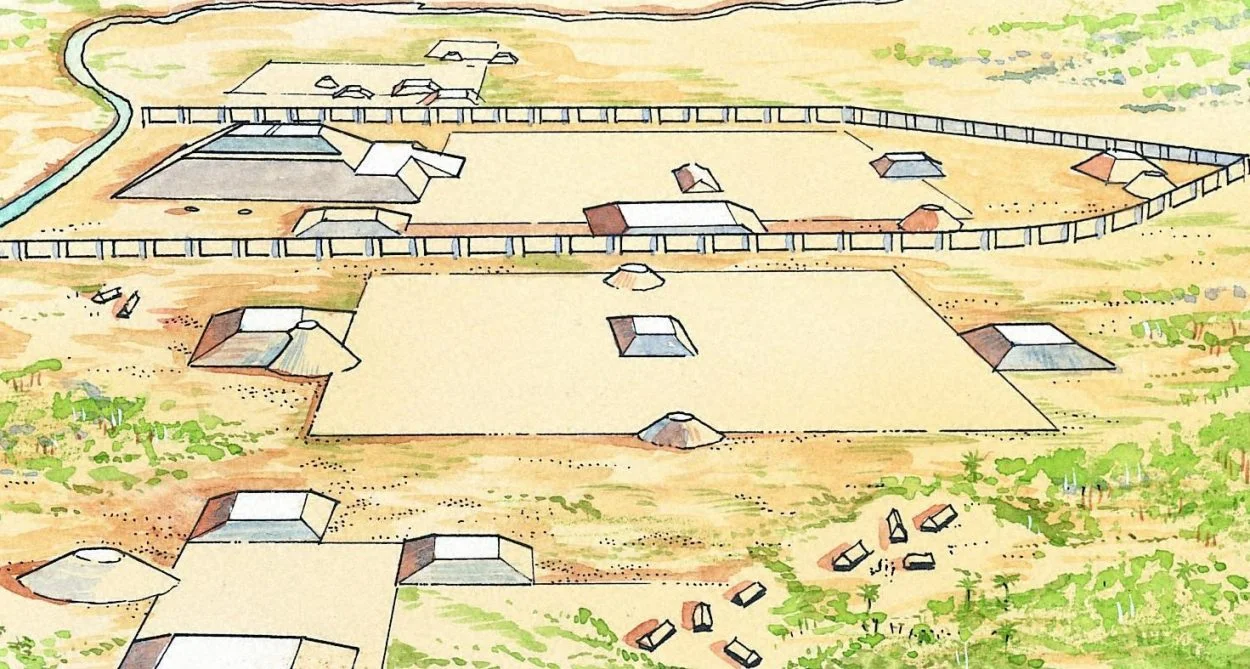
Cahokia was the largest urban settlement of the Mississippian culture, a mound-building pre-Columbian civilisation that emerged in the Midwestern, Eastern, and South-eastern United States.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the city was founded around AD 1050 along the banks of the Mississippi River, located near present-day St. Louis, Missouri.
The city covered an area between six to nine square miles (notably larger than many contemporary European cities such as London) and was home to up to 20,000 inhabitants at its peak.
Following the tradition of the Mississippian culture, the people of Cahokia constructed large earthen mounds – ranging from raised platforms, conical, and ridge-top designs – involving the movement of 55 million cubic feet of earth over a period that lasted several decades.
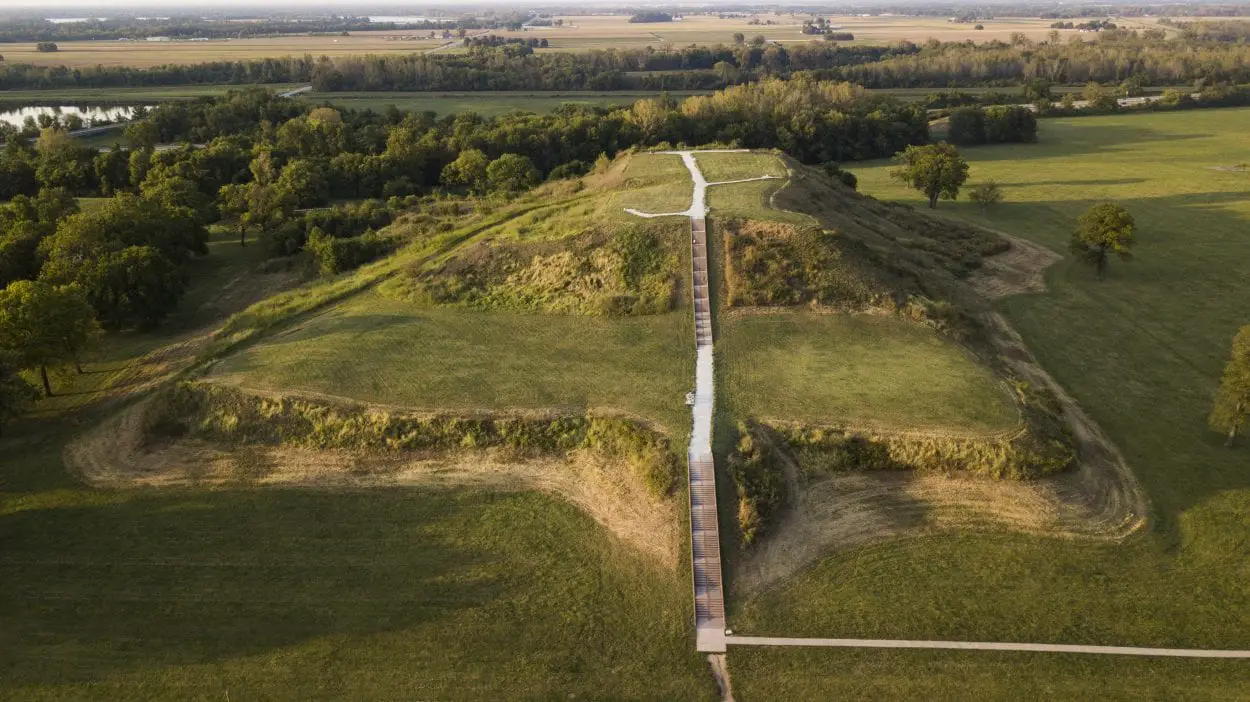
The largest mound is known as “Monks Mound,” named after a group of Trappist monks, which rises to a height of 290 metres and was once the tallest building construction in North America.

Archaeologists and students from Saint Louis University (SLU) have recently conducted a series of excavations on the western periphery of the Cahokia Mounds.
The team unearthed 900-year-old ceramics, microdrills, structures, and wall trenches dating from around AD 1100 to 1200, during the Sterling Phase of the Mississippian Period. According to the archaeologists, the finds offer new insights into a crucial period in the chiefdom’s development, coinciding with Cahokia’s rapid population growth.
The excavations follow an aerial survey by SLU and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency using Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) to conduct Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) to determine whether further mounds or archaeological features lie within the acres of thick forests and swampy land near the site’s main complex.
Header Image Credit : Alamy
Sources : KSDK