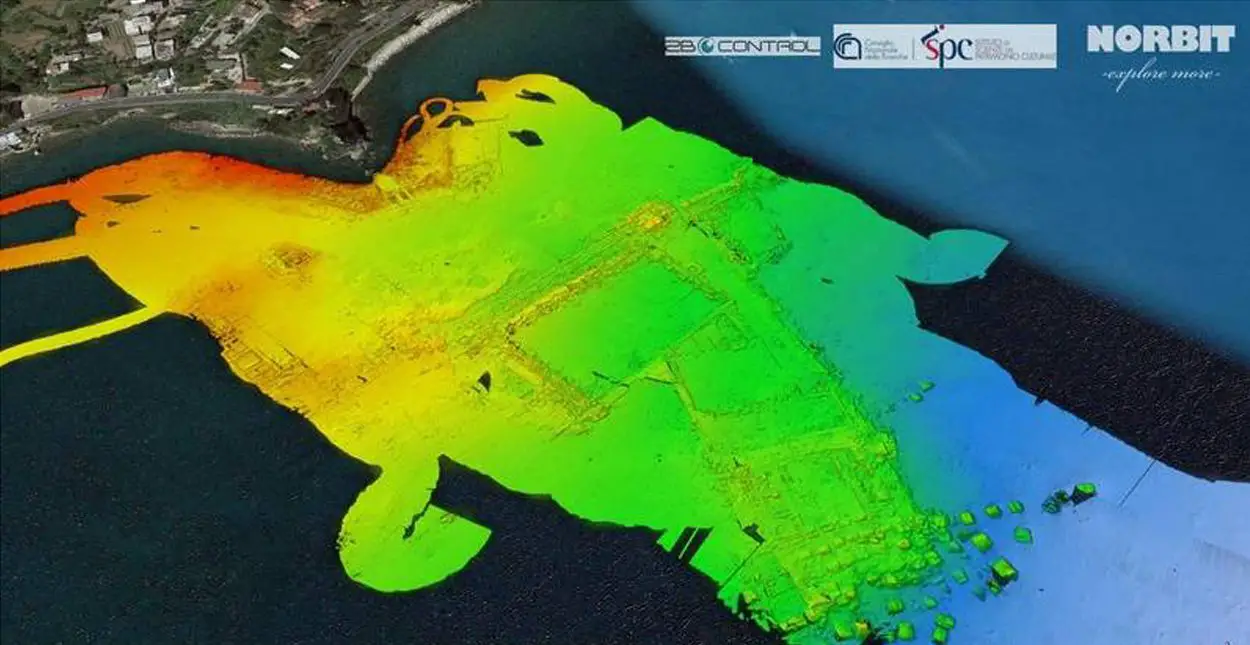
NORBIT Subsea and 2BControl, in collaboration with the Institute of Heritage Science of the Italian National Research Council, have conducted a study of the partially submerged Roman city of Baia in the Gulf of Naples, Italy.
Baia was a fashionable Roman resort for centuries in antiquity, visited by many notable Roman figures such as Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (also known as Pompey the Great) and Julius Caesar. Baiae was noted by Sextus Propertius, a poet of the Augustan age during the 1st century BC, who wrote that the city was a “vortex of luxury” and a “harbour of vice”.
Due to the position of the city on the Cumaean Peninsula in the Phlegraean Fields (an active and volatile volcanic region which the Romans believed was the home of the Roman god of fire, Vulcan), local volcanic bradyseismic activity raised and lowered the geology on the peninsula, leading to the lower parts of the city being submerged beneath the sea.
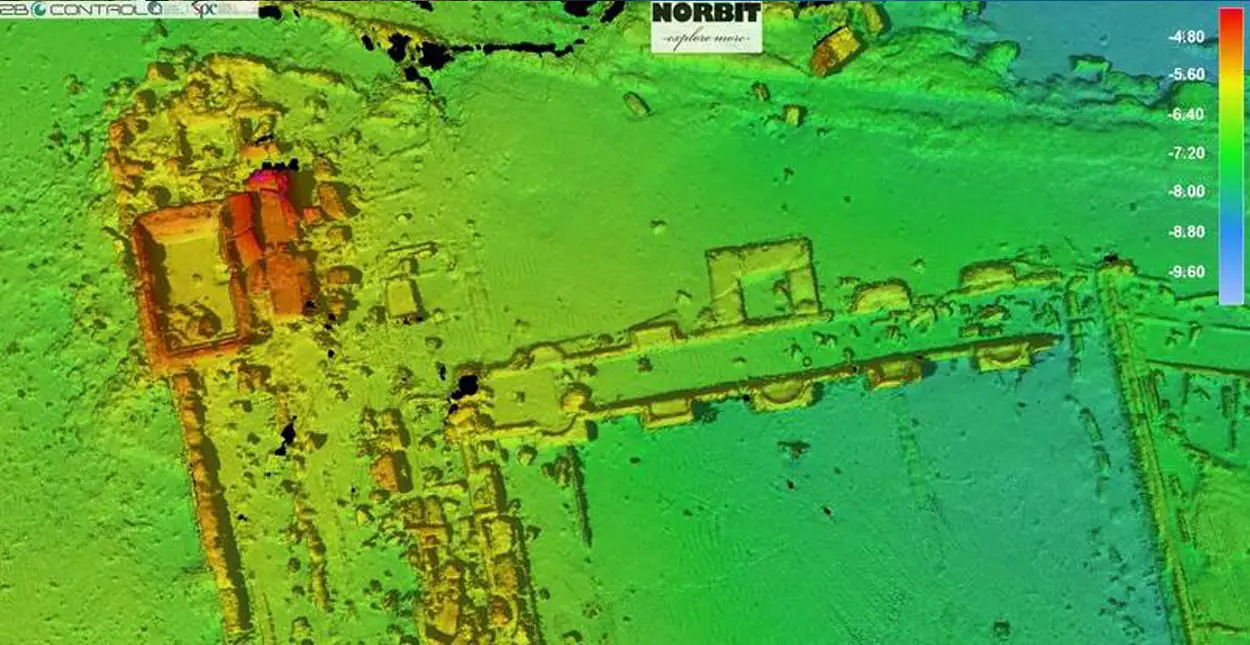

As part of a demonstration within the Baia Archaeological Park, NORBIT Subsea and 2BControl used high frequency acoustic mapping, combined with surface imaging that has centimetric resolution and multibeam sonar, revealing a detailed reconstruction of submerged objects and archaeological features on the seabed.
A 10 cm DTM is the first result of the high data density and resolution acquired, a primary record of the current state of the submerged archaeological features that will allow archaeologists to start to refine the overall mapping and measurements of the submerged remains at Baia.
Header Image Credit : NORBIT