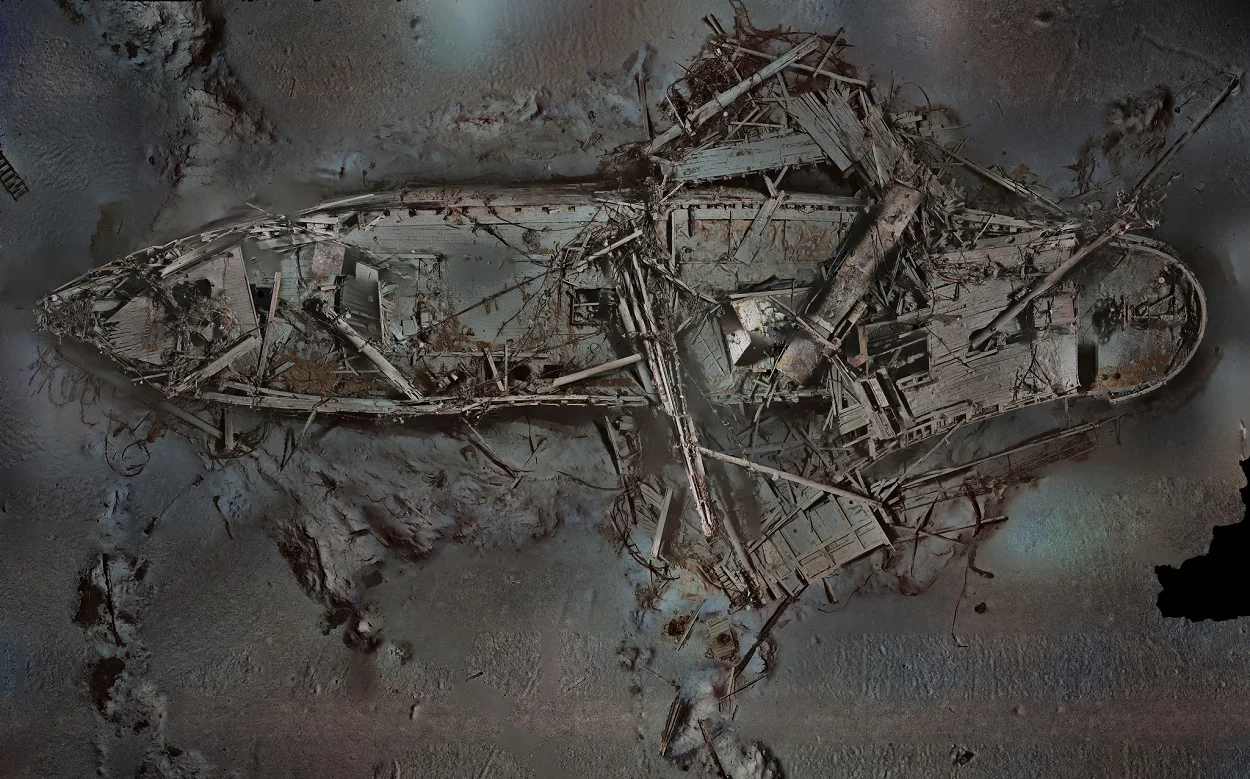
Researchers from the Endurance22 project have revealed high detailed 3D scans of the Endurance, Sir Ernest Shackleton’s ship from the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition of 1914–1917.
The expedition was an attempt to make the first land crossing of the Antarctic continent, from the Weddell Sea on one side to the Ross Sea on the other, via the South Pole.
The Endurance left South Georgia in December 1914, however, just weeks into the voyage the ship was caught in dense pack ice in the Weddell Sea and became completely trapped.
After 10 months of drifting, the pack ice started to crush the ship’s hull, forcing Shackleton and his crew to abandon Endurance and set up temporary camps on the exposed ice as they watched the vessel sank.
The crew eventually reached Elephant Island, an uninhabited ice-covered island situated 245 kilometres (152 miles) north-northeast of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula.
Shackleton and five others then made a 1,300 km (800 mile) open-boat voyage to reach South Georgia. After four and a half months, on August 30th, 1916, the tug Yelcho arrived with Shackleton on board and rescued his remaining crew.
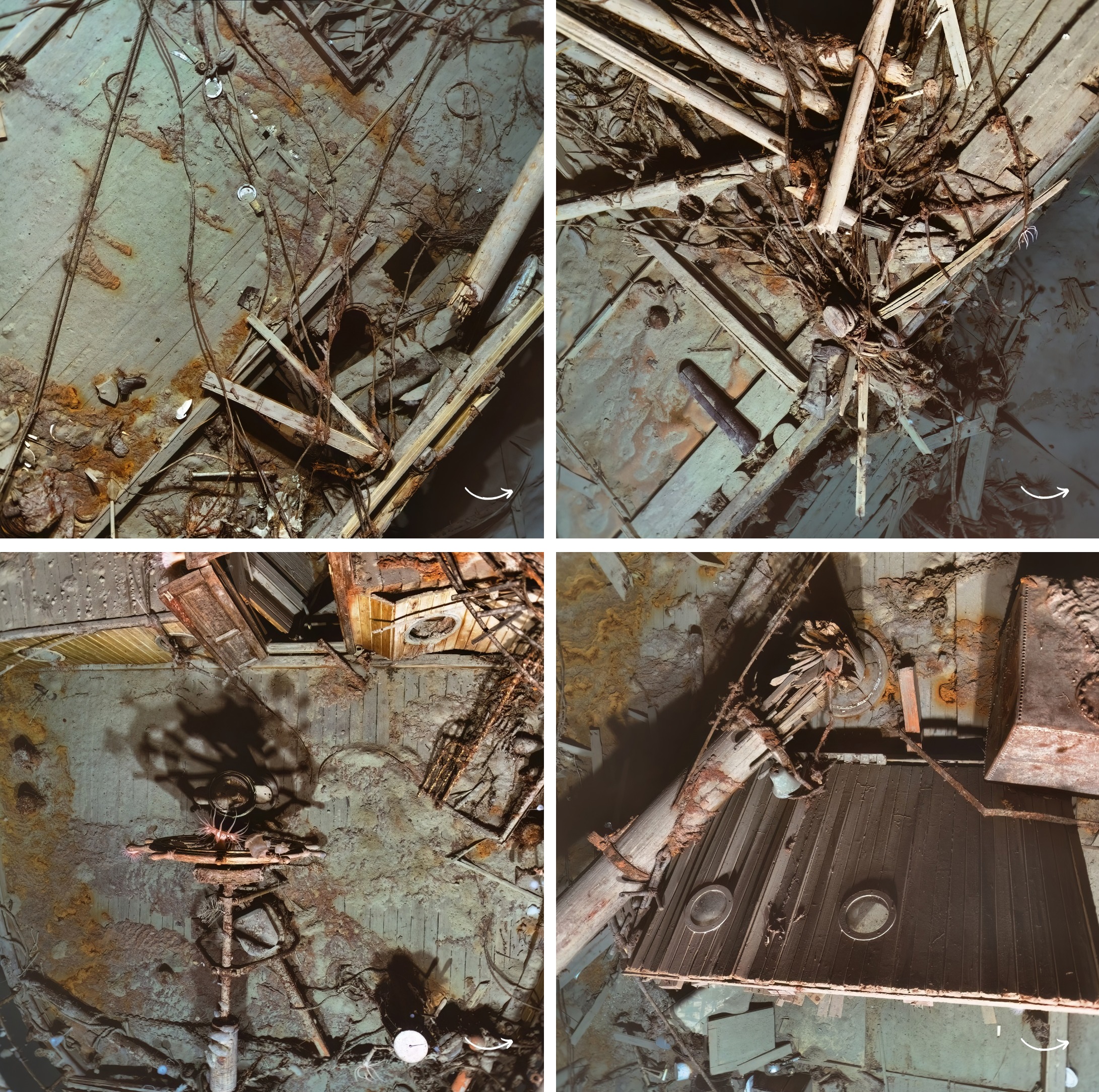

A joint survey was conducted by researchers from Voyis, Sonardyne International Ltd, EIVA a/s, DECAR, Deep Ocean Search, and SEARCH Inc. The team made 25,000 high-resolution images, which have been applied with machine-learning “True-Colour” technology to create the shipwreck’s natural hues in 3D.
Mensun Bound, the director of exploration for the Endurance22 expedition, said: “The preservation is ridiculous. You could still lean against the standing rails at the bows and peer through the portholes into the inky black cabin where Shackleton slept.”
An examination of the imagery shows that the paintwork and the ship’s name “ENDURANCE” are still clearly visible, as well as several artefacts such as Frank Hurley’s flare gun which he fired in tribute as the ship sank. Also visible is a preserved lone boot that likely belonged to Shackleton’s second-in-command, Frank Wild.
Header Image Credit : Falklands Heritage Trust / National Geographic Documentary Films
Sources : SEARCH Inc