Archaeologists have discovered a 7000-year-old Neolithic mega-site near the village of Jarkovac in Serbia.
The discovery was made by a team from the Cluster of Excellence ROOTS, an initiative launched by several research institutions from across academia.
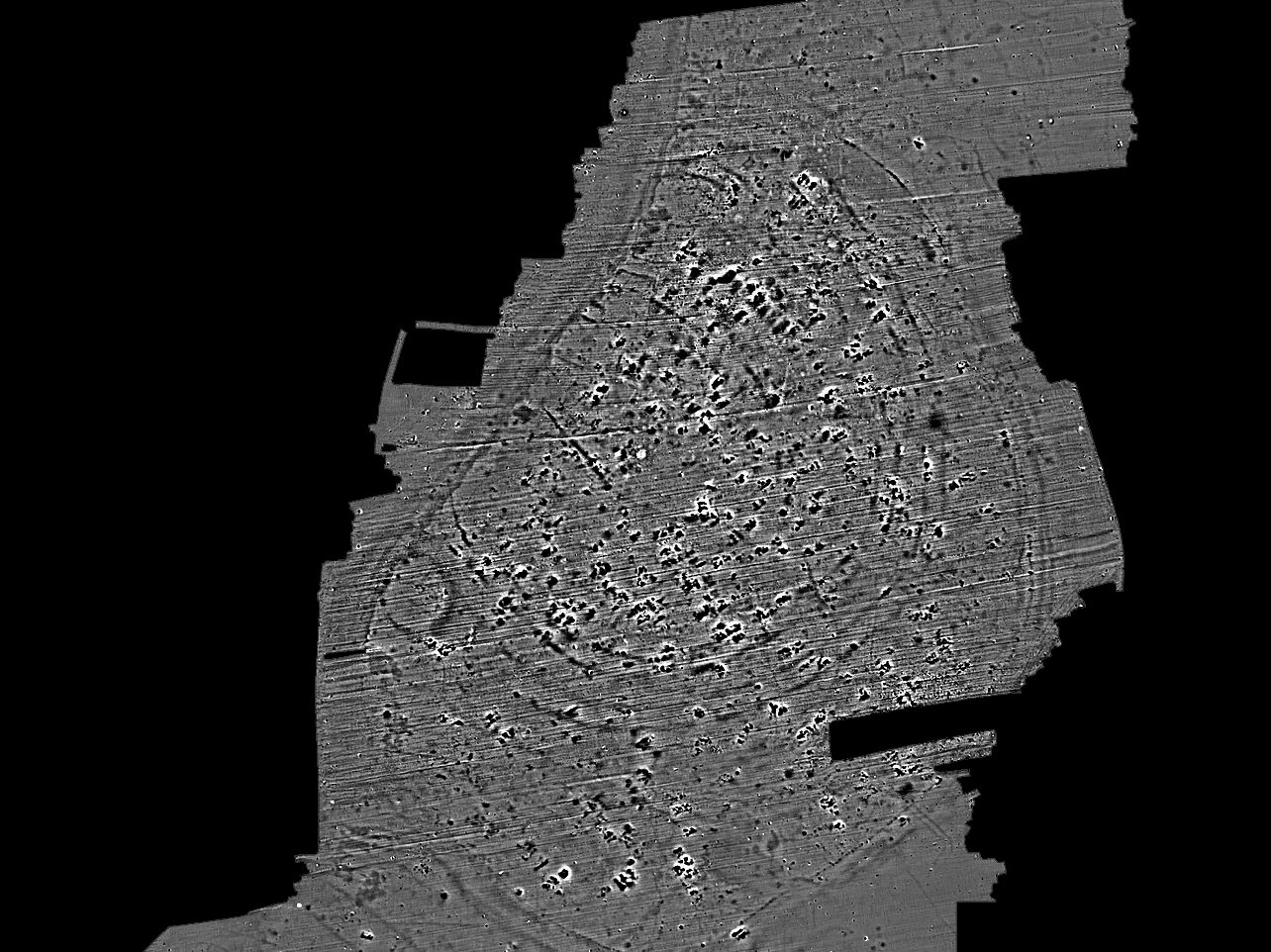
In a press statement announced by the Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel (CAU), a geophysical study has led to the discovery of a 13-hectare settlement with defensive ditches near the Tamiš River in Serbia’s Vojvodina province.
Based on the objects found in situ, the settlement is associated with the Vinča culture (also known as Turdaș culture), a Neolithic people that lived in Southeast Europe between 5400 to 4500 BC.
Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo (a large tell settlement in Belgrade), the culture is most known for constructing mega-site settlements, many of which were considerably larger than most other contemporary culture settlements in Europe.
ROOTS doctoral student and co-team leader Fynn Wilkes, said: “A settlement of this size is spectacular. The geophysical data also gives us a clear idea of the structure of the site 7000 years ago.”
Black angular anomalies apparent in the geophysics indicate a large number of burnt houses, suggesting that the settlement may have been abandoned or destroyed during conflict.
Archaeological evidence from other Vinča sites have led archaeologists to speculate that intergroup competition, conflict, and likely violence might have been a characteristic of the region during the Neolithic period.
Also uncovered are material traces of the Banat culture (5400-4400 BC), a regional people that emerged in the Banat area of the Pannonian Basin. “This is also remarkable, as only a few settlements with material from the Banat culture are known from what is now Serbia,” added Fynn Wilkes.
During the same research campaign, the team investigated several Late Neolithic circular features in Hungary together with partners from the Janus Pannonius Museum in Pécs. These so-called “rondels” are attributed to the Lengyel culture (5000/4900-4500/4400 BC).
Header Image Credit : ROOTS
Sources : CAU