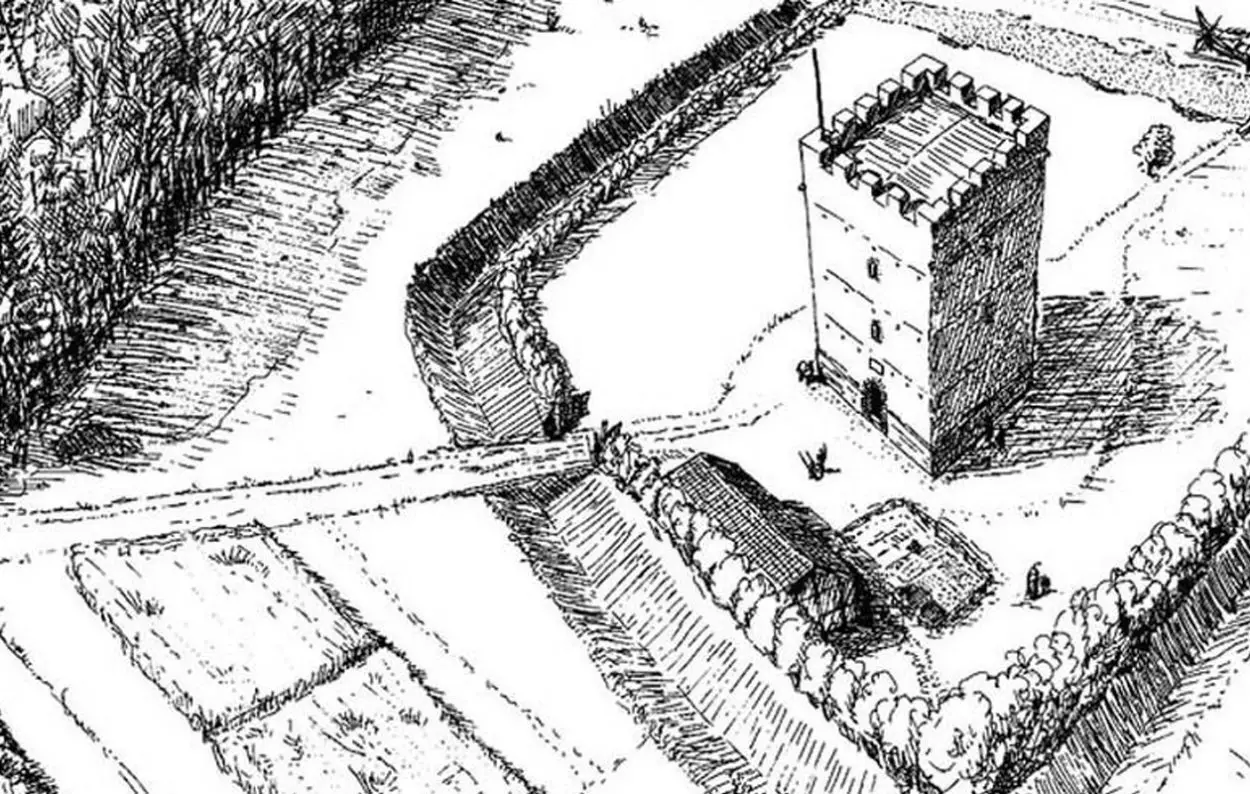
A survey conducted in the Schaaren am Hochrhein, a nature reserve in Switzerland on the shores of the Rhine, has led to the discovery of a Roman watch tower from the 4th century AD.
The history of Switzerland under Roman rule dates from the Augustan period up until around AD 400. As the Empire’s frontiers receded to the Rhine, a chain of watchtowers was constructed from Lake Constance to Basel, with each tower no more than 2 kilometres apart.
The defensive line protected the border from the Alemanni, a confederation of Germanic tribes on the Upper Rhine River that raided the frontier and eventually conquered parts of northern Switzerland.
The reserve is already known for being rich in archaeological remains, including a Bronze Age settlement, fortifications from the Napoleonic Wars, WW2 bunkers, and a previously discovered Roman watch tower.
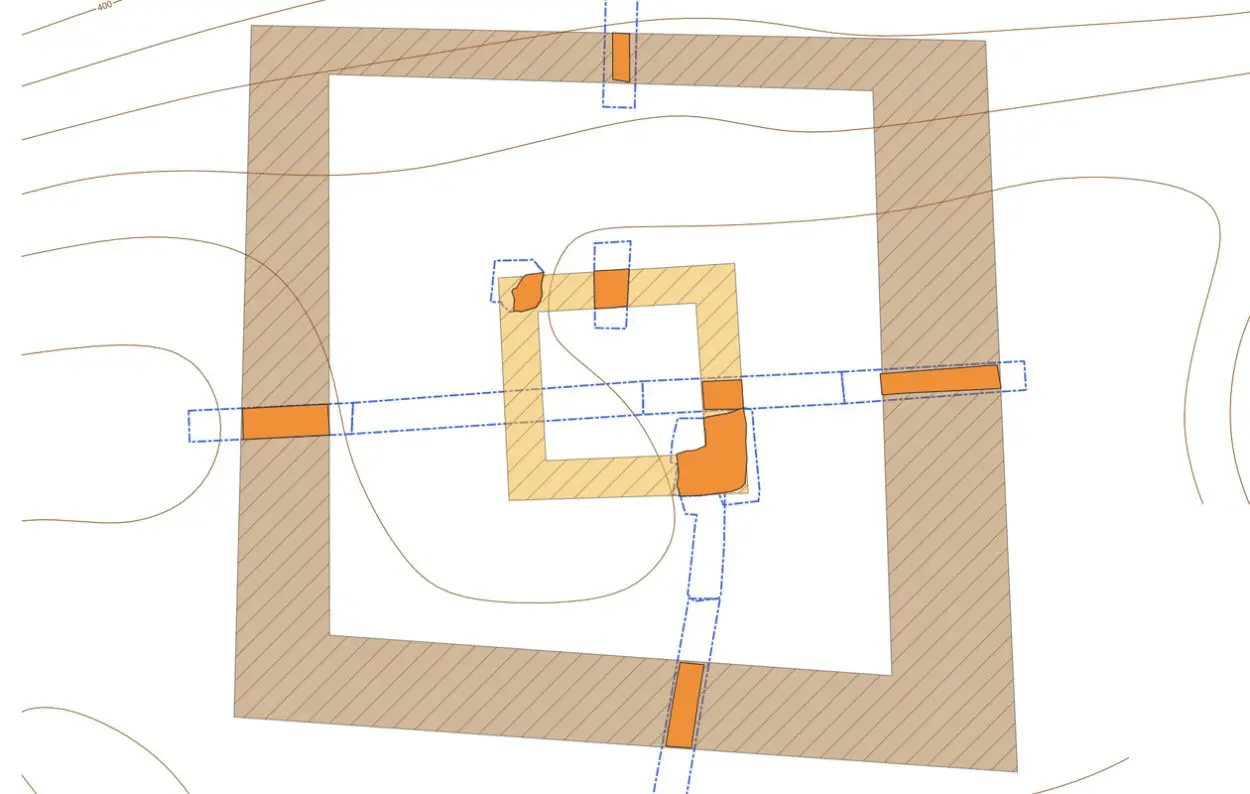
A visual inspection showed no physical remains above the surface; however, excavations confirmed the foundations of a square building measuring 7×7 metres with walls around 1 metre thick.
Only the mortar and several stones indicating the outline of the building have remained, with the rest of the structure’s stones likely being removed and reused during later times. With the exception of large amounts of roofing tiles, finds within the building’s interior are limited to a military belt, a fibula, an amphora-shaped strap end, and a coin of Emperor Constantine I dated to after AD 311.
Excavations also revealed the traces of a V-shaped trench surrounding the watch tower, which was likely reinforced with a palisade or wooden fortification and supporting buildings for animals or storage.
Header Image Credit : Scharenwiese