Archaeologists have discovered 134 ancient settlements north of Hadrian’s Wall from around the period of the Roman occupation.
Hadrian’s Wall (Vallum Aulium) was a defensive Roman fortification that ran 73 miles (116km) from Mais (Solway Firth) to the banks of the River Tyne at Segedunum (Wallsend).
Following Hadrian’s accession to the throne in AD 117, he constructed a wall like no other in the Roman world, a wall that was a physical expression of Rome’s power to solidify the Roman policy of defence and indicate the most northern frontier of the Empire.
Whether this would have deterred a threat from the northern tribes invading from Caledonia is unknown, with some scholars suggesting that the wall served to provide a means of immigration control and customs for taxation.
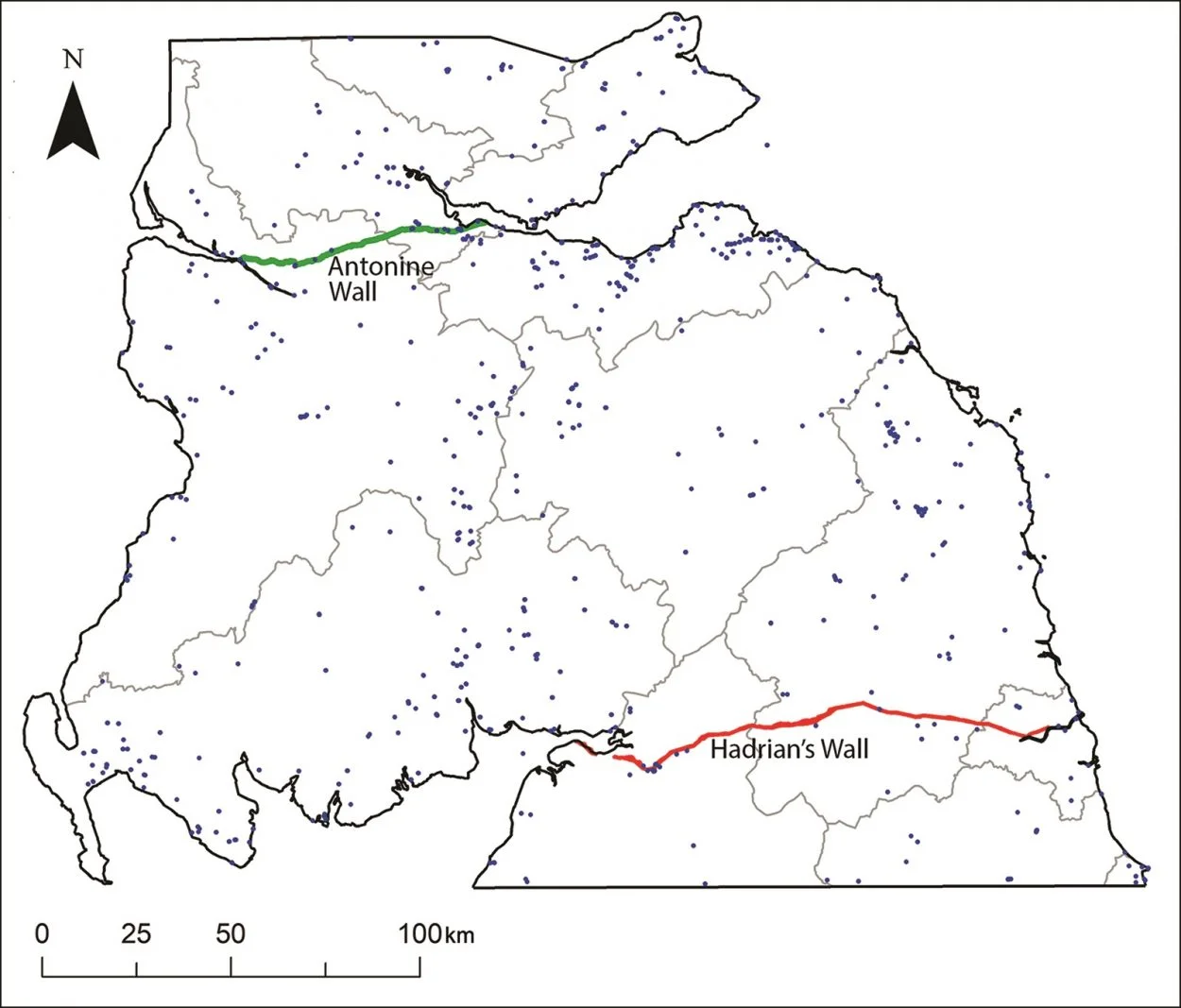
In AD 142, Emperor Antoninus Pius extended the frontier further north and constructed the Antonine Wall (Vallum Antonini). This wall ran 39 miles (62.7 km) and annexed lands formerly ruled by the Damnonii, Otadini, Novantae, and the Selgovae tribes.
Previous studies have mainly focused on the Roman archaeology, i.e. forts, road network, encampments and Roman settlements extending north into parts of Caledonia (Scotland) between the two walls.
“This is one of the most exciting regions of the Empire, as it represented its northernmost frontier, and because Scotland was one of very few areas in Western Europe over which the Roman army never managed to establish full control,” said lead author Dr FernándezGötz, from the University of Edinburgh.
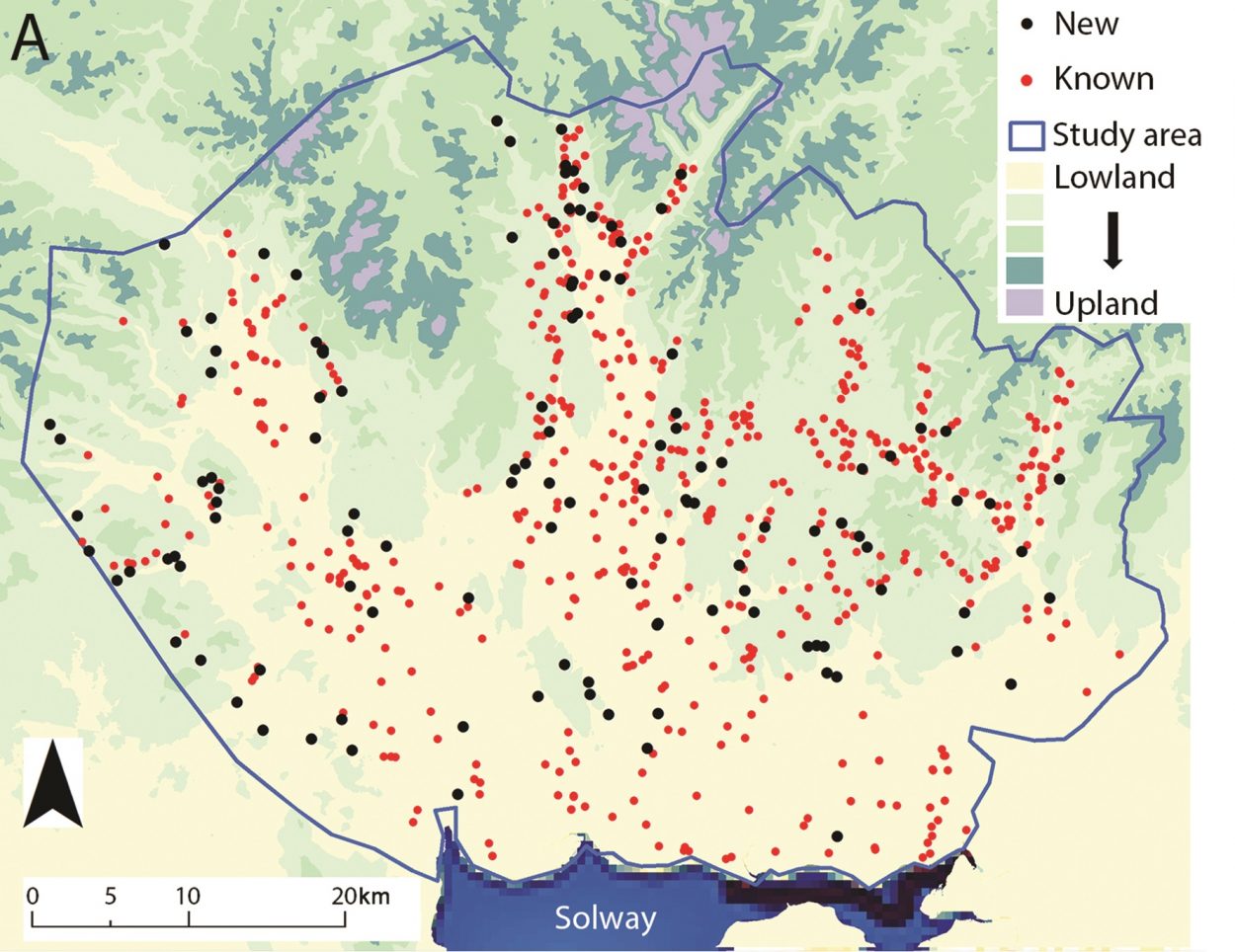
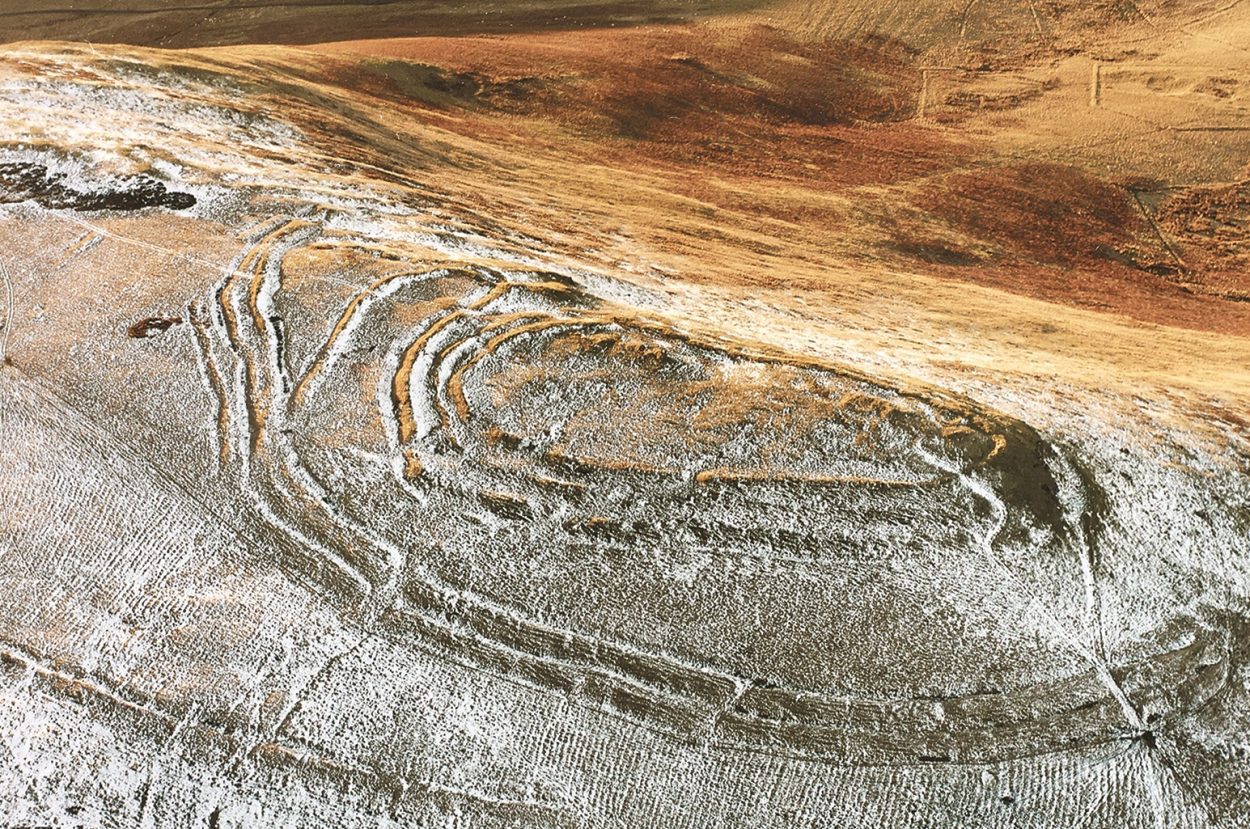
As part of a new research project published in the journal Antiquity, archaeologists from the University of Edinburgh have focused on the region around Burnswark hillfort in Scotland and expanded their study using Lidar (light detection and ranging) over an area of around 579 square miles (1500 km2).
The team discovered 134 previously unknown Iron Age settlements mainly consisting of ancient farmsteads inhabited by the indigenous tribal population of Caledonia. The Lidar data paints a fuller picture of the ancient landscape, revealing often dense distributions of sites dispersed across the region with a regularity that speaks of a highly organised settlement pattern.
The archaeologists are also surveying notable discoveries in greater detail using geophysics and applying radiocarbon dating to gain a more complete picture of the settlements. The researchers hope that they will get a clearer picture of how life changed before, during, and after the Roman occupation, gaining a more complete view of this part of Iron Age Britain.
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2022.47
Header Image Credit : Antiquity





