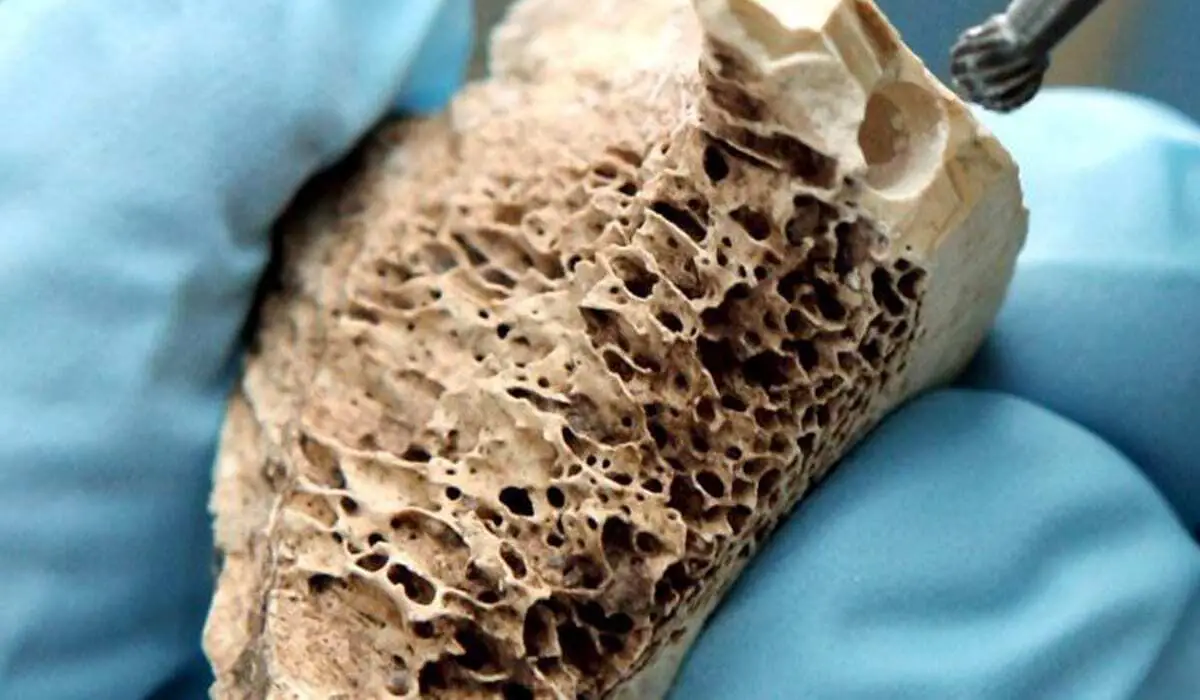
The results of a study from Stajnia Cave in Poland have revealed the oldest remains of Neanderthals in Central Europe.
Stajnia Cave is located north of the Carpathians and was first studied as part of a research project in 2008, where the remains of Neanderthals, in particular, a molar was unearthed in a Micoquian context.
Researchers had initially dated the remains to approximately 52-42 thousand years ago, but a new study has now proposed the remains date from around 116 thousand years ago.
The revelation makes the discovery the oldest Neanderthal population in Poland, in addition to Central Europe.
An international team of scientists, that included the University of Wrocław, the Polish Academy of Sciences, and the Polish Geological Institute conducted a genetic analysis of a Neanderthal molar, including mitochondrial DNA.
The researchers also determined that the Neanderthals from Stajnia Cave were closely related to Neanderthals from the North Caucasus, rather than populations living in Western Europe (compared to DNA from Scladina Cave in Belgium and Hohlenstein-Stadel Cave in Germany).
Header Image Credit : PAP/EPA/Waltraud Grubitzsch