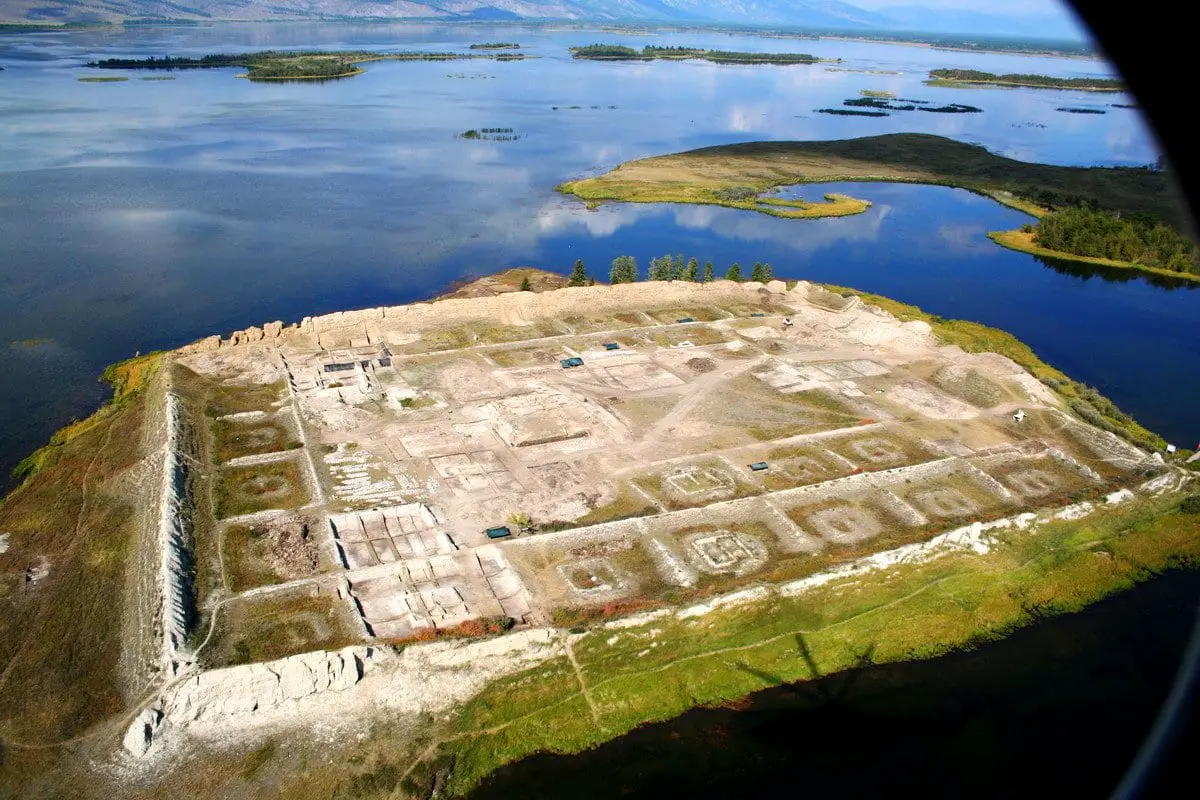
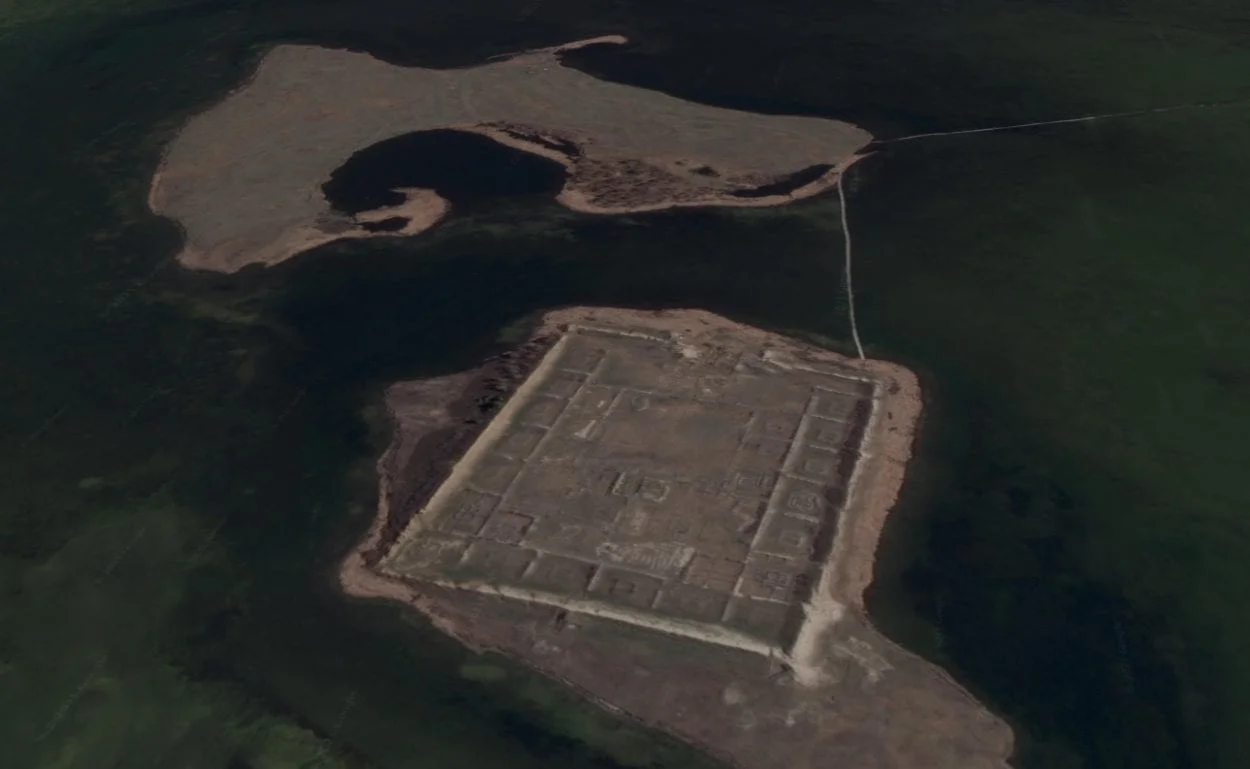
Por-Bazhyn, meaning “Clay House” in the Tuvan language are the remains of an adobe monastery or a fortified palace, that was built on a small island in Lake Tere-Khol, located in the Sengelen mountains of southern Siberia, Russia.
Radiocarbon dating and dendrochronological studies suggest that Por-Bazhyn was built around AD 777 by the Uighurs, a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur that ruled from AD 742 to 848.
The Chinese called the Uighurs the Jiu Xing, meaning “nine clans”, with Por-Bazhyn demonstrating several characteristics of Chinese architecture in the Tang style, such as the hangtu technique for the construction of a curtain wall, and dougong ceilings in the interior structures (although recent studies now suggest that they are a distinctive Uyghur stylistic typology).
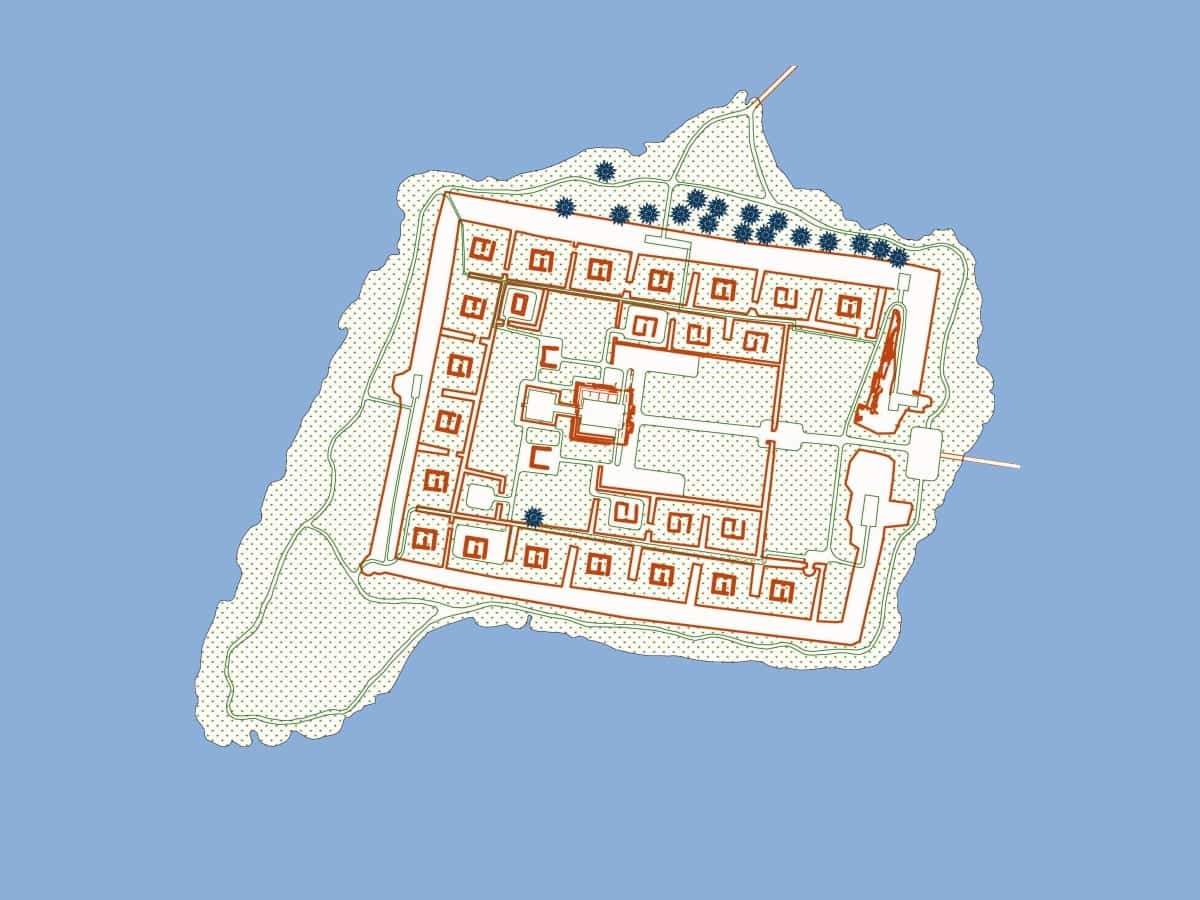
The plan of Por-Bazhyn covers an area of 7.5 acres and resembles the Uyghur capital of the first Uyghur Khaganate at Karabalgasu. The layout can also be interpreted as the Chinese ‘ideal town’, that contained two successive courtyards, with a series of small, enclosed courtyards that ran along the interior of the northern, western, and southern curtain walls.

Approximately 30 buildings stood within the interior, centred on a central complex consisting of two pavilions that likely served a ceremonial and religious purpose, with various one or two chamber structures located in each of the smaller enclosure courtyards.
The lack of definitive archaeological material has led to various interpretations of Por-Bazhyn over the years, that includes a border fortress, a fortified palace, an astronomical observatory, and a ritual site.
Recent studies released in 2020 by the Lomonosov Moscow State University, and the Institute of Geography of the Russian Academy now suggest that Por-Bazhyn was a seasonal Manichaean monastery built during the reign of Tengri Bögü Khan (the Third khagan of Uyghurs).
During his reign, Bögü Khan converted to Manichaeism (a religion founded in the 3rd century AD that teaches a dualistic cosmology describing the struggle between a good, spiritual world of light, and an evil, material world of darkness) and declared it the state religion of the Uyghur Khaganate in AD 763.
In AD 779, Bögü Khagan was killed as the result of an anti-Manichaean rebellion led by zealous Tengriists, that likely explains the absence of an occupation layer and the rapid abandonment of Por-Bazhyn after the abolition of Manichaeism.
Header Image – Replicated with kind permission – Copyright – Philipp Chistyakov





