The existence of a tectonic plate called Resurrection has long been a topic of debate among geologists, with some arguing it was never real.
Others say it subducted – moved sideways and downward – into the earth’s mantle somewhere in the Pacific Margin between 40 and 60 million years ago.
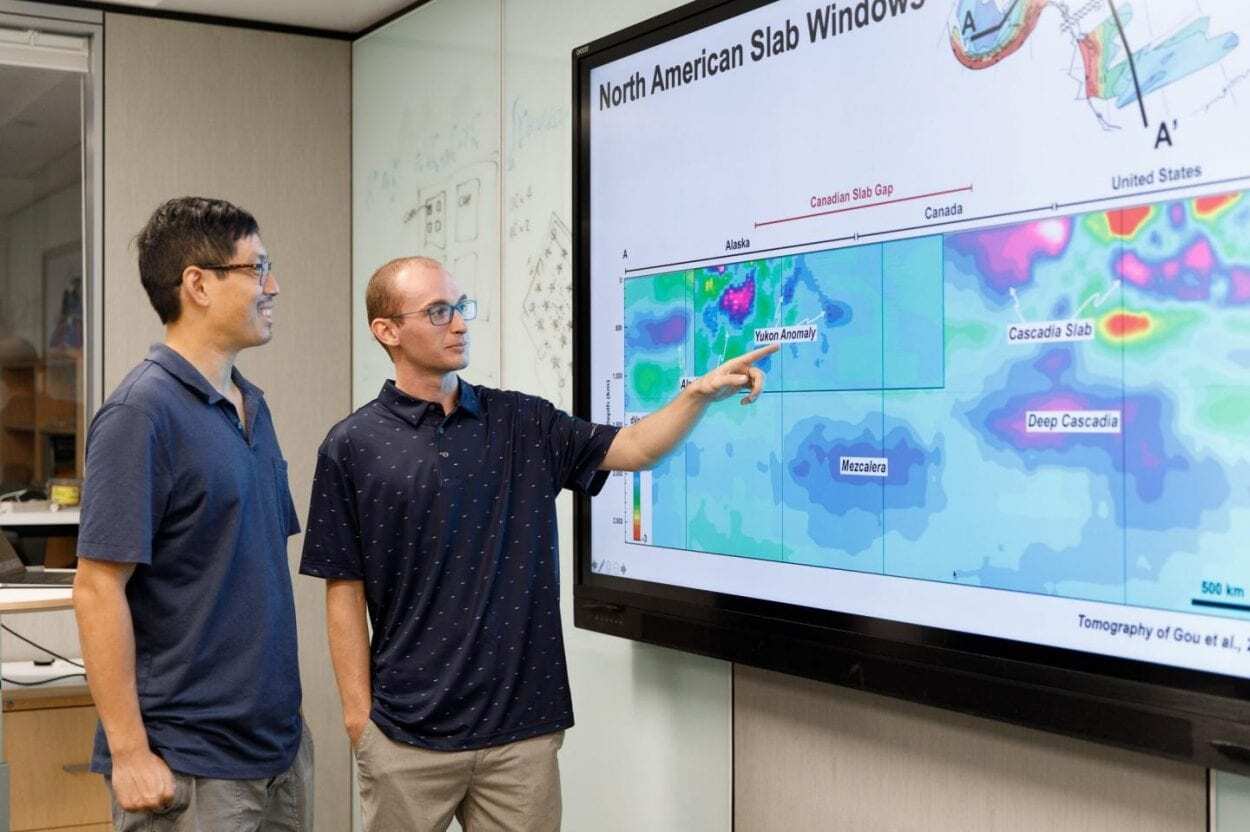
A team of geologists at the University of Houston College of Natural Sciences and Mathematics believes they have found the lost plate in northern Canada by using existing mantle tomography images – similar to a CT scan of the earth’s interior. The findings, published in Geological Society of America Bulletin, could help geologists better predict volcanic hazards as well as mineral and hydrocarbon deposits.
“Volcanoes form at plate boundaries, and the more plates you have, the more volcanoes you have,” said Jonny Wu, assistant professor of geology in the Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences. “Volcanoes also affect climate change. So, when you are trying to model the earth and understand how climate has changed since time, you really want to know how many volcanoes there have been on earth.”
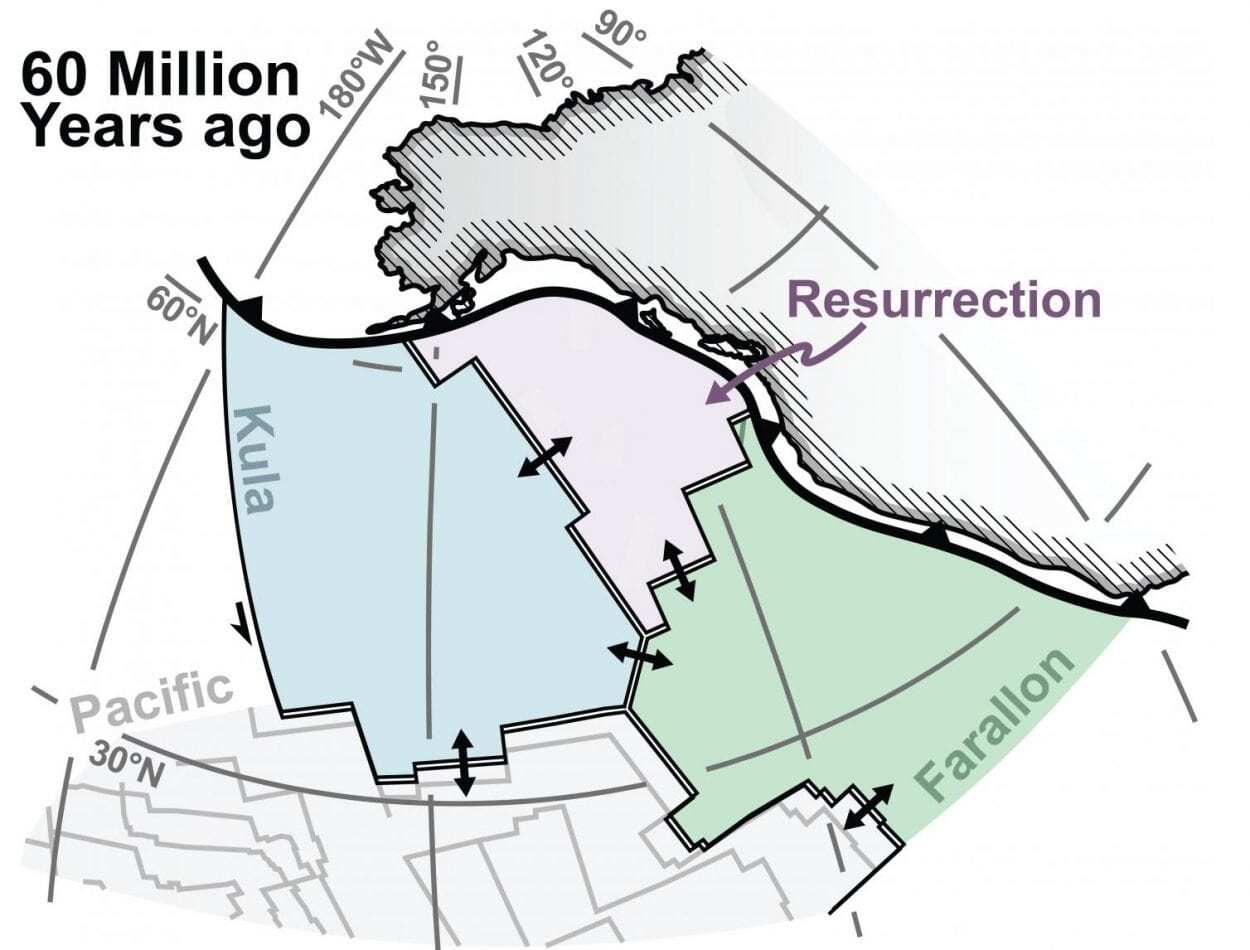
Wu and Spencer Fuston, a third-year geology doctoral student, applied a technique developed by the UH Center for Tectonics and Tomography called slab unfolding to reconstruct what tectonic plates in the Pacific Ocean looked like during the early Cenozoic Era. The rigid outermost shell of Earth, or lithosphere, is broken into tectonic plates and geologists have always known there were two plates in the Pacific Ocean at that time called Kula and Farallon. But there has been discussion about a potential third plate, Resurrection, having formed a special type of volcanic belt along Alaska and Washington State.
“We believe we have direct evidence that the Resurrection plate existed. We are also trying to solve a debate and advocate for which side our data supports,” Fuston said.
Using 3D mapping technology, Fuston applied the slab unfolding technique to the mantle tomography images to pull out the subducted plates before unfolding and stretching them to their original shapes.
“When ‘raised’ back to the earth’s surface and reconstructed, the boundaries of this ancient Resurrection tectonic plate match well with the ancient volcanic belts in Washington State and Alaska, providing a much sought after link between the ancient Pacific Ocean and the North American geologic record,” explained Wu.
Header Image – (l-r) Jonny Wu, assistant professor of geology in the UH Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences and Spencer Fuston, a third-year geology doctoral student, applied a technique developed by the UH Center for Tectonics and Tomography called slab unfolding to reconstruct what tectonic plates in the Pacific Ocean looked like during the early Cenozoic Era. – Image Credit : University of Houston





