Archaeologists excavating in the province of Soria, Spain, have uncovered a previously unknown Celtoiberian city.
The Celtiberians were a tribal people that inhabited an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula. In 195 BC, part of Celtiberia was conquered by the Romans, and by 72 BC, the entire region had become part of the Roman province of Hispania Citerior.
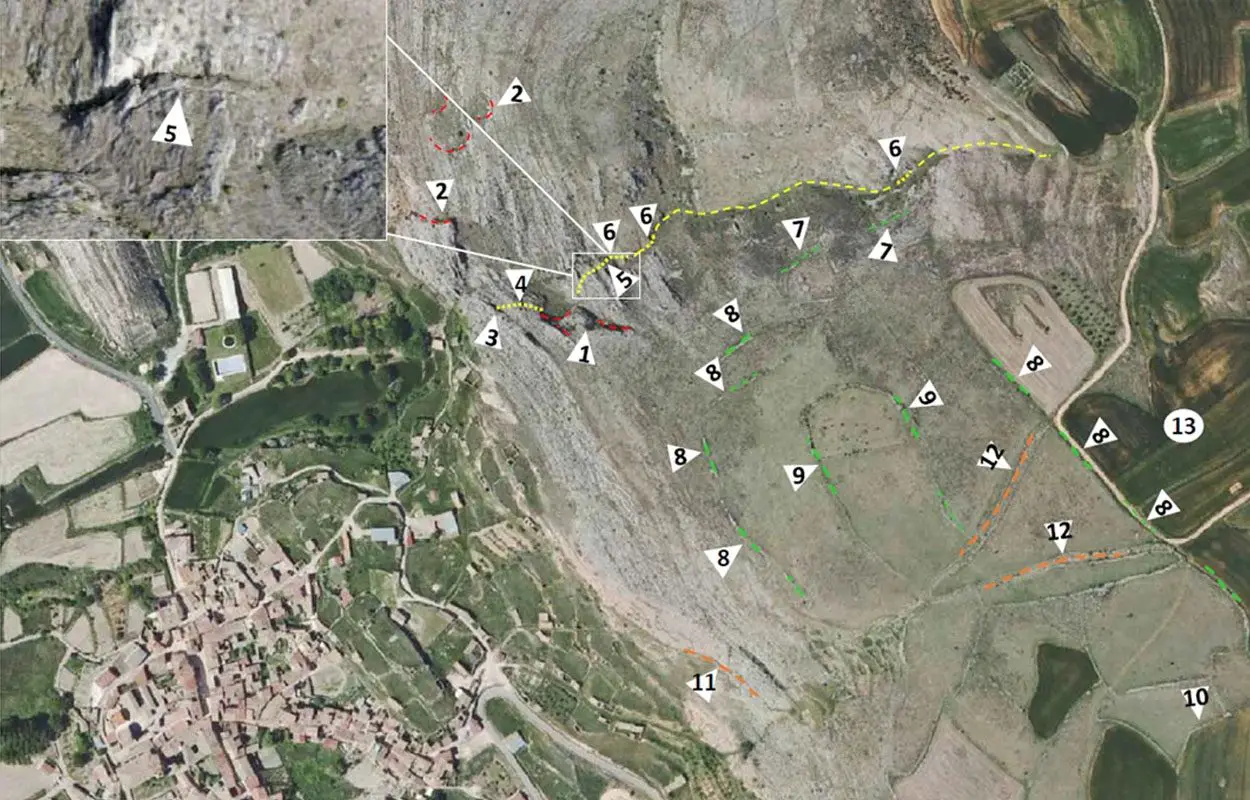
Excavations conducted by the Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM) have found the ruins of a Celtoiberian city that dates from more than 2,000-years-ago. According to the researchers, the site could be the lost city of Titiakos, a Celtoiberian stronghold from during the Sertorian War.
The Sertorian War was a civil war fought from 80 to 72 BC between a faction of Roman rebels (Sertorians) and the government in Rome (Sullans) in the Iberian Peninsula. The war takes its name from Quintus Sertorius, the leader of the opposition, a Roman general and statesman.
“Despite its relevance, this site has never been studied and has remained ignored. To date no systematic study has been carried out that has tried to discover its historical importance”, says Vicente Alejandre, mayor of Deza.
Part of the reason why the ruins have been left unexplored, is due in part to the site being camouflaged by an adjacent quarry where the city stone was sourced.
To the north east at an elevated position, the researchers also discovered the remains of a large Roman military camp.
The team suggest that the fort was likely built to protect the city mint by allied Sertorians, as excavations have revealed warlike elements and evidence of conflict such as projectiles, and also coins that came from the mint.
According to the researchers: “The results obtained are relevant for the advancement of scientific and historical knowledge of the Celtiberian and Roman world in the context of the Sertorian Wars. On the one hand, it points to the existence of the capital of the Titiakos ethnic group and of a Roman military camp of considerable importance. Further studies would be necessary to confirm this statement with a systematic geophysical survey of the battlefield in order to increase the monetary record.”
Header Image Credit : UPM