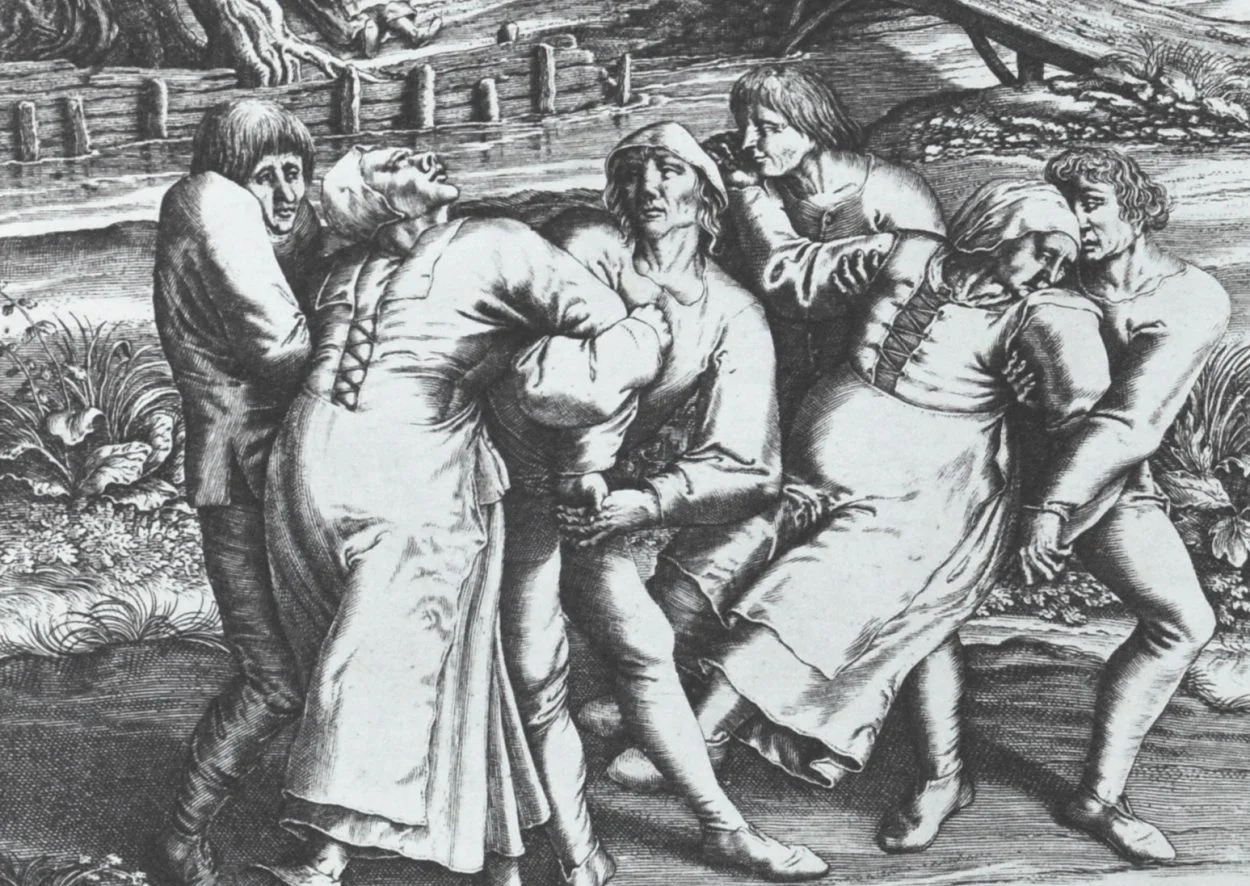
The city of Strasbourg in Alsace (now France) was the site of one of the strangest ‘plagues’ in human history.
In July of 1518, a resident named Frau Troffea was seemingly bitten by the ‘dancing bug’. While walking through the streets, she suddenly and uncontrollably began twisting, gyrating, and dancing on the spot. Surprisingly, a week later she was still dancing, and several other people began to show the same odd behaviour.
By August of the same year, around 400 people were afflicted by this strange and dangerous behavior, resulting in people collapsing in the streets and according to some accounts, dozens even danced themselves to death after suffering from strokes, heart attacks and/or exhaustion (although there are conflicting accounts that give no mention of death).
There are several theories as to the cause of the plague. Sixteenth century fervent Catholics believed that Saint Vitus, whose name is sometimes rendered Guy or Guido, cursed the residents with the “St. Vitus’ Dance”, because of the Diocletianic Persecution in AD 303 that led to his martyrdom.
St. Vitus’ Dance was diagnosed in the 17th century as Sydenham chorea, an autoimmune disorder that can occur after an infection of Streptococcus with a resulting rheumatic fever. It causes ‘dance’ type symptoms such as twitching, arm and leg movements, gyrations and facial distortions. While not impossible, Sydenham’s chorea would unlikely affect so many people in such a short time in one area.
Another theory to the dancing mania involves a fungus called ergot. The psychoactive properties of ergot (similar to LSD) include the ability to induce hallucinations and cause other mental and visual disturbances, dilated pupils and paranoia. Ergot grows on many of the grains used to make breads, however, experts believe the affects of the hallucinogen would wear off in less than a day, evidently not sustaining the symptoms in those affected that would last for days, or even weeks.
We can’t forget the anxieties of medieval Europe at the time. Dire situations involving starvation, incurable diseases and other extreme stresses can cause mass panic events ranging from collective concerns to a full-blown mass hysteria.
An event such as the 1518 dancing plague could be the result of years of mental torment of the residents of the area. It is not unreasonable to imagine how the constant fear of death over a long period of time can undoubtedly cause some form of panic leading to a mass psychogenic illness event.
The events of 1518 were the best known of the numerous accounts of dancing plague affecting people in (what is now) Europe during the 14th-17th centuries. Whatever the cause of the strange phenomenon, dancing mania remains one of the world’s most intriguing mysteries.
Written by Julie St Jean
Header Image : Dancing mania on a pilgrimage to the church at Sint-Jans-Molenbeek, a 1642 engraving by Hendrick Hondius – Image Credit : Public Domain