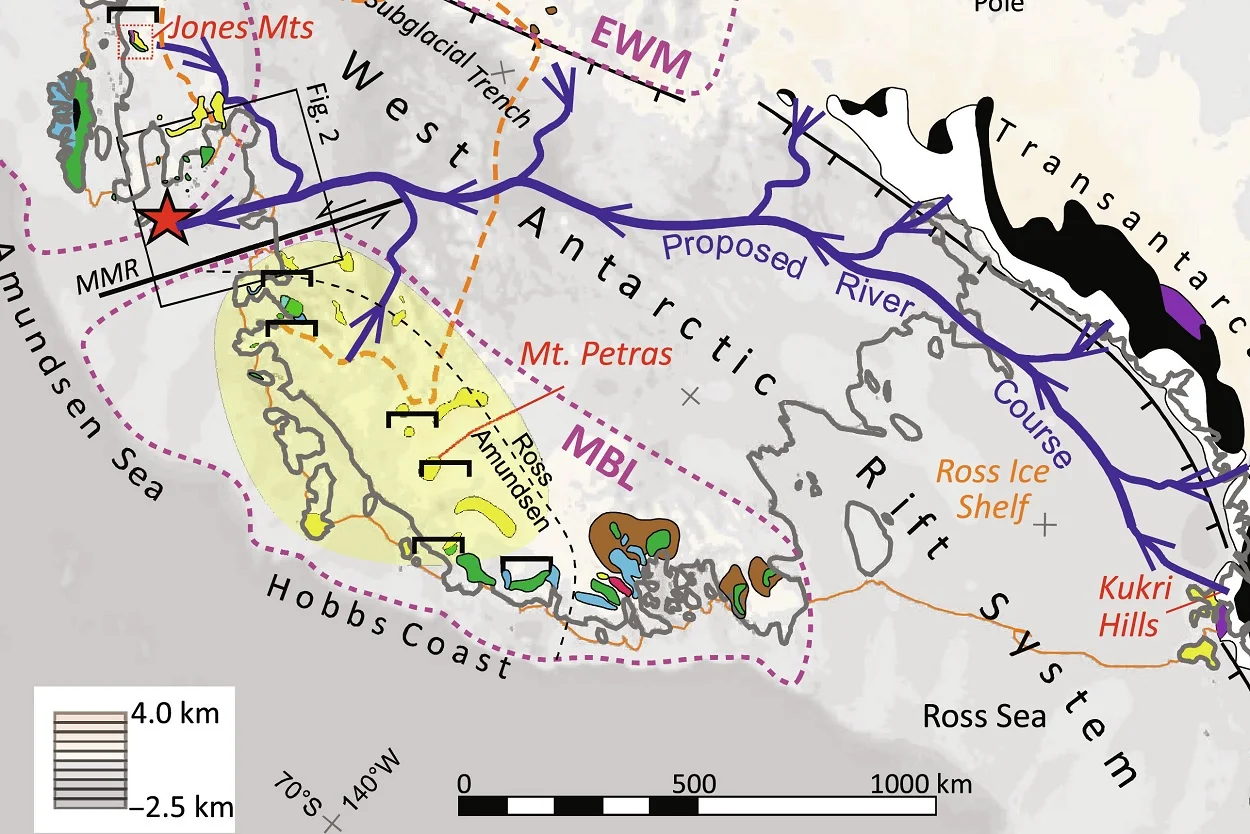
A large-scale transcontinental river system from the Eocene era, dating back 44 to 34 million years ago, has been discovered beneath the Antarctic ice.
The results of a study, published in the journal Science Advances, documents a geochronological and sedimentological analysis of drill cores taken from the Amundsen Sea shelf in Western Antarctica.
The analysis revealed sediments with layers from two distinct periods. The earliest period dates from the mid-Cretaceous period around 85 million years ago, and contains traces of fossils, spores, and pollen from a temperate rainforest.
Scientists already knew that Antarctica has an unglaciated past, first indicated by the ill-fated Terra Nova expedition of 1910–1913. The expedition discovered fossils from the Glossopteris tree, a genus of extinct seed ferns that perished during the end-Permian (Changhsingian) mass extinction.
The upper sediment contains mostly sand from the mid-to-late Eocene, which upon closer inspection resembled a stratified pattern from a river delta system.
Biogeochemical data for the loading of terrestrial organic matter further supports this interpretation, indicated by the comparable values to similar environments that suggest a paleoenvironmental setting receiving a substantial contribution of riverine transported organic and siliciclastic material.
Based on recovered sediments, the researchers suggest that the material was deposited into a coastal-estuarine swamp environment by a >1500-km-long transcontinental river system, draining from the rising Transantarctic Mountains into the Amundsen Sea.
According to the study authors: “An Eocene river delta in today’s Amundsen Sea Embayment is also implied by seismic reflection data from the shelf between MeBo70 drill sites PS104_20-2 and PS104_21-3. These show reflectors in the late Eocene seismic unit ASS-2 that are characteristic of fluvial plains and delta systems.”
Header Image Credit : Science Advances
Sources : A large-scale transcontinental river system crossed West Antarctica during the Eocene. Sci. Adv.10, eadn6056 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adn6056