The Earth’s crust is under constant stress. Every now and then this stress is discharged in heavy earthquakes, mostly caused by the slow movement of Earth’s crustal plates.
There is, however, another influencing factor that has received little attention so far: intensive erosion can temporarily change the earthquake activity (seismicity) of a region significantly. This has now been shown for Taiwan by researchers from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences in cooperation with international colleagues. They report on this in the journal Scientific Reports.
The island in the western Pacific Ocean is anyway one of the most tectonically active regions in the world, as the Philippine Sea Plate collides with the edge of the Asian continent. 11 years ago, Typhoon Morakot reached the coast of Taiwan. This tropical cyclone is considered the one of the worst in Taiwan’s recorded history.
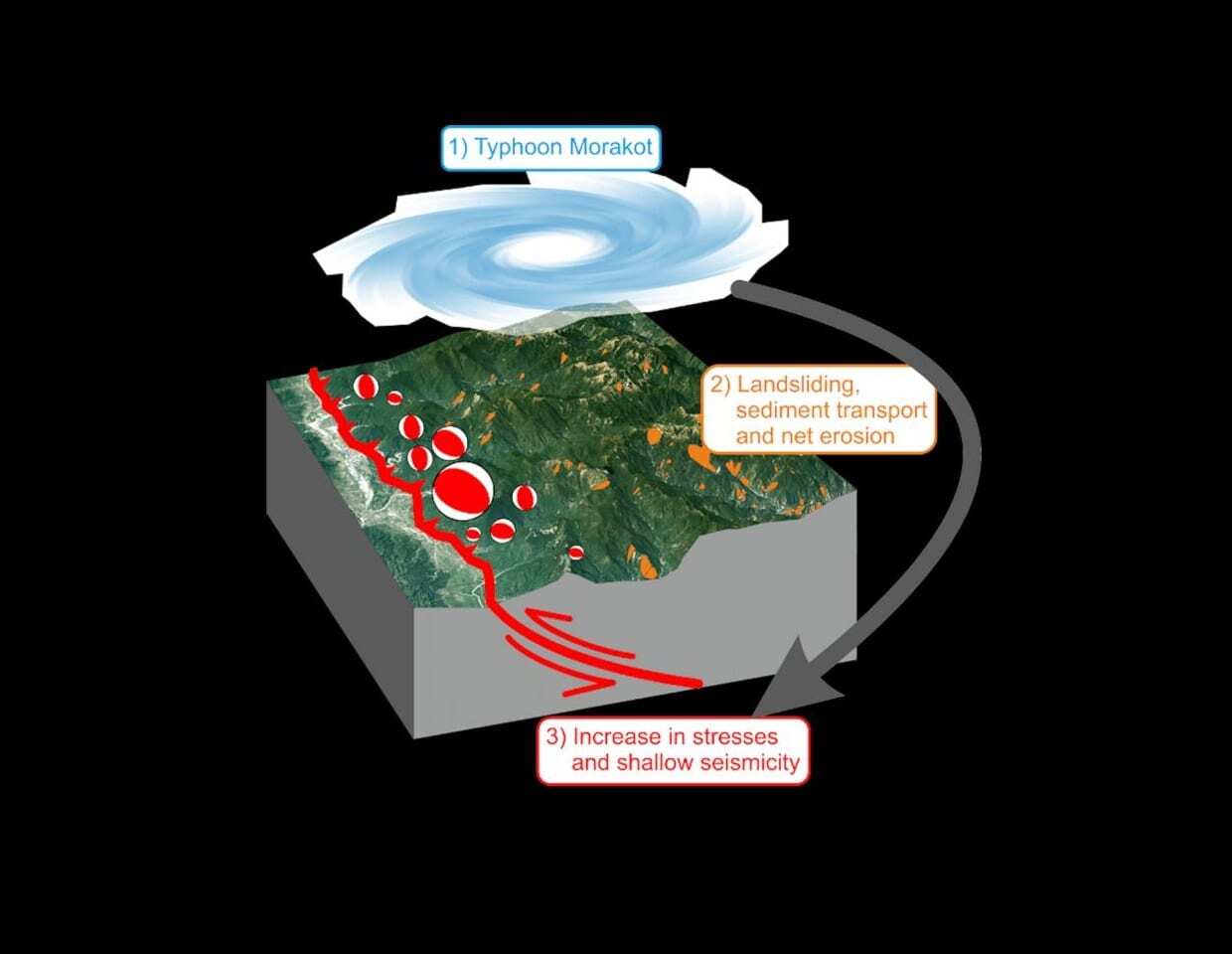
Within only three days in August 2009, three thousand litres of rain fell per square metre. As a comparison, Berlin and Brandenburg receive an average of around 550 liters per square meter in one year. The water masses caused catastrophic flooding and widespread landsliding. More than 600 people died and the immediate economic damage amounted to the equivalent of around 3 billion euros.
The international team led by Philippe Steer of the University of Rennes, France, evaluated the earthquakes following this erosion event statistically. They showed that there were significantly more small-magnitude and shallow earthquakes during the 2.5 years after typhoon Morakot than before, and that this change occurred only in the area showing extensive erosion. GFZ researcher and senior author Niels Hovius says: “We explain this change in seismicity by an increase in crustal stresses at shallow depth, less than 15 kilometres, in conjunction with surface erosion”.
The numerous landslides have moved enormous loads, rivers transported the material from the devastated regions. “The progressive removal of these loads changes the state of the stress in the upper part of the Earth’s crust to such an extent that there are more earthquakes on thrust faults,” explains Hovius.
So-called active mountain ranges, such as those found in Taiwan, are characterized by “thrust faults” in the underground, where one unit of rocks moves up and over another unit. The rock breaks when the stress becomes too great. Usually it is the continuous pressure of the moving and interlocking crustal plates that causes faults to move. The resulting earthquakes in turn often cause landslides and massively increased erosion.
The work of the GFZ researchers and their colleagues now shows for the first time that the reverse is also possible: massive erosion influences seismicity – and does so in a geological instant. Niels Hovius: “Surface processes and tectonics are connected in the blink of an eye.” The researcher continues: “Earthquakes are among the most dangerous and destructive natural hazards. Better understanding earthquake triggering by tectonics and by external processes is crucial for a more realistic assessment of earthquake hazards, especially in densely populated regions.”
GFZ GEOFORSCHUNGSZENTRUM POTSDAM, HELMHOLTZ CENTRE
Header Image Credit : Public Domain





