Archaeologists conducting a study on the Phoenician Island city of Motya, located off the coast of Sicily have identified that an artificial lake was a sacred pool aligned with the stars.
Motya, known today as San Pantaleo Island was a Phoenician port founded during the first Millenium BC in the Stagnone Lagoon between Drepanum (modern Trapani) and Lilybaeum (modern Marsala).
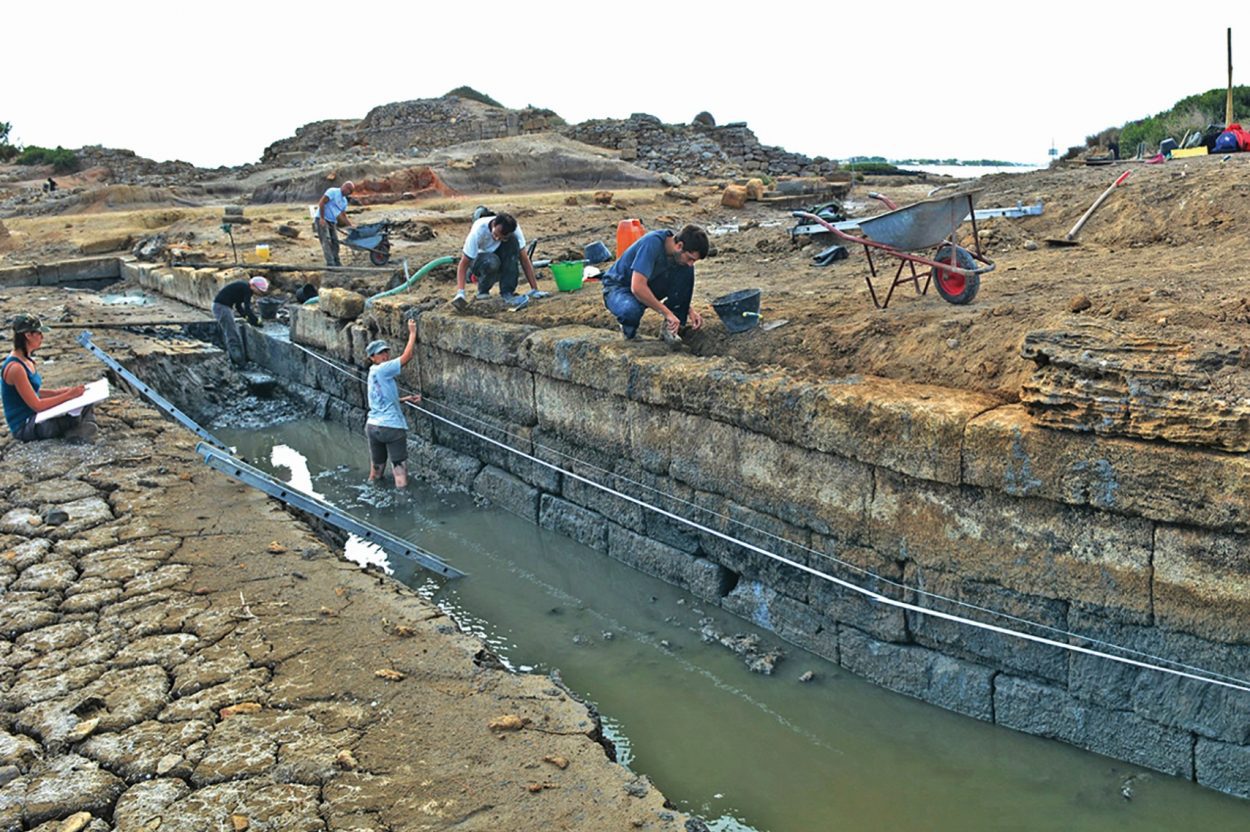
Archaeologists excavating a 2,500-year-old artificial basin, once identified as a military harbour called a Kothon during the 1920s is actually one of the largest sacred pools in the Mediterranean. The pool was added around 550 BC when the city was rebuilt after an attack by Carthage as a centrepiece of a massive religious sanctuary aligned with the stars.
Professor Nigro from Sapienza Università di Roma said: “For a century it was thought Motya’s ‘Kothon’ was a harbour, but new excavations have drastically changed its interpretation: It was a sacred pool at the centre of a huge religious compound.”
Previous research had found a Temple of Ba’al on the edge of Motya’s Kothon, rather than the expected harbour buildings. This unexpected discovery prompted the reinvestigation of the Kothon starting in 2010.
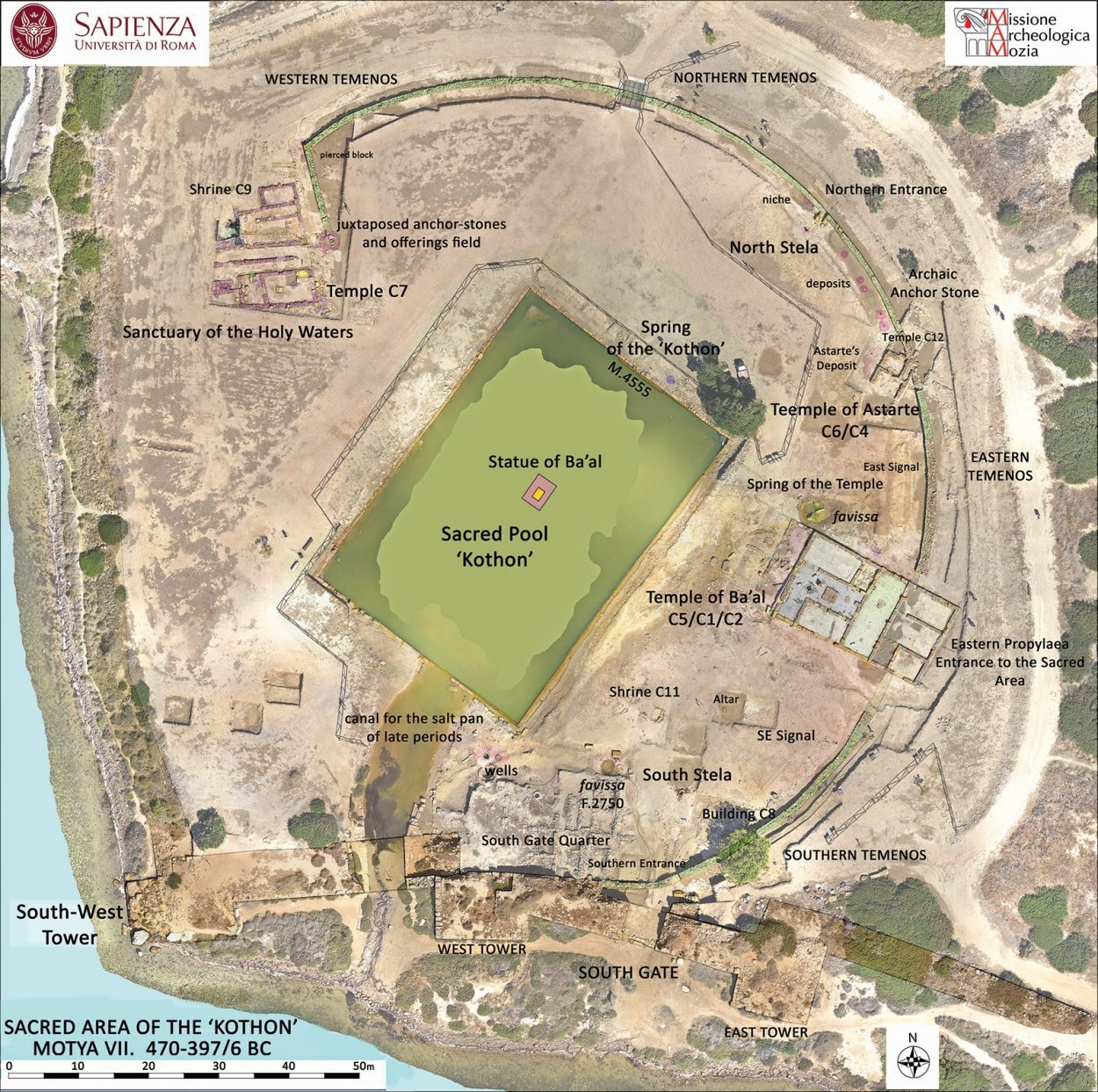
During the next 10 years, Professor Nigro and the team drained and excavated the basin, which is longer and wider than an Olympic swimming pool.
“This revealed it could not have served as a harbour, as it was not connected to the sea. Instead, it was fed by natural springs,” said Professor Nigro.
Crucially, the team also found additional temples flanking the Kothon, along with stelae, altars, votive offerings, and a pedestal in the centre of the lake that once held a statue of Ba’al. Together, these indicate this was not a harbour but a sacred pool at the centre of one of the largest cultic complexes of the pre-Classical Mediterranean.
Mapping this site revealed it was aligned with the stars: “The nearby Temple of Ba’al is aligned with the rise of Orion at the winter solstice, whilst stelae and other features were aligned with other astronomical events,” said Professor Nigro. “This points to the deep knowledge of the sky reached by ancient civilisations.”
Additionally, the flat surface of the pool may have been used to track these celestial movements, which were important for both navigation and religious holidays.
Notably, many of these stem from other ancient culturesm suggesting Motya remained an open and accepting cultural melting pot. Historical records also attest to an open attitude, indicating it caused animosity with Carthage that contributed to Motya’s eventual downfall.
The basin has since been refilled and a replica of the statue of Ba’al placed back on its plinth. Find out more
Header Image Credit : Antiquity





