Archaeologists from the Regional Association of Westphalia-Lippe (LWL) have uncovered a Neolithic arrowhead in an Iron Age burial, which according to the researchers may have been used as a talisman.
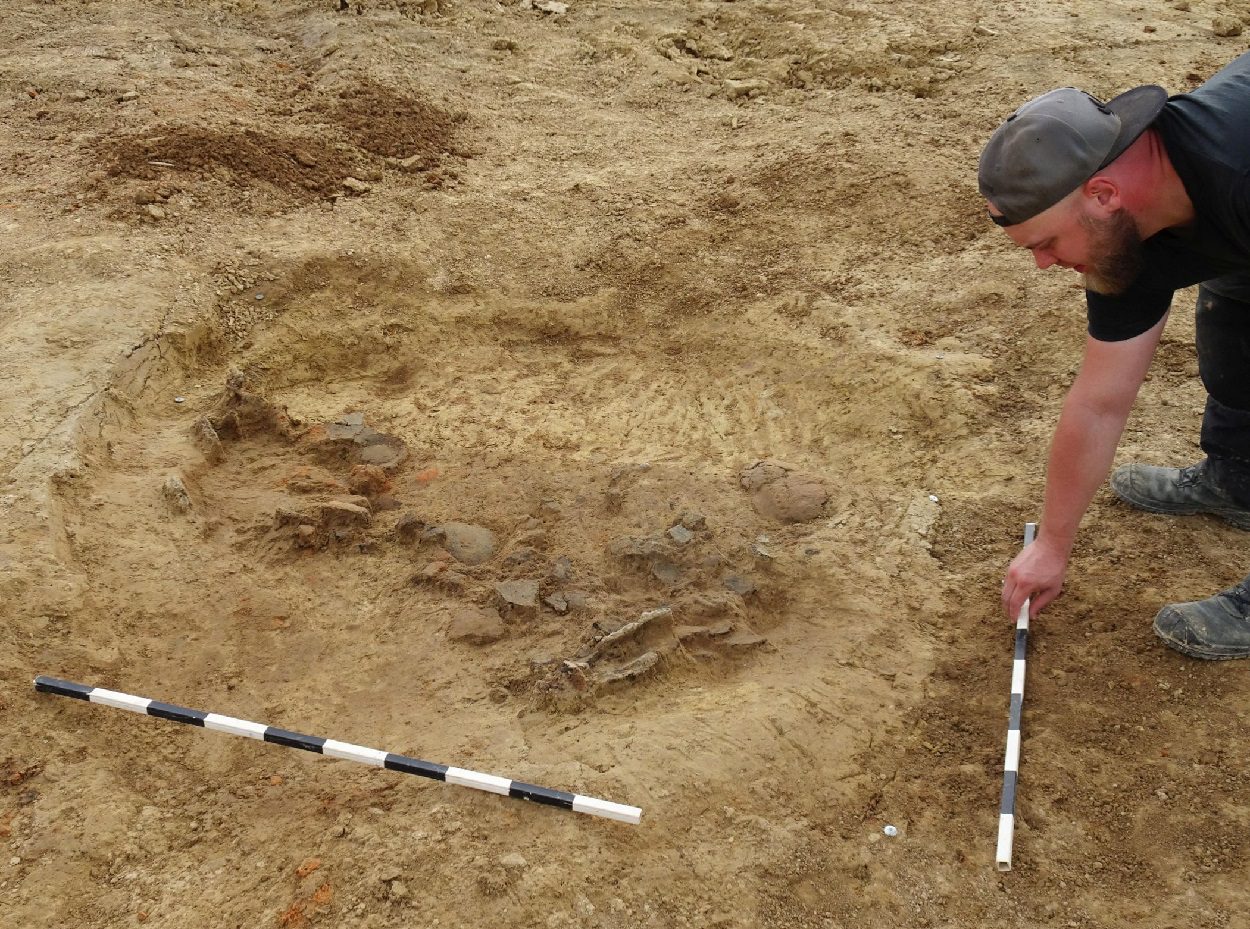
LWL archaeologists have been excavating an Iron Age cemetery containing cremation burials near Fröndenberg-Frömern in Germany’s Unna district.
Dr. Eva Cichy from the Olpe branch of LWL Archeology, said: “When a few remains of corpses were uncovered, it quickly became clear that we had found a small burial ground. In some graves, the remains of vessels used as urns were still preserved, while most of the burials had already been destroyed by agriculture.”
Two large burials have been noted by the archaeologists. One slightly oval pit at a depth of 15 centimetres contained large ceramic shards deposited as funerary offerings, some of which still have the finger impressions from their production around 2,000-years-ago.

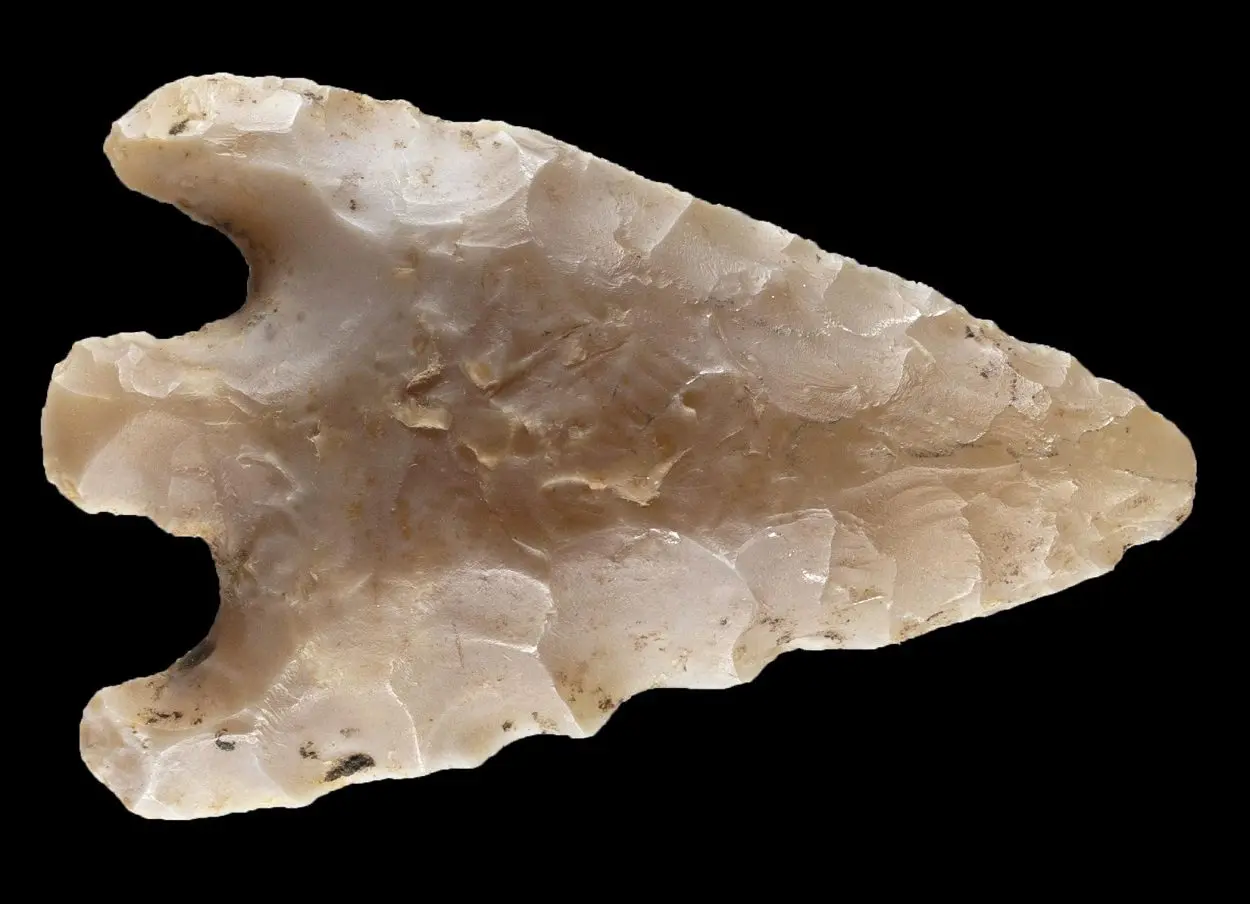
In a neighbouring pit, excavations have found a complete, winged and stalked arrowhead made of flint from the Bell Beaker culture during the Chalcolithic – Early Bronze Age. The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel.
The culture extended across Western Europe, encompassing Iberia, extending eastward to the Danubian plains, reaching northward to encompass the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. The culture also had a presence on the islands of Sardinia and Sicily, as well as certain small coastal regions in northwestern Africa.
According to the researchers, the arrowhead may have been collected as a talisman or a curiosity, however, the artefact may have simply fallen into the pit by chance while digging or filling. The re-use of prehistoric objects as talismans has been documented from various later cultures across Europe as symbols of protection.
Header Image Credit : LWL/Petra Fleischer