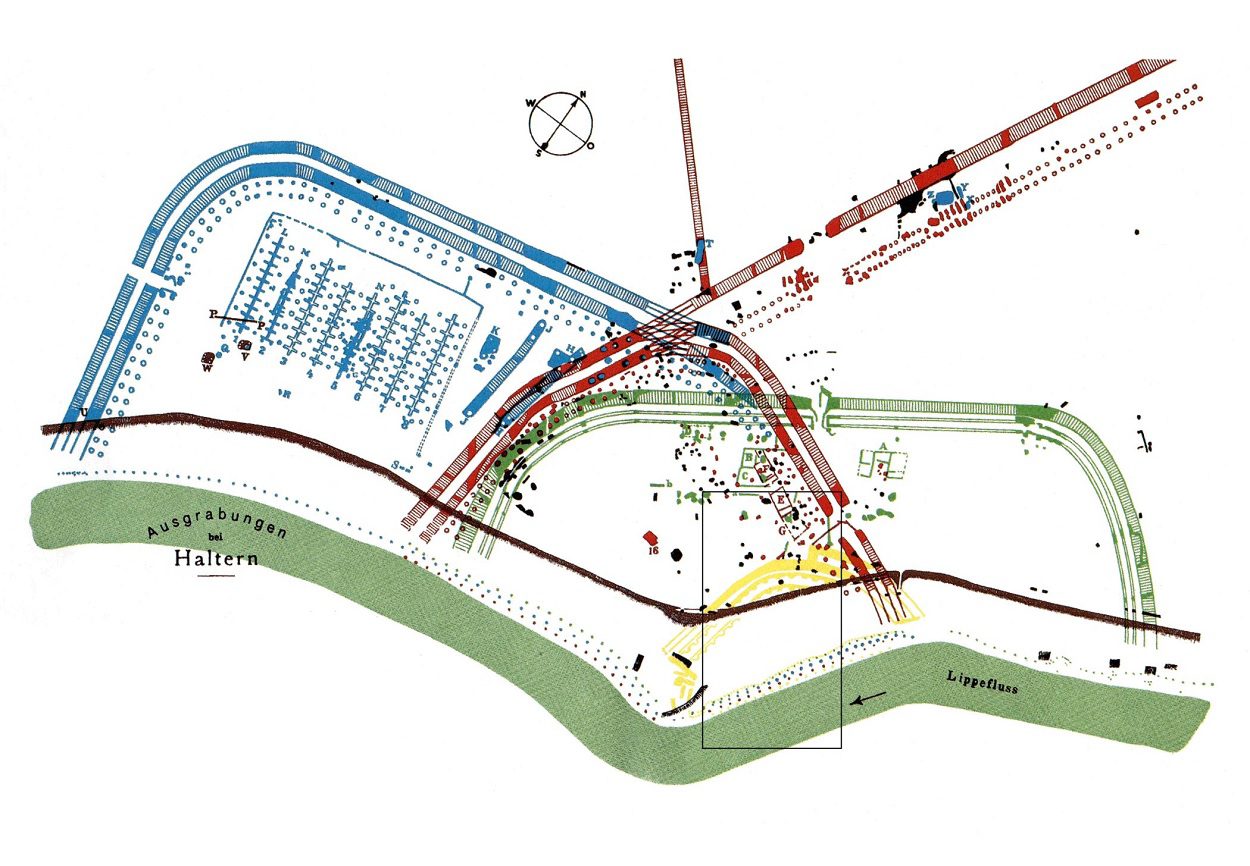
Archaeologists excavating a Roman shore fort in Haltern am See have discovered that the site was completely rebuilt four times with a different floor plan 2,000-years-ago.
During the Roman period, Haltern am See in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, was a major military fortress and civilian colony. Historians suggest that the fortress was built by the emperor Augustus who named it Aliso.
The fortress was supported by a naval base or shore fort called the Hofestatt (C) on a spur-like terrace that sheltered boats in a natural harbour. The Hofestatt advanced like a peninsula far into the Lippe Valley, where patrol boats and ship transports carrying Roman soldiers docked.
Excavations by the Regional Association of Westphalia-Lippe (LWL) have conducted a study of two neighbouring sites in preparation for planned construction works on the Hofestatt, revealing that the Romans rebuilt the base four times with a different floor plan.
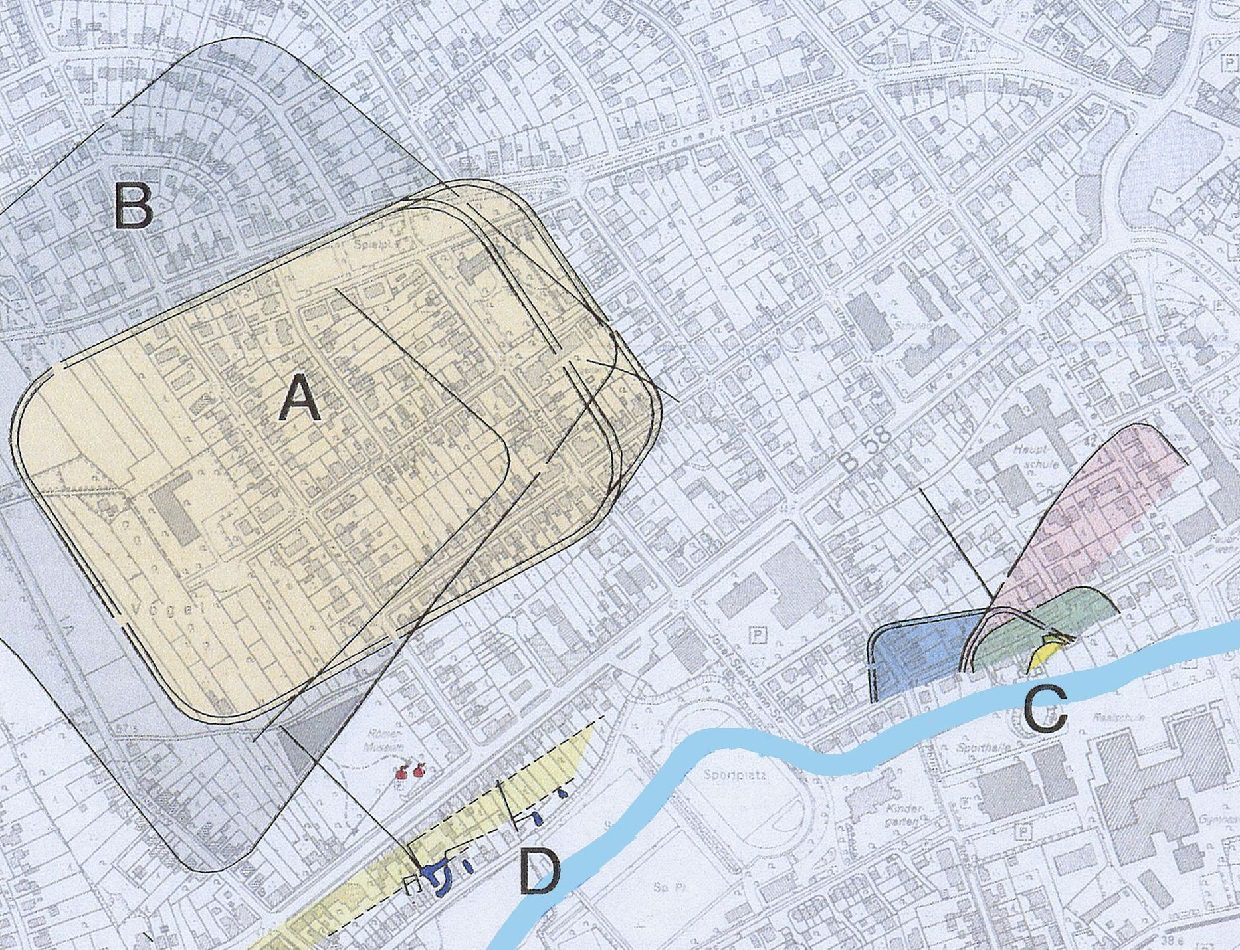
The Hofestatt was extensively built over during the 1950’s, however, the construction project now gives the LWL experts the opportunity to research the archaeological remains using modern methods.
The team also found a large number of pits and ditches, most of which are from the oldest phase of construction showing similarities in plan to the Roman camp at Bergkamen-Oberaden.
Post traces from the third phase were dug vertically into the ground and served as the framework for a wood-earth wall, similar to the reconstructed wood-earth wall in the main fortress (A) found in the Aliso Roman Park in the LWL Roman Museum.
Header Image Credit : Antiquities Commission for Westphalia