In a study published in the journal Antiquity, archaeologists have used LiDAR to reveal WWII features within the forested Ardennes landscape.
The Battle of the Bulge marked the final significant German offensive on the Western Front. The battle lasted for five weeks from the 16th of December 1944 to the 28th of January 1945 in the Ardennes region between Belgium and Luxembourg.
The Wehrmacht’s code name for the offensive was Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein (‘Operation Watch on the Rhine’). The primary military aims were to disrupt Allied access to the Belgian Port of Antwerp and to create a division in the Allied front, a move that had the potential to encircle and dismantle the four Allied forces.
Archaeologists have conducted a study on an area between St Vith and Schönberg using drone-mounted 1m-resolution LiDAR and very high-resolution simultaneous localisation and mapping (SLAM).
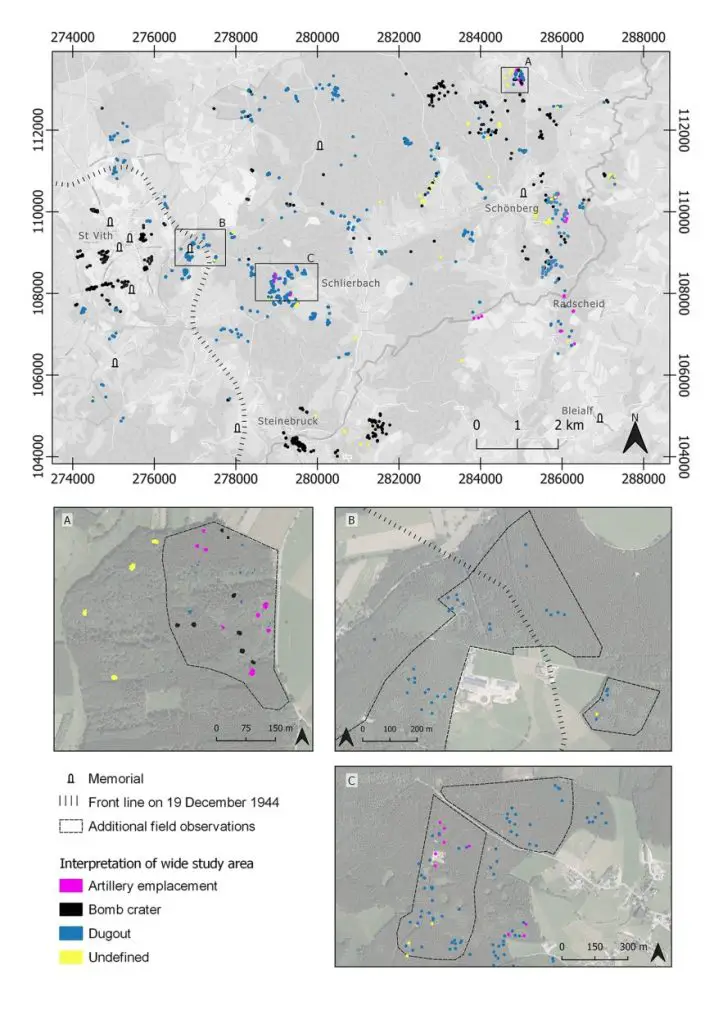
The researchers have identified more than 940 features, which include artillery emplacements, bomb craters, dugouts with an entrance, dugout shelters or storage places, fox holes, trenches, and undefined features.
According to the study authors: “Our study of the landscape and material remains of the Battle of the Bulge through the lens of very-high and low-resolution LiDAR data has identified a rich archaeological landscape associated with US Army defensive lines and both ground combat and aerial bombing in late 1944 and early 1945 in the central sector of the Ardennes Offensive.”
This new layer of information will contribute to heritage considerations around the Second World War landscapes of the Ardennes and complements the existing collection of commemorative monuments.
“Our results indicate that the combination of heavily wooded landscapes and the complexity and large scale of the Ardennes Offensive offer great research potential at St Vith and elsewhere across the region’s former battlefields, in Belgium and neighbouring Luxembourg and Germany. Our work also prompts debate on managing the region’s heritage and the need for a more comprehensive archaeological survey and analysis of this important theatre of operations in north-western Europe,” said the study authors.
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2023.95
Header Image Credit : Public Domain





