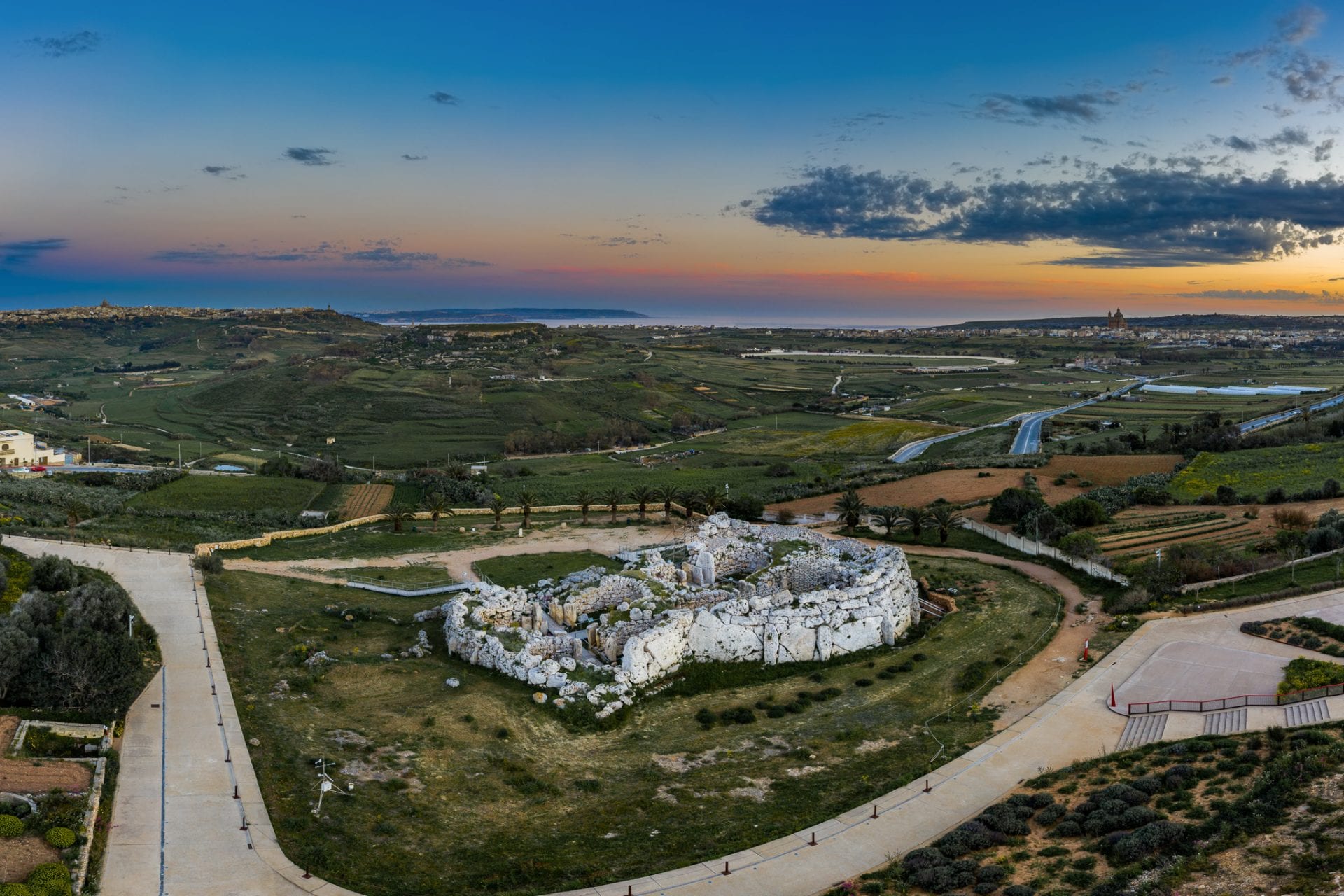
Ġgantija is an archaeological site, and ancient Neolithic temple complex located on the Xagħra plateau in the Mediterranean island of Gozo, in the Republic of Malta.
Evidence of occupation on the island dates from as early as 5000 BC, during the Għar Dalam phase in the Early Neolithic Period, with a later wave of settlers to the island, who started a temple building phase during the 4th millennium BC.
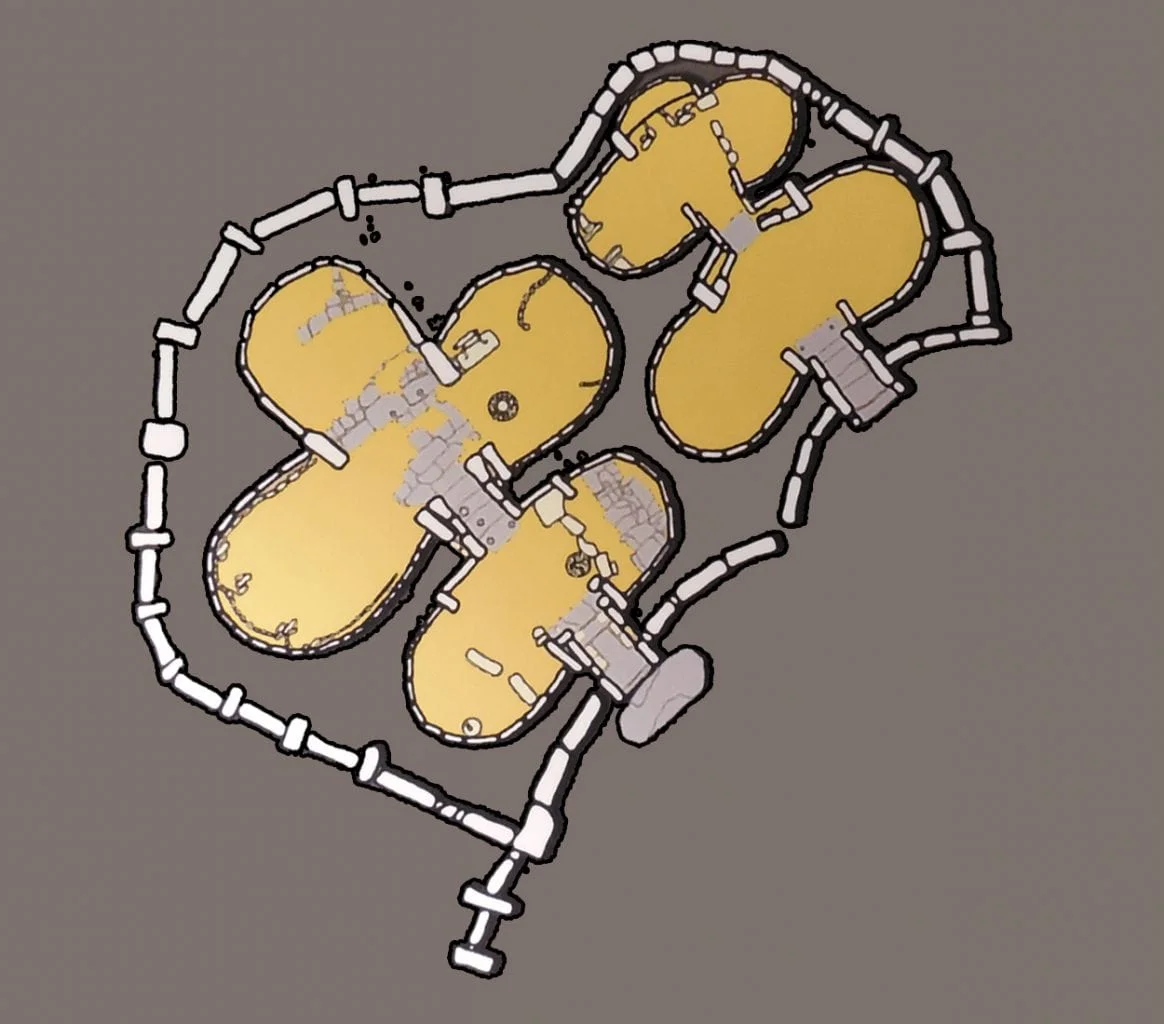
The Ġgantija complex consists of two stone temples (and an incomplete third temple), called the “Giants’ Tower” from local Gozitan folklore, with the name Ġgantija stemming from the Maltese word “ġgant,” meaning giant.
The temples – designated the southern temple (constructed around 3600 BC), and the northern temple (constructed around 2900 BC), were built in a period known as the Ġgantija phase (3600–3000 BC), making Ġgantija the world’s second oldest existing manmade religious structures, and amongst the earliest free-standing stone buildings in the world.
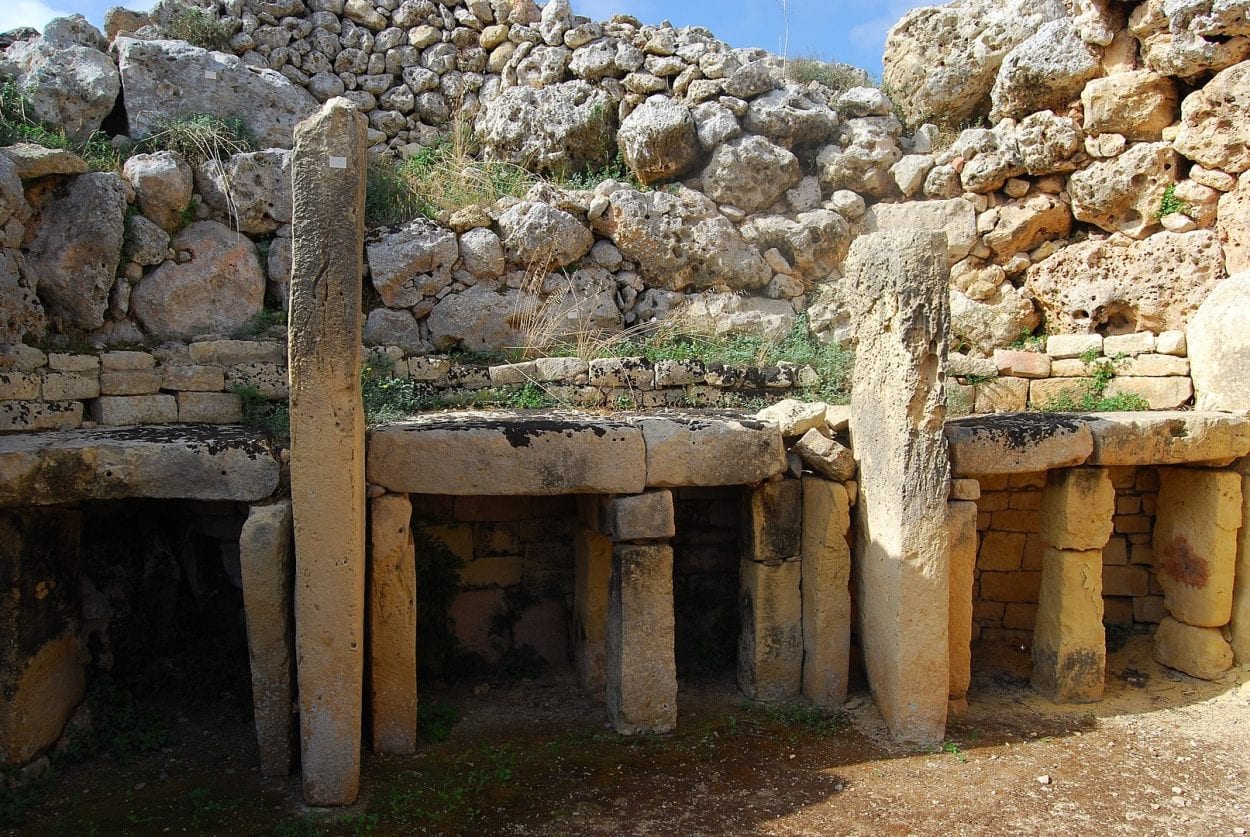

Corresponding to other megalithic sites in Malta, the temples face towards the southeast and are aligned to the celestial cycles of the equinox sunrise. They are built in the typical clover-leaf (trefoil) floor plan, housing a series of semi-circular apses containing an altar and plastered walls. The internal apses were connected with a central passageway, whilst the wider temple complex was encircled with a singular boundary wall.
We know from the archaeological evidence that worship in the temples included animal sacrifice, with further suggested theories of religious fertility rites in dedication to a mother goddess.
Ġgantija was occupied for around a thousand years into the mid-third millennium BC, when the Maltese Temple Culture abruptly vanished, possibly due to climate conditions and drought on the island.
The temples were rediscovered and carefully restored by European and native Maltese archaeologists during the beginning of the 19th century.
The Ġgantija temples were listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. In 1992, the Committee decided to expand the listing to include five other megalithic temples located across the islands of Malta and Gozo, with Ġgantija’s listing being renamed amongst “the Megalithic Temples of Malta.”
Header Image Credit : FritzPhotography – CC BY-SA 4.0





