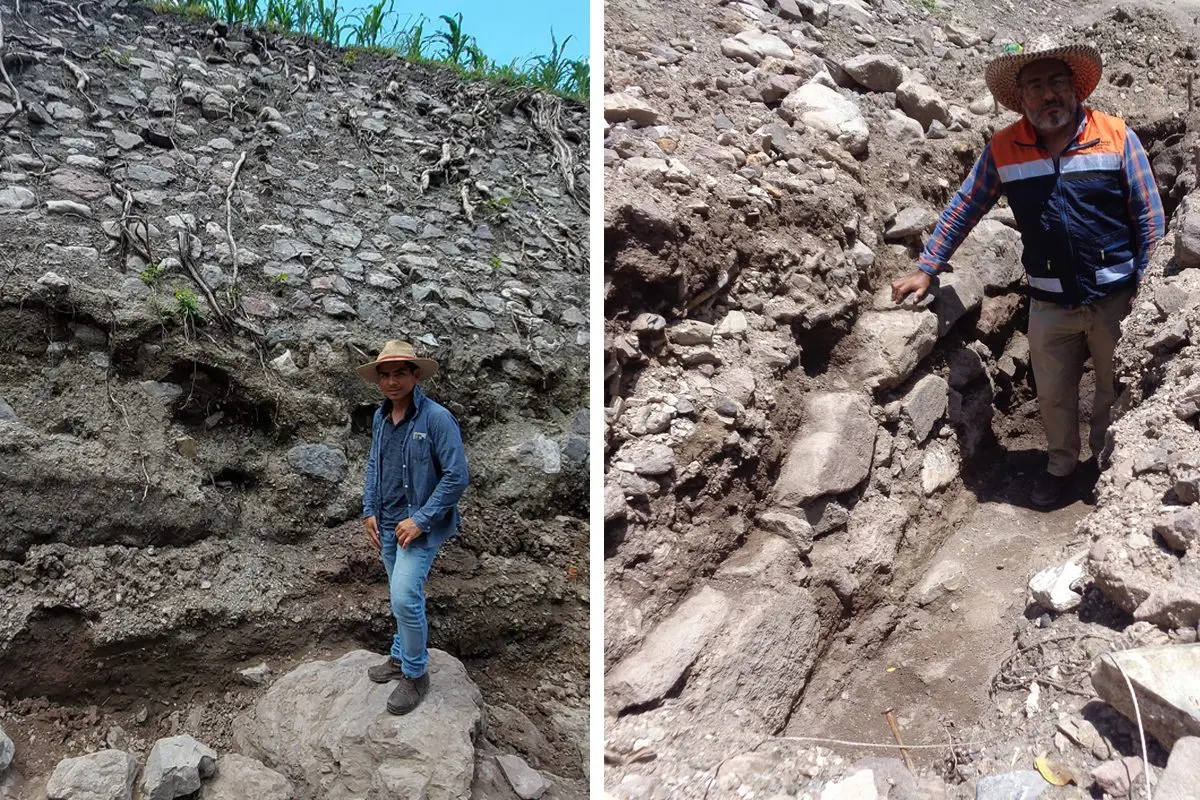
Archaeologists have uncovered vestiges of the Tepuztecos during an expansion of the Puerto del Varal-Corral de Piedra highway at Barranca Chihuila-Corral de Piedra.
The Tepuztecos, also known as the Tlacotepehuas, were a pre-Hispanic culture that inhabited the area around present-day Tlacotepec in the state of Guerrero, south-western Mexico.
Very little is known about the Tepuztecos except for their name recorded by the Aztecs, who referred to the metal works of the culture as “tepuzque”, the Mexica word for copper alloy.
During expansion works of the highway at Barranca Chihuila-Corral de Piedra, archaeologists from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) uncovered a 34 metre long wall which corresponds to the first of three stepped levels of a larger structure.
Excavations at the site found fragments of human and animal bones as part of construction fillers for the wall, in addition to the burial of an infant who died around three to four years of age.
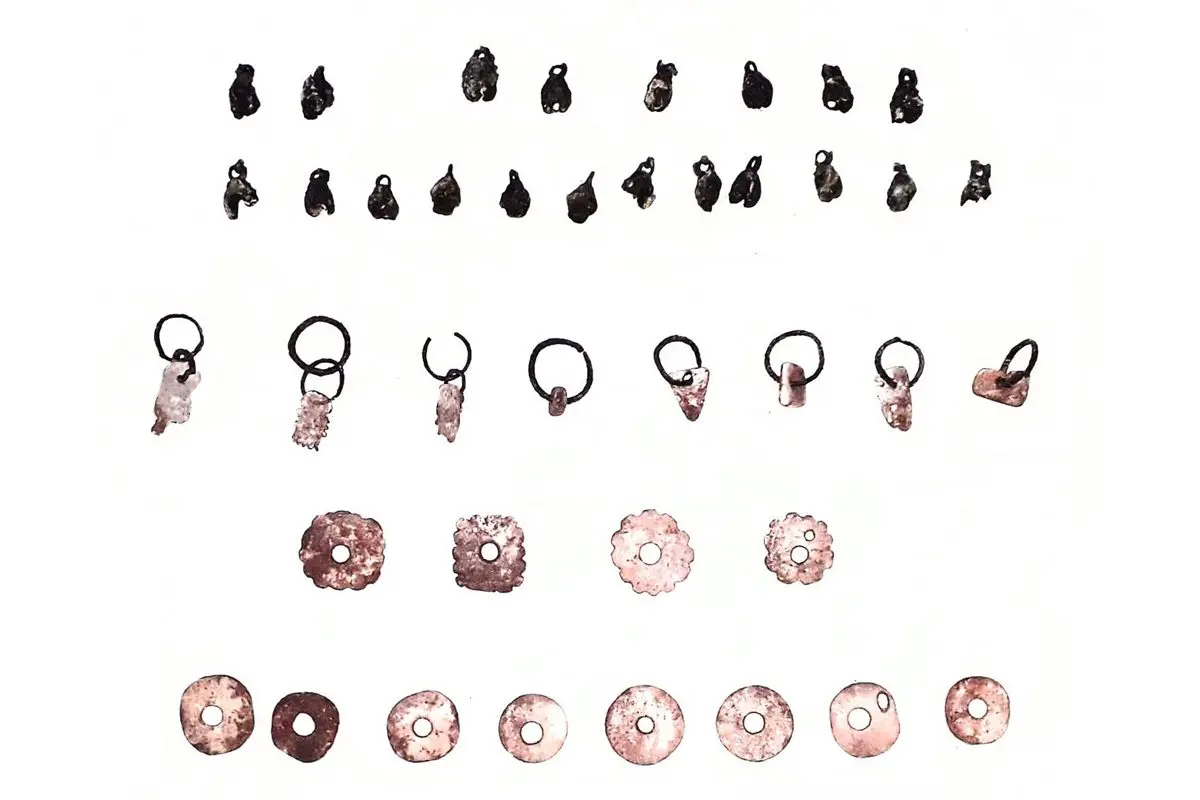
Placed in the burial are offerings consisting of green stone beads, copper bells, shell earrings, and a Yestla-El Naranjo-type tripod bowl which dates from between AD 1000 to 1521 before the Spanish Conquest.
“There is little information about this ethnic group and its culture, we know that they had a god called Andut and a goddess that received the name of Macuili Achiotl, whose figure of a woman was represented in sculpture or painting on stone,” says archaeologist, Pérez Negrete.
Archaeologists also discovered a system of walls made from large limestone blocks covered with lime stucco, in addition to stucco floors with red pigment. Among the objects found associated with the walls are pieces of obsidian and a large quantity of ceramic material from the Postclassic period (AD 500 to 1500), indicating that the site had two periods of occupation.
Archaeologist, Lucero Hernández, said: “It is the start of investigations that will offer new insights into the region of the extinct Tepuztecs, to know the social and cultural characteristics of the extensive pre-Hispanic occupations of the area, as well as to understand the cultural period of the societies that created the Yestla-Naranjo ceramics.”
Header Image Credit : INAH





