A study by the University of Bradford could provide the key to studying submerged civilisations by looking for anomalies in magnetic fields.
According to Ben Urmston from the University of Bradford, magnetic fields could indicate the presence of archaeological features without the need for exploratory underwater excavations.
Magnetometry has previously been used by terrestrial archaeologists but has not been used extensively to examine submerged landscapes.
The pioneering technique could be applied in Doggerland, a submerged land mass beneath what is now the North Sea, that once connected Britain to continental Europe.
The landscape of Doggerland was a diverse mix of gentle hills, marshes, wooded valleys and swamps during the later Palaeolithic and Mesolithic periods.
Small groups of hunter-gatherers took advantage of Doggerland’s rich migrating wildlife, with evidence of ancient animal bones and tools being brought to the surface by fishing trawlers operating in the North Sea.
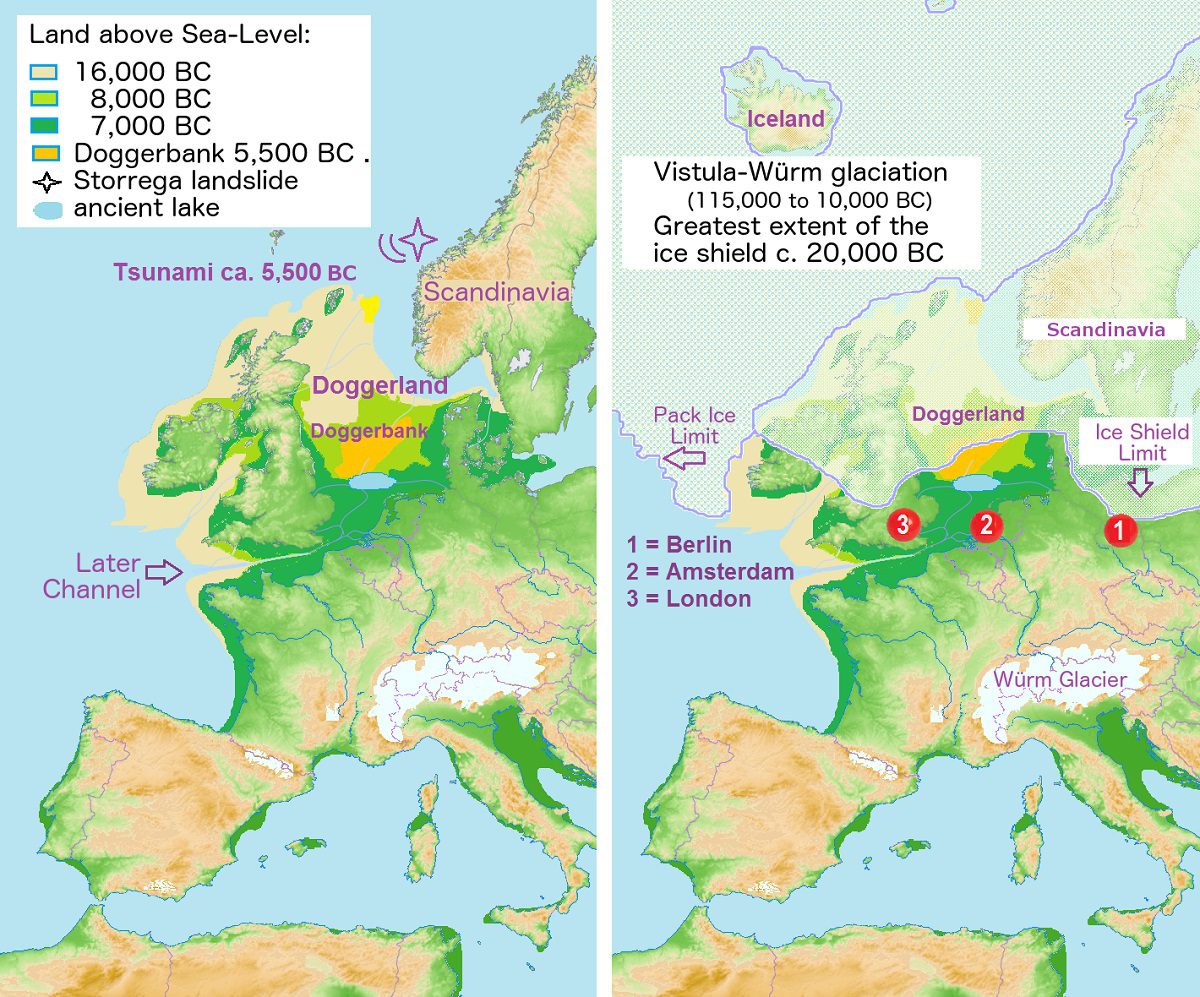
Over time, the area was flooded by rising sea levels after the last glacial period around 6,500 to 6,200 BC. Melting water that had been locked away caused the land to tilt in an isostatic adjustment as the huge weight of ice lessened.
Doggerland eventually became submerged leaving only Dogger Bank, a possible moraine (accumulation of glacial debris) which also succumbed to the sea around 5000 BC.
According to Urmston: “Small changes in the magnetic field can indicate changes in the landscape, such as peat-forming areas and sediments, or where erosion has occurred, for example in river channels. As the area we are studying used to be above sea level, there’s a small chance this analysis could even reveal evidence for hunter-gatherer activity.”
“We might also discover the presence of middens, which are rubbish dumps that consist of animal bone, mollusc shells and other biological material that can tell us a lot about how people lived,” added Urmston.
Such features could be analysed closer by taking samples of the seabed which are then sent for carbon dating and a microscopic analysis.
Professor Vince Gaffney, academic lead for the project, said: “Exploring the submerged landscapes beneath the North Sea represents one of the last great challenges to archaeology. Achieving this is becoming even more urgent with the rapid development of the North Sea for renewable energy.”
Header Image Credit : Cloudinary – CC BY-SA 4.0





