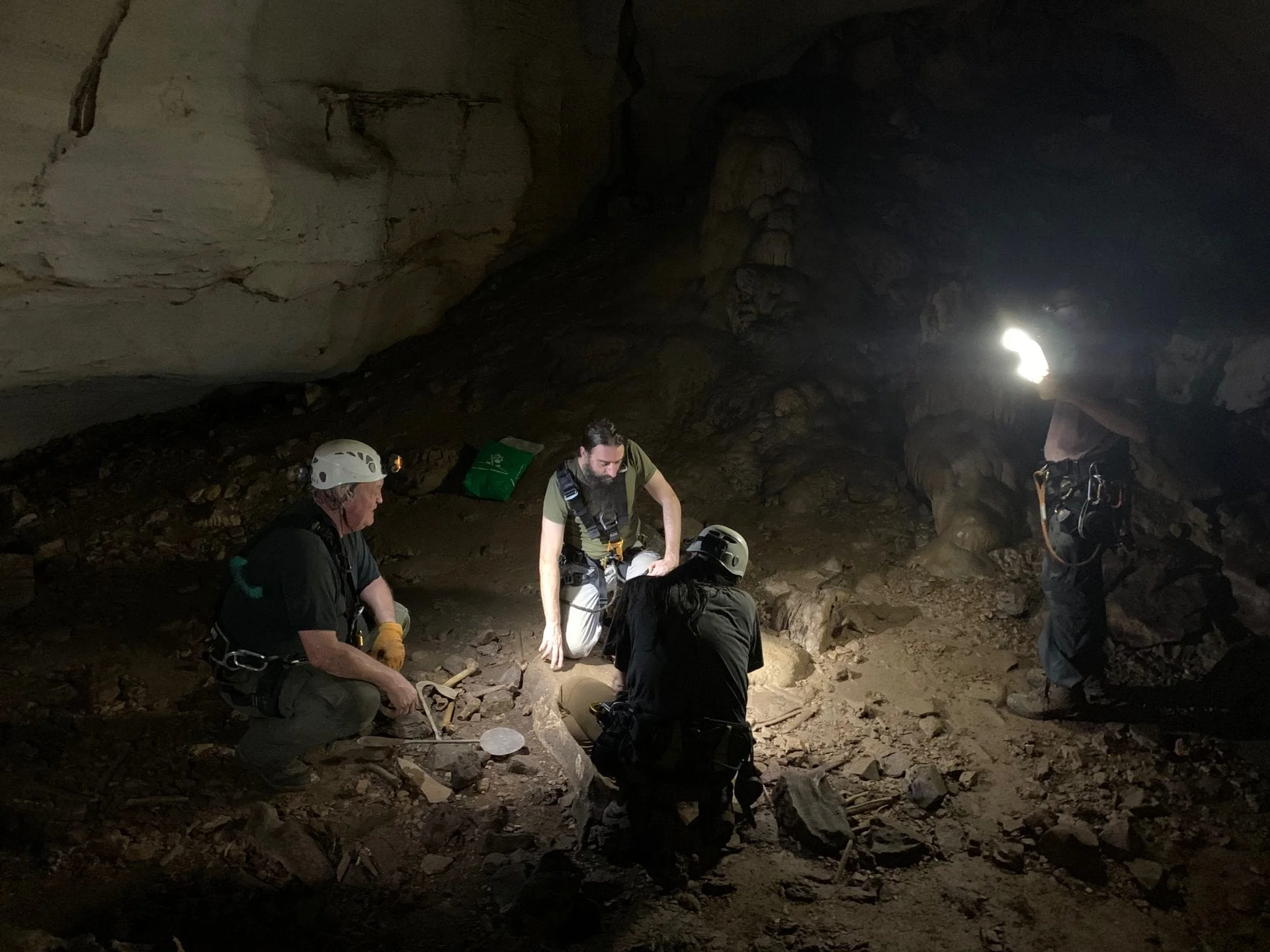
Archaeologists excavating in Iroungou, a cave in Ngounié Province of Gaban have discovered thousands of pre-colonial human remains, consisting of at least 28 identified individuals from the 14th-15th centuries AD.
In order to access the cave, an international team of researchers from Agence Nationale des Parcs Nationaux abseiled though a hole in the cave roof to reach the burials, in which the deceased would also have had to be lowered, or dropped, through the opening.
A study of the remains has determined at least 28 people interred, consisting of males and females of all age groups. The researchers also found that all the adults had their upper incisors removed earlier in life. This would have dramatically changed the shape of the face, perhaps serving as an indicator they belonged to a certain group that practised body modification, or had special status.
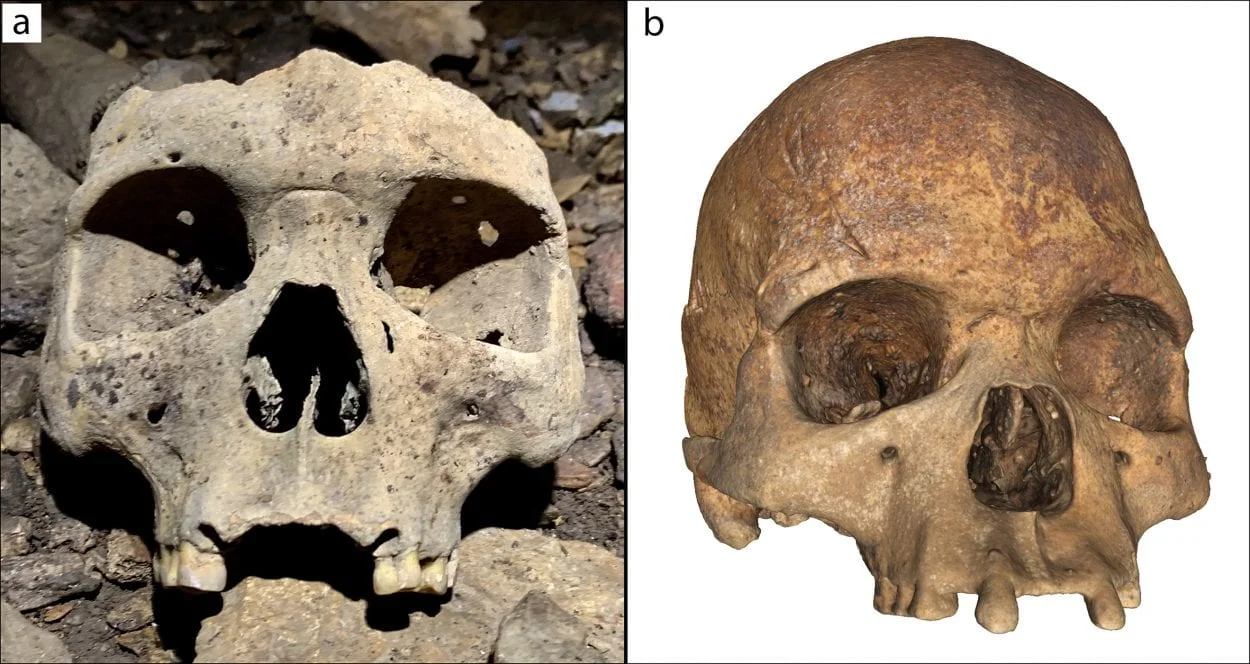
Dr Sébastien Villotte from the Université de Bordeaux said: “Intentional dental modification has a long history in Africa, but the removal of all four upper incisors is a relatively uncommon form. It has been reported in West Central Africa, so this find suggests it may have a long history and possible continuity.”
Alongside the burials, the researchers also uncovered hundreds of metal objects made from Iron such as knives, axes, hoes, and jewellery, in addition to copper items imported over a distance spanning hundreds of miles.
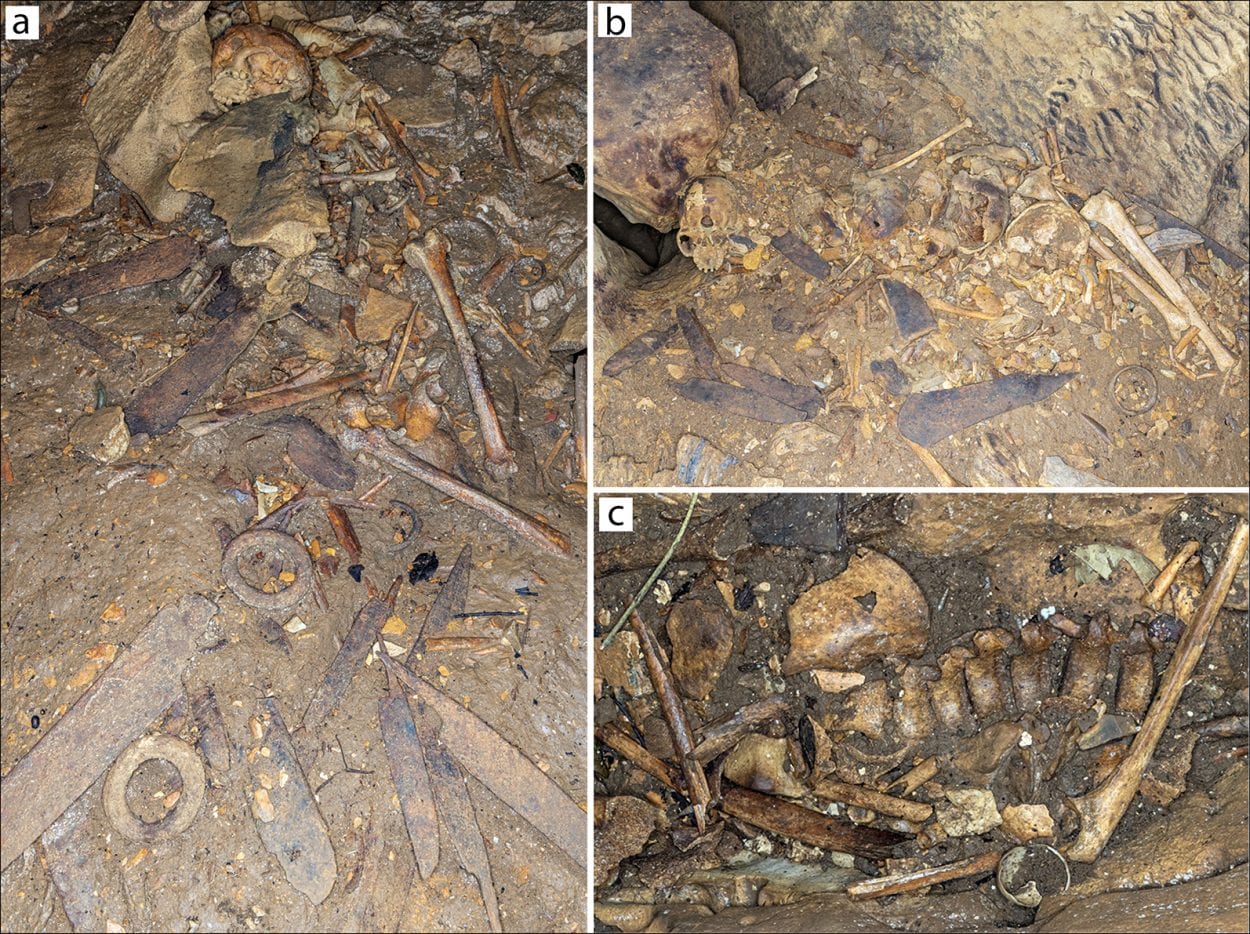

“It may have been a special burial place for important individuals, and possibly their accompanying dead – sacrificed retainers,” said Dr Villotte.
The team plans to return to the site and investigate this possibility further. They are also analysing the 3D models and photogrammetry from their previous expedition, which allowed them to map the site so thoroughly that they could leave the human remains in place. Find out more
Header Image Credit : Antiquity





