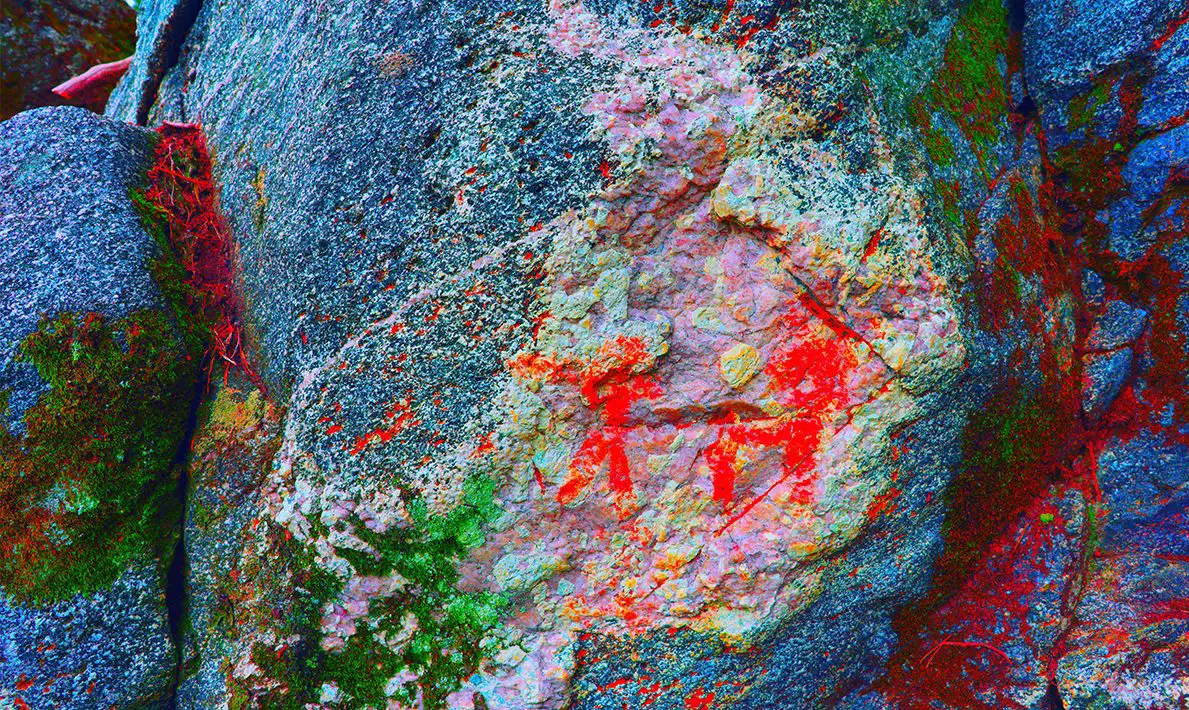A hiker has discovered a collection of pictographs in Norway’s Østfold region.
The discovery was made by Tormod Fjeld who noticed mysterious shades of colour in a rockface where he and his family had stopped for a rest break.
Using an app on his phone, Fjeld was able to highlight the different colour shades by applying various filters, revealing images of a boat with rowers, an animal, and several human figures.
Østfold is among Norway’s oldest inhabited regions, with petroglyphs, pictographs, and burial mounds being documented throughout the area.
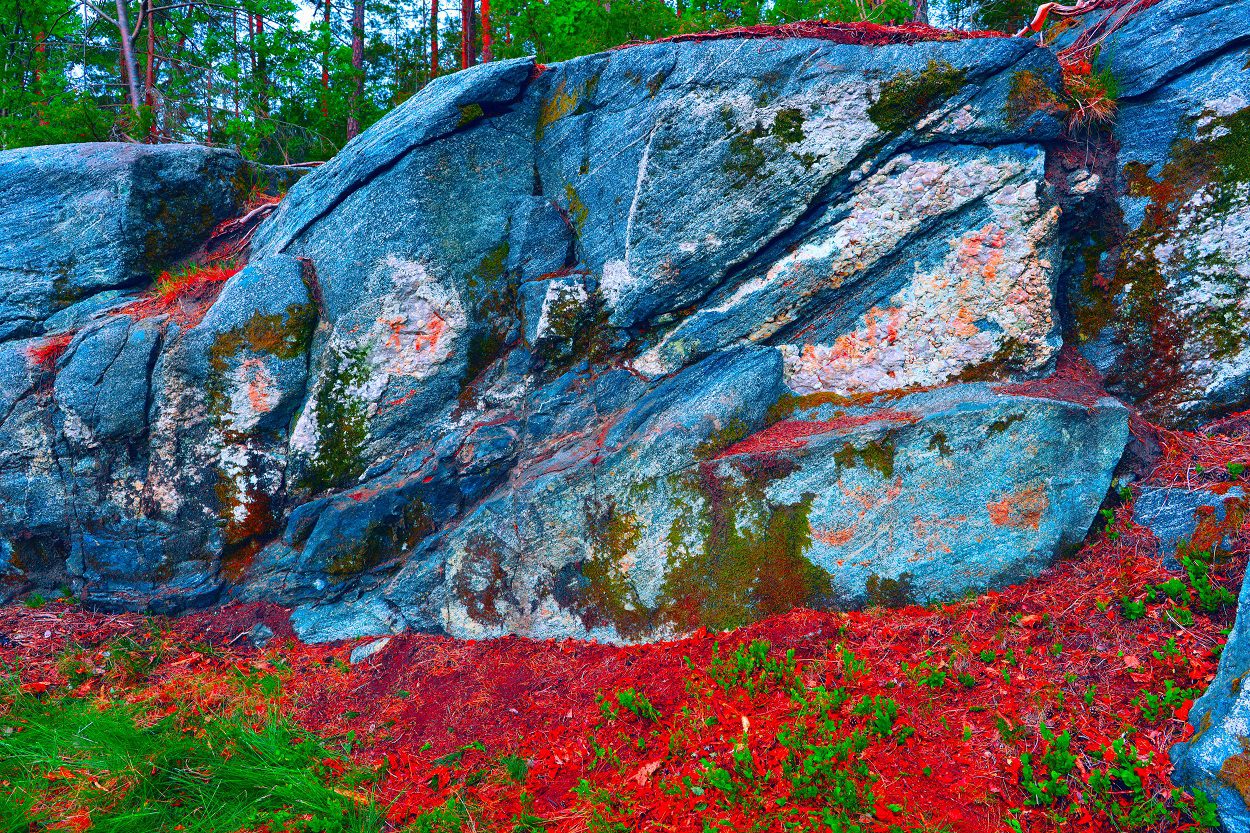

Mr Fjeld contacted local authorities and archaeologist, Jone Kile-Vesik (a specialist in rock art), which led to researchers from the Norwegian Institute for Cultural Heritage Research (NIKU) being sent to assess the site.
The team from NIKU confirmed the discovery which has been dated to Norway’s Bronze Age, with Professor Jan Magne Gjerde from NIKU stating that the discovery is one of the earliest rock art sites in this part of the country.
The Bronze Age in Scandinavia is said to begin shortly after 2000 BC with the introduction and use of bronze tools, followed by a more systematic adoption of bronze metalworking technology from 1750 BC.
“It is easy to think that such parts are randomly formed from natural pigments. But here there are so many “coincidences” gathered together that is not random”, says Jan Magne Gjerde from NIKU.
Due to the historical importance, the exact location is being kept confidential, with NIKU only stating that the site is in the Moss municipality. This is because the pigments used for the pictographs are easily damaged, with even human touch being enough to cause irreparable damage.
Header Image Credit : Jan Magne Gjerde, NIKU