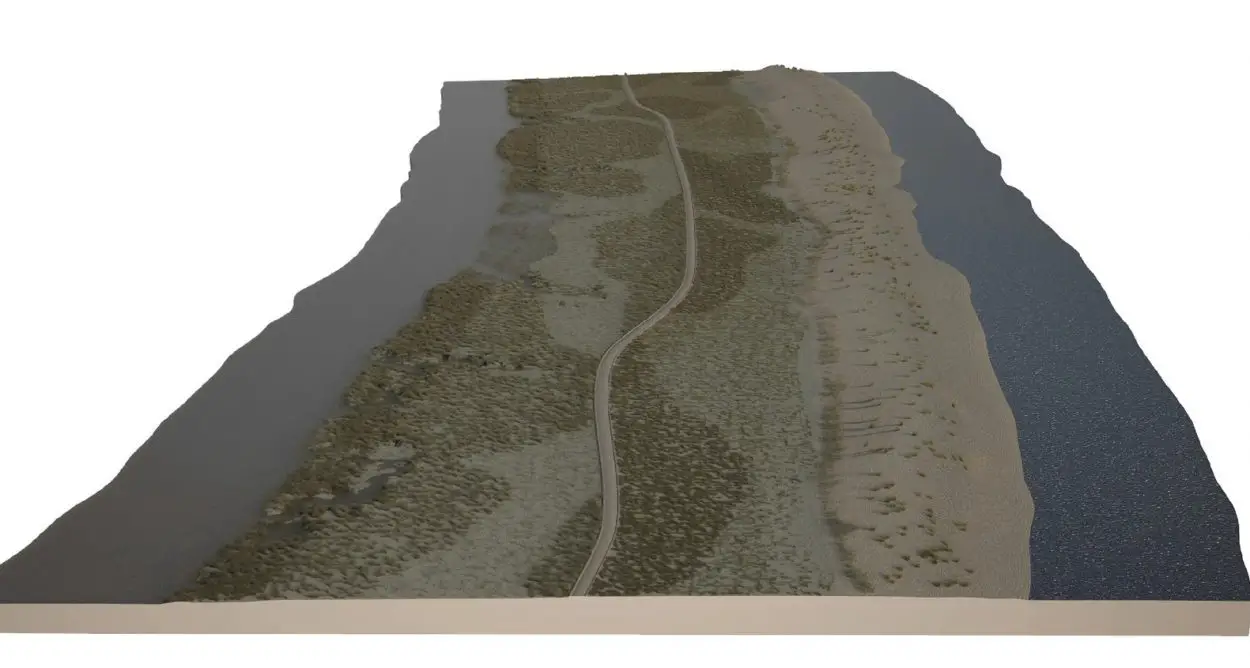
An archaeological mapping project has located a Roman road submerged in the Venice Lagoon, that suggests extensive settlements may have been present centuries before the founding of Venice in the fifth century.
During the Roman era, large areas of the Venice Lagoon which are now submerged were accessible by land. Roman artefacts have been found in lagoon islands and waterways, but the extent of human occupation of the lagoon during Roman times has been unclear.
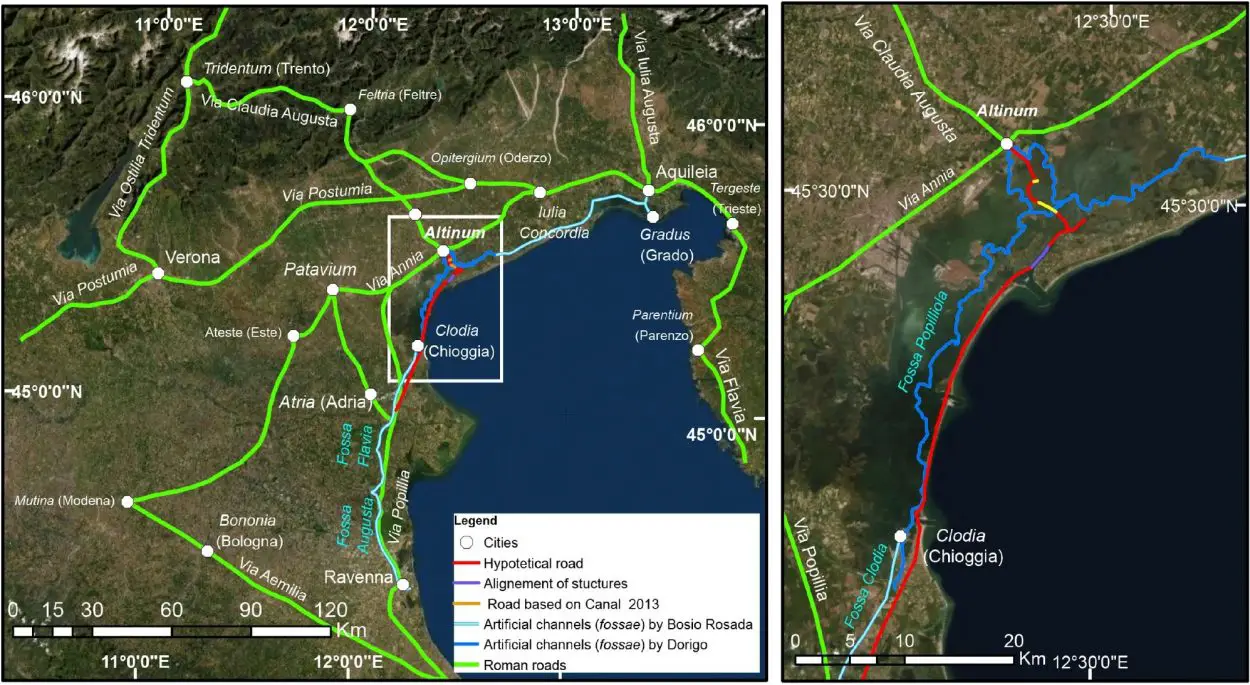
Mapping the lagoon floor using sonar, Fantina Madricardo and colleagues discovered 12 archaeological structures aligned in a north-easterly direction for 1,140 metres, in an area of the lagoon known as the Treporti Channel.
The structures were up to 2.7 metres tall and 52.7 metres long. Previous surveys of the Treporti Channel uncovered stones similar to paving stones used by Romans during road construction, indicating that the structures may be aligned along a Roman road.
The researchers also discovered an additional four structures in the Treporti Channel that were up to four metres tall and 134.8 metres long. Based on its dimensions and similarity to structures discovered in other areas, the largest of these structures is thought to be a potential harbour structure, such as a dock.
Previously collected geological and modelling data indicates that the road is located on a sandy ridge that was above sea level during the Roman era but is now submerged in the lagoon.
The findings suggest that a permanent settlement may have been present in the Treporti Channel during the Roman era. The authors propose that the road may have been linked to a wider network of Roman roads in the Italian Veneto Region and may have been used by travellers and sailors to journey between what is now the city of Chioggia and the Northern Venice Lagoon.
Header Image Credit : Scientific Reports





