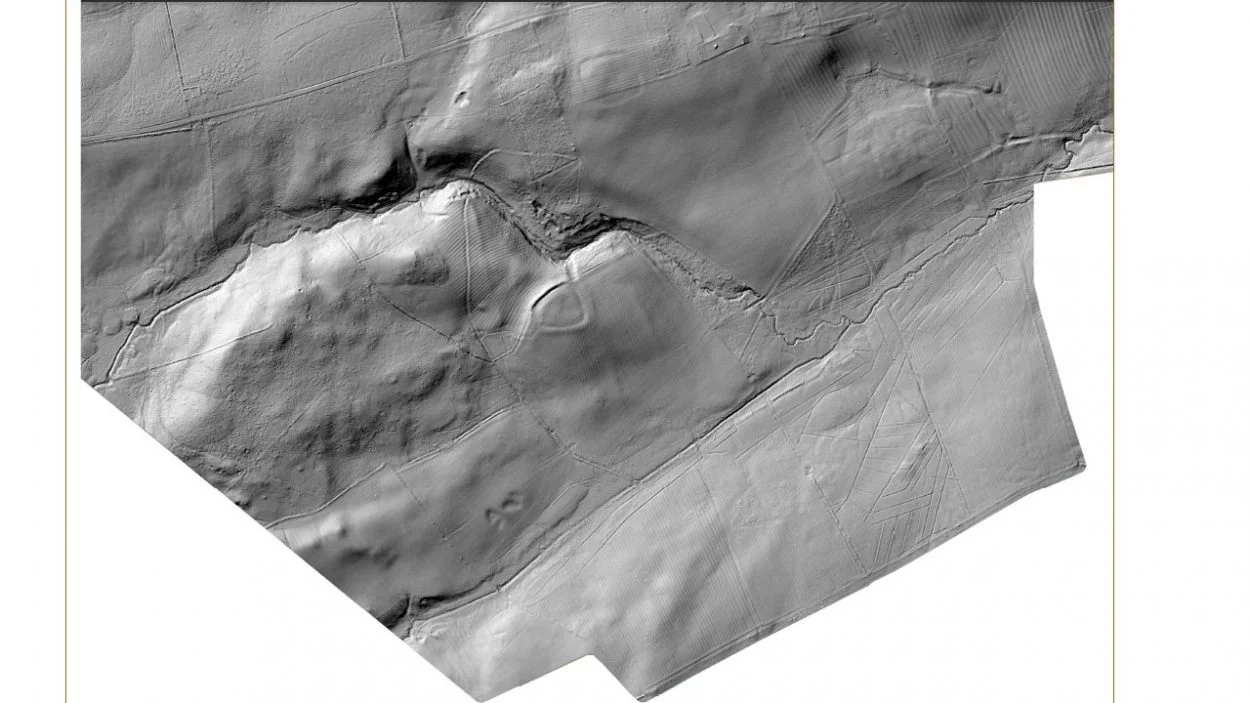
An aerial mapping project undertaken by the National Trust on the Wallington Estate in Northumberland, England, has identified 120 new archaeological features, including prehistoric sites from as early as 2000 BC.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDar) is a method of remote sensing using light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth. The differences in the laser return times and measuring the wavelengths can be used to compile a 3-D digital map of the landscape, removing obscuring features such as woodland that could hide archaeological features.
The technology was applied to the National Trust’s Wallington 13-hectare estate, where the trust is identifying potential sites for planting 75,000 British native trees, as part of a project to plant 20 million trees by 2030 in order to help tackle climate change.
The lidar-created map found evidence of archaeological sites dating from 2000 BC to AD 1900, including traces of historic, healthy woodlands dating from the mid-eighteenth century which were cleared and not replanted.
Other findings include the discovery of early farming systems which were cast aside in the 18th century by the previous owner of the estate, and at least half a dozen different forms of ‘ridge and furrow’ cultivation.
Previously known Iron Age camps and hillforts have been surveyed with greater precision to reveal eroded outlying features; such as possible annexes to the main enclosures; linear features, and suspected prehistoric pathways.
National Trust archaeological consultant Mark Newman said: “This is an exciting moment in the 5,000-year history of this special estate. The lidar findings have shone a light on much more than we could have imagined so that we can better understand the history of the landscape to help inform plans for its future.”
Additional fieldwork to record the landscape will be carried out before planting begins in November to complement the lidar remote sensing.
Header Image Credit : National Trust