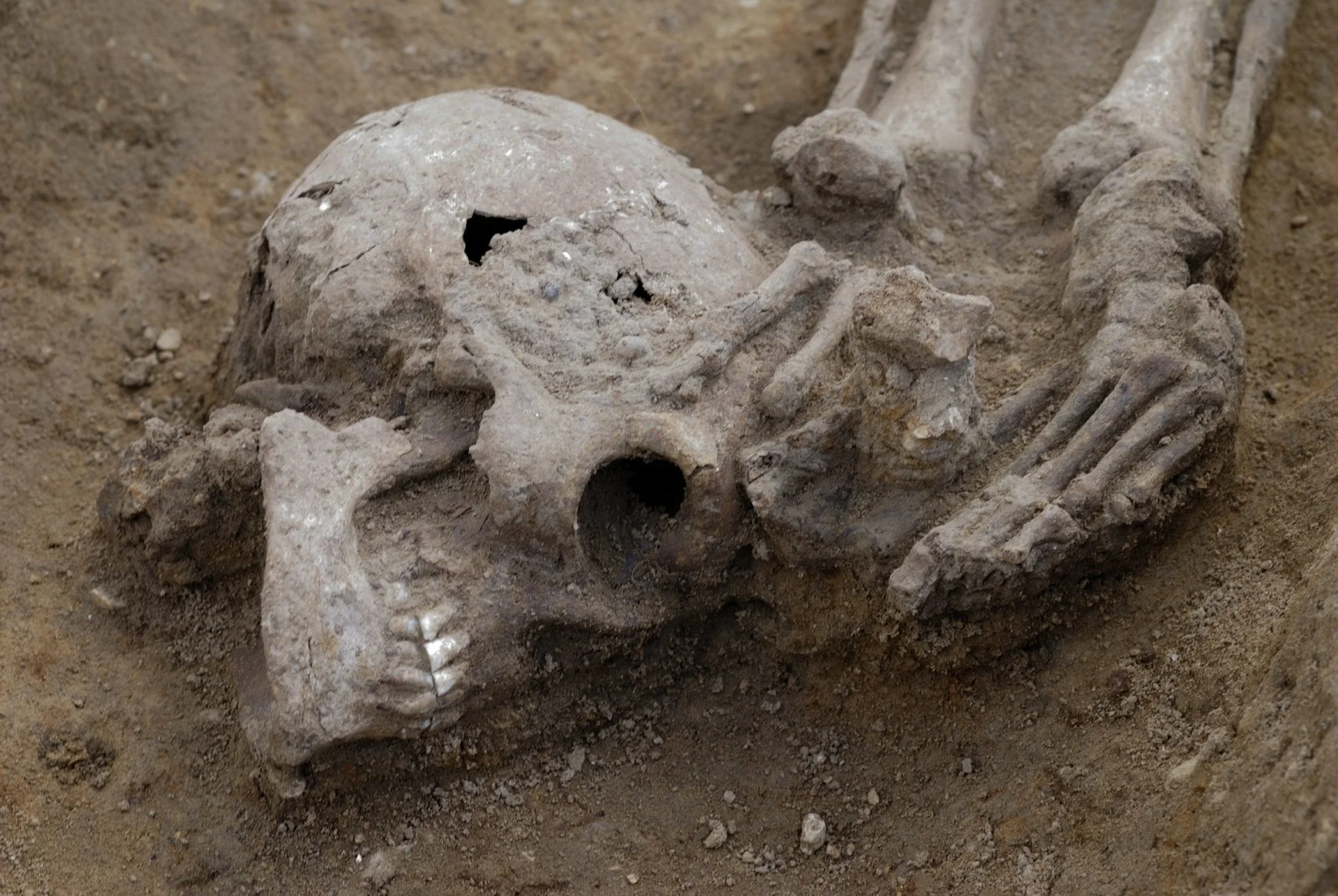
Archaeologists excavating between 2001 and 2010 at Knobbs Farm Quarry in Somersham, England, uncovered three late Roman cemeteries at the edge of a farming settlement, that has evidence of judicial executions using decapitation.
The research recently published in Britannia (Roman Journal of Archaeology) was undertaken by Cambridge Archaeology Unit and Dr Isabel Lisboa of Archaeologica Ltd, on behalf of Tarmac, a CRH company that funded the work.
The three cemeteries date to around the 3rd century AD, and total 52 burials mainly placed in an extended position, whilst 13 were prone, and 17 showing indications of decapitation. During the Roman period, decapitation was a standard method of execution referred to frequently in historical text and Roman legal documents.
Three of the decapitated skeletons show cut marks that was likely caused by a sword (decollatio), whilst osteological evidence implies that they were still alive when killed. One of the female skeletons has evidence of mutilation, which in reported Roman sources is paralleled by the destruction of the head or face of executed criminals.
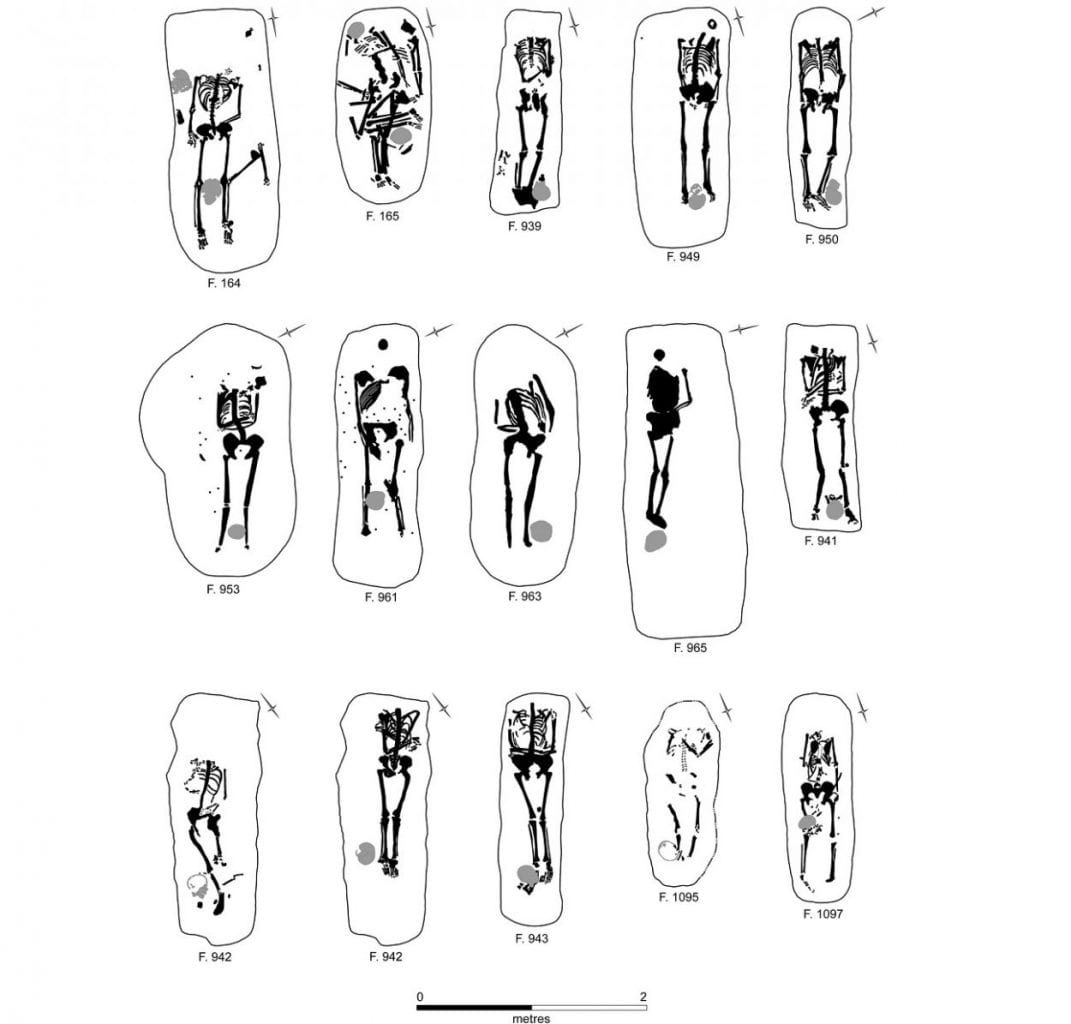
The study suggests that Knobbs Farm Quarry has an exceptionally high proportion of decapitated bodies and prone burials (33 per cent and 25 per cent) when compared with burial grounds locally and across Roman Britain.
One explanation is the proximity to several farming settlements known as ‘Fen Roman Villages’ that likely supplied the military. The inhabitants would presumably have been under particular scrutiny, and malfeasance would have been treated harshly.
The late date of the executions: the rise in decapitations in Britain also coincided with increasing severity in Roman law. The number of crimes that carried the death penalty more than doubled in the third century and quadrupled in the fourth century. Read full paper
Header Image Credit : Dave Webb, Cambridge Archaeological Unit





