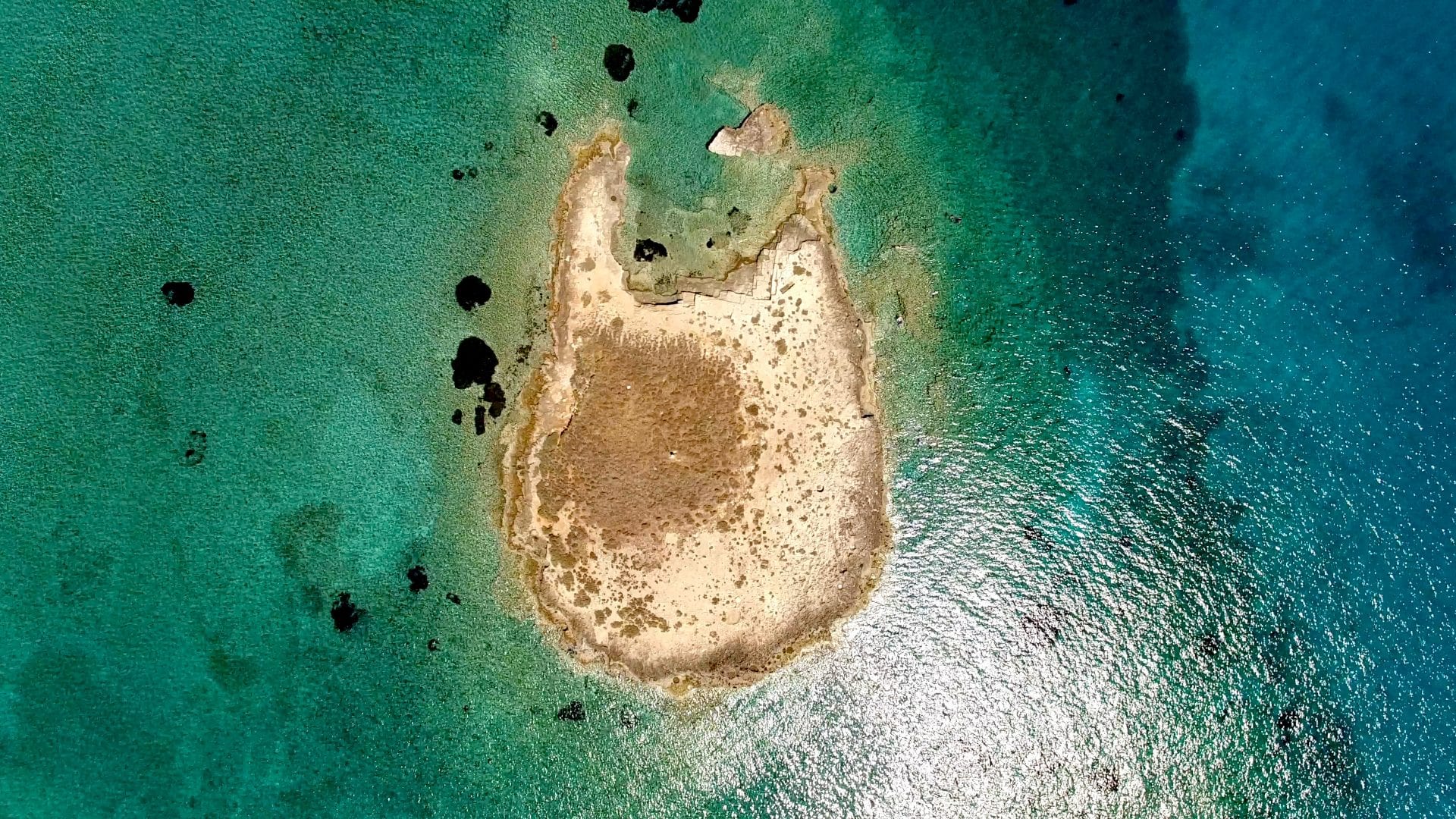
Pavlopetri, also called Paulopetri, is a submerged ancient town, located between the islet of Pavlopetri and the Pounta coast of Laconia, on the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece.
Evidence of the submerged remains were first identified by the geologist Folkion Negris in 1904, but the scale of the site would not be realised until it was re-discovered in 1967 by Nicholas Flemming, and surveyed by a team of archaeologists from the University of Cambridge in 1968.
The physical remains are found 20 metres from the Pounta coast shoreline and run for over 300 metres south to Pavlopetri Island, covering an approximate area of around 19.7 acres.
Ceramics recovered in situ confirms that Pavlopetri had Mycenaean occupation, but further archaeological evidence suggests that the town was occupied as early as 3500 BC.
The remains are indicated by a network of stone walls up to three stones in height, constructed from uncut aeolianite, sandstone and limestone blocks. Tracing the walls reveals the foundations of a network of streets, courtyards, and up to 15 rectilinear buildings, as well as cist graves and Bronze Age pithos burials at a depth of 3 to 4 metres. The discovery of various loom weights and imported pitharis pots from Crete, suggests that the town was a centre of a thriving textile industry, and a major trading port.
The site was initially abandoned during the post-palatial period of Minoan chronology, and re-occupied during the Classical and Hellenistic periods (indicated by Skyphos wine-cups that date from the 4th century BC, and 3rd century BC sherds and doublebarrel handles).
Geologists theorise that the submergence of the town was the result of local and regional faulting of the Cretan Arc (an arcuate mountain chain of the southern Aegean Sea), that led to the convergence and subduction of the tectonic plate causing the town to drop beneath the sea level. Other examples of convergence and subduction can be found locally, with the archaeological site of Plitra that was submerged by several metres, and the site of Antikythera that uplifted.
Whilst an exact date for submergence is unknown, the evidence so far indicates that Pavlopetri was probably inundated and awash by the time of the Roman period, and thus completely abandoned.
View Full Map – Click Here
Header Image Credit : Licensed from iStock